External-rotor variable excitation motor
A technology of external rotor and electric motor, which is applied in the direction of electric components, magnetic circuit rotating parts, magnetic circuit shape/style/structure, etc., and can solve the problems of motor full length lengthening, non-automatic variable excitation, pressure angle becoming large, etc. , to achieve the effect that the effect of the magnet will not decrease, the structure is simple, and the output is easy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
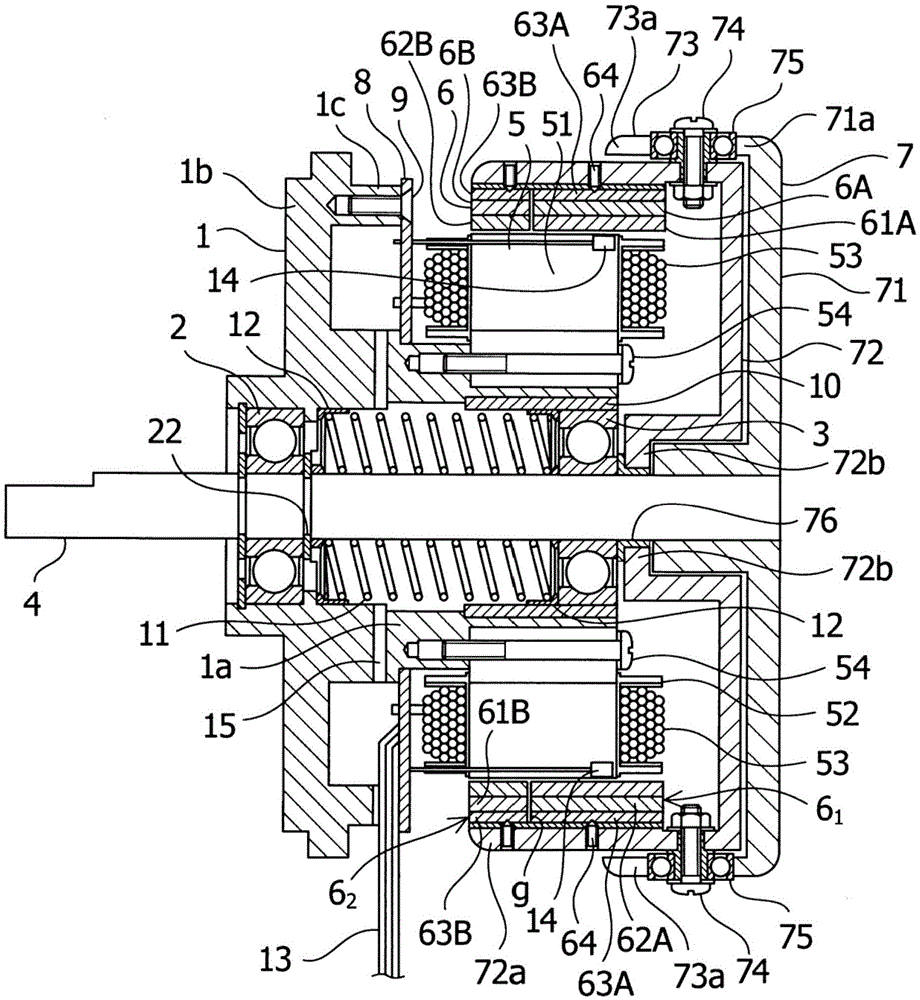
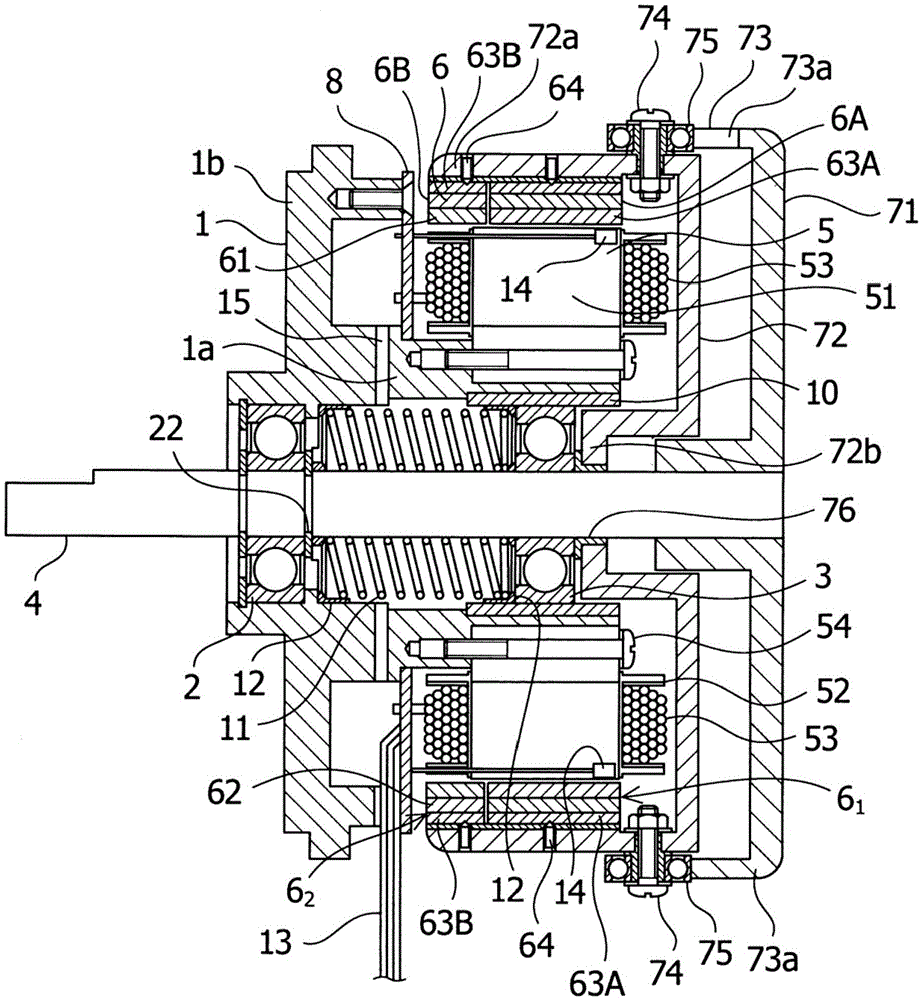
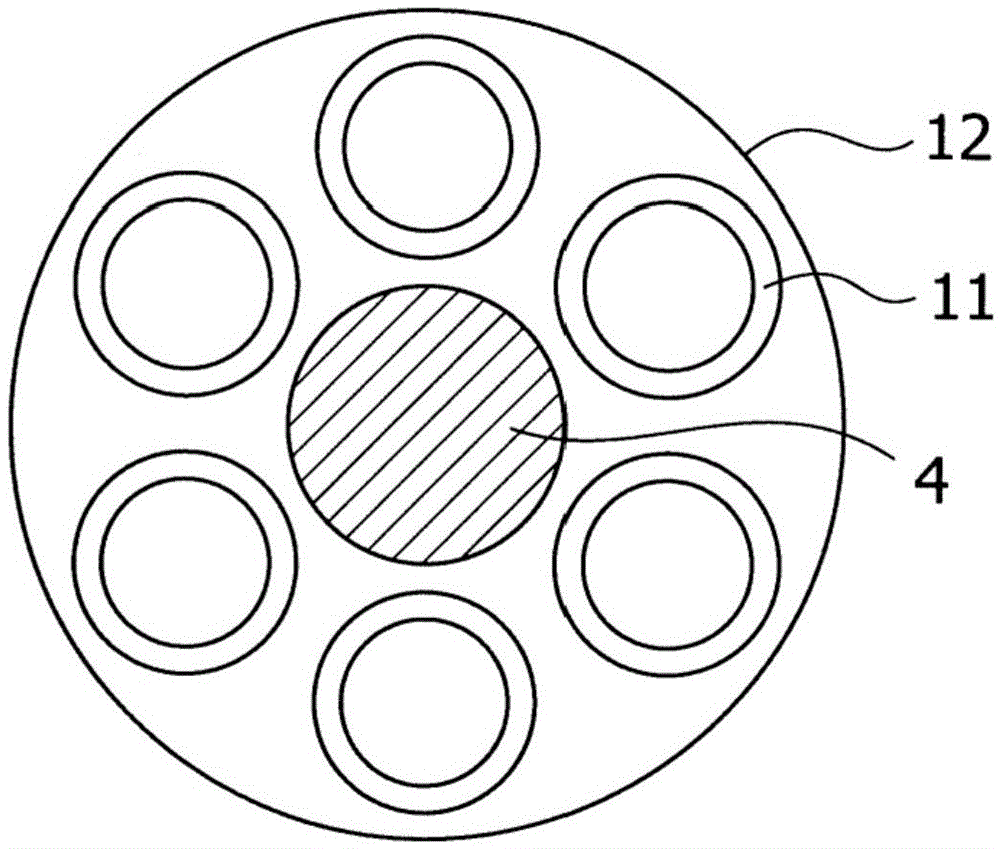
[0095] Refer to the following side Figure 1 to Figure 14 shown attached Figure 1 Embodiments of the outer rotor type variable field motor of the present invention will be described in detail.
[0096] figure 1 It shows the structure of an open type outer rotor type variable excitation motor that automatically performs variable excitation in both forward and reverse rotation directions according to the magnitude of the load torque applied to a brushless motor. figure 2 is to use figure 1 A diagram of the state in which the inner rotor main body is moved by the action of the cam and the cam follower of the outer rotor type variable field motor.
[0097] exist figure 1 and figure 2 Among them, the outer rotor type variable field motor of the present embodiment includes: a motor main body 1; and a motor shaft 4 rotatably supported on the inner periphery of the cylindrical portion 1a of the motor main body 1 via a pair of rotary bearings 2 and 3. The surface side; the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com