Clustering devices and methods
A device and clustering technology, applied in the field of data analysis, can solve the problems of poor clustering quality, difficult to define the weight of spatial attributes and thematic attributes, etc., and achieve the effect of reliable clustering results.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
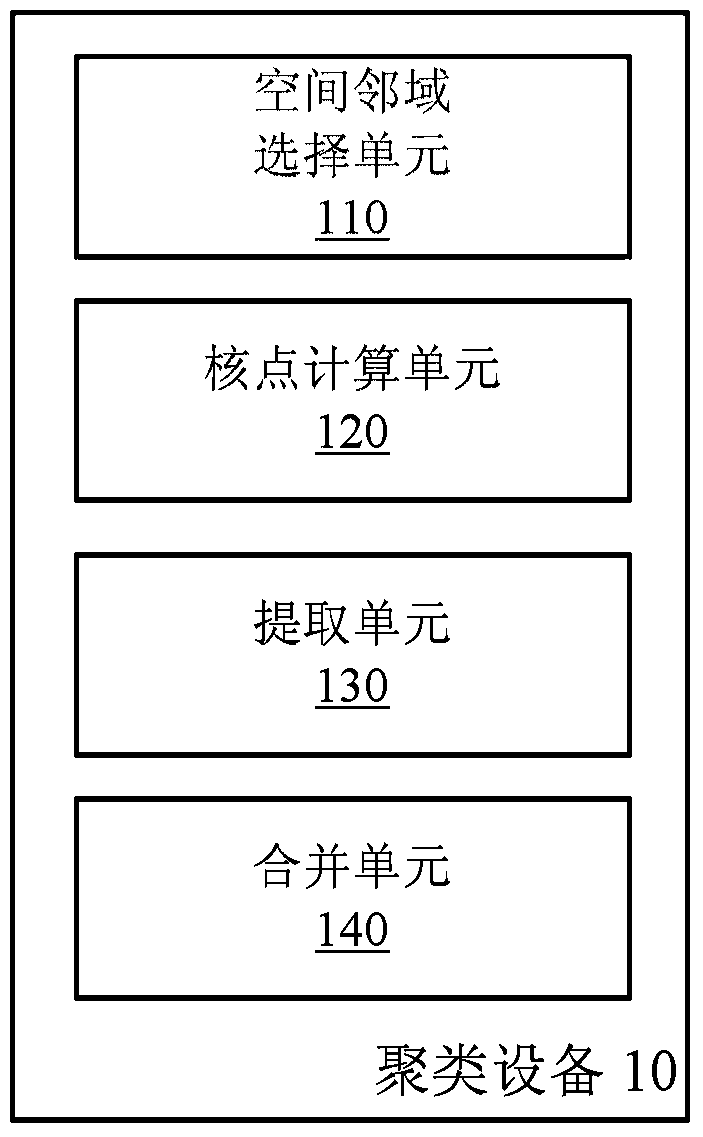
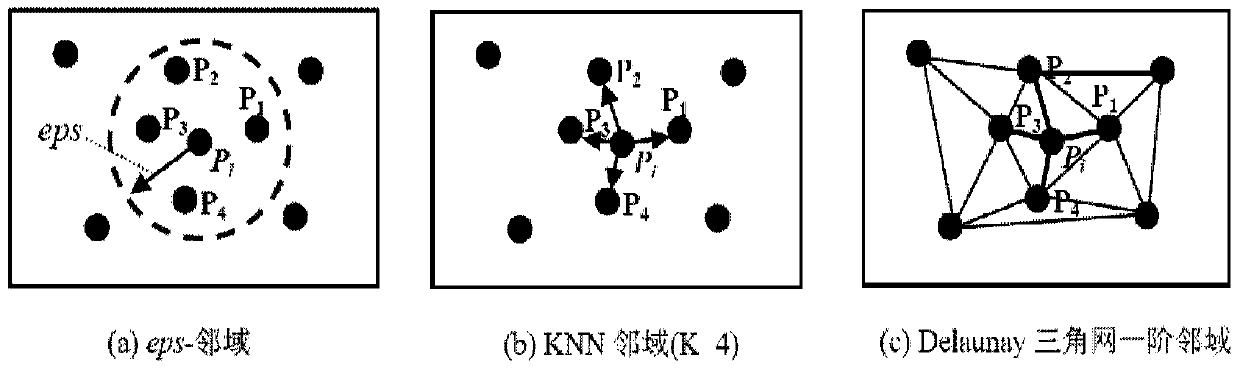
[0060] In this example, the kernel calculation unit 120 first calculates the local variance between each object in the spatial dataset and other objects in the object's spatial neighborhood. Then, the kernel point calculation unit 120 performs multiple random rearrangements in the spatial data set. Finally, the kernel point calculation unit 120 judges whether the object is a kernel point based on the significance of the local variance of each object. The calculation process in Example 1 is described in detail below.
[0061] Using this example, the user does not need to subjectively select parameters when calculating the kernel point, but finds the kernel point according to the characteristics of the data itself, which has a strong adaptive ability and can produce more robust results.
example 2
[0063] In this example, the kernel calculation unit 120 first calculates the local variance between each object in the spatial dataset and other objects in the object's spatial neighborhood.
[0064] Then, the kernel point calculation unit 120 performs multiple times of Bootstrap random sampling in the spatial data set. Bootstrap random sampling is to use the attribute values of all objects as a set, for each object P i , randomly select n from the set sequentially i (n i for object P i The number of objects in the spatial neighborhood) attribute values, and then calculate the object P once i The local variance of , in this way, it is randomly selected multiple times, and each time it is randomly selected, it is extracted from the most original attribute value set, that is, the sampling process with replacement. For example, the existing set of attribute values is {1, 2, 3, 4}, P i There are 3 objects in the neighborhood of the object space, the results of two random ...
example 3
[0067] The inventors of the present invention found that the local variance of the kernel points approximately obeys the chi-square distribution. Therefore, it is possible to randomly rearrange multiple times and calculate the local variance after the rearrangement, and then perform chi-square distribution curve fitting, that is, estimate the parameter k of the chi-square distribution through the local variance value after multiple rearrangements, and then according to Chi-Square Distribution Density Function with Local Variance Calculates the p-value of the local variance.
[0068] Specifically, the kernel point calculation unit 120 calculates the local variance between each object in the spatial dataset and other objects in the spatial neighborhood of the object, and then performs multiple random rearrangements in the spatial dataset. Afterwards, the kernel point calculation unit 120 calculates the local variance of each object and performs chi-square curve fitting, and calc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com