Hyperspectral image target detection method based on tensor matching subspace
A hyperspectral image and target detection technology, which is applied in image enhancement, image analysis, image data processing, etc., can solve the problems of low utilization rate of spatial information and low accuracy of target detection in hyperspectral images, and achieve the goal of improving the utilization rate of spatial information Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
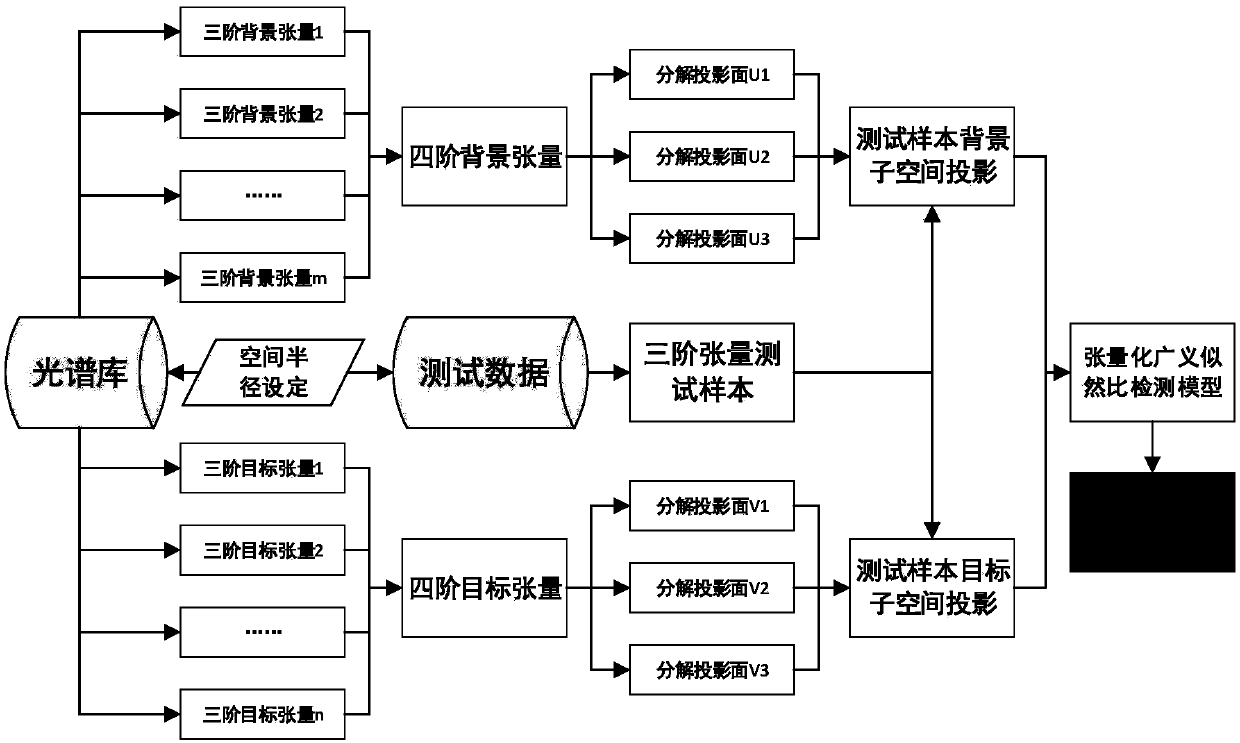
[0023] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 Describe this embodiment, the hyperspectral image target detection method based on tensor matching subspace in this embodiment, specifically referred to as:
[0024] Step 1. Establish the target sample H under the tensor representation 1 and the background sample H 0 The signal representation model of
[0025] Step 2. According to the hyperspectral sample data and window size, respectively establish the target sample H 1 and the background sample H 0 The space X, space Y, spectrum and fourth-order tensor matrix of atoms;
[0026] Step 3. According to the tensor matching subspace projection algorithm, obtain the target sample H 1 and the background sample H 0 Orthogonal projection matrices of the space X, space Y and spectrum three background directions and three target directions in the fourth-order tensor matrix of space X, space Y, spectrum and atom;
[0027] The data space of the signal to be detected under th...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0030] Specific implementation mode two: combination Figure 2a , Figure 2b This embodiment is described. The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that the target sample H under the tensor representation is established in the first step. 1 and the background sample H 0 The signal representation model of ; the specific process is:
[0031]
[0032] in, Represents the third-order tensor representation of the signal to be detected; Indicates the fourth-order tensor space formed by background samples; Indicates the fourth-order tensor quantum space formed by the target sample; x 4 Indicates that the weighted sum operation is performed on the fourth dimension of the tensor; α and β represent the corresponding abundance coefficients, that is, the corresponding weights; is a third-order tensor representation of Gaussian random noise;
[0033] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0034] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is that in the step two, according to the hyperspectral sample data and the window size, the target sample H is respectively established 1 and the background sample H 0 The space X, space Y, spectrum and fourth-order tensor matrix of atoms; the specific process is called:
[0035] Step 21, randomly selecting hyperspectral sample data from the hyperspectral sample database and setting the window size of the hyperspectral sample data;
[0036] Step 22: Convert the background sample of each selected hyperspectral sample data into a third-order tensor form, and then form all the background samples in the third-order tensor form into a fourth-order tensor;
[0037]Step two and three, converting the target sample of each selected hyperspectral sample data into a form of third-order tensor, and then forming all target samples in the form of third-order tensor into a fourth-ord...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com