Rope gripper
A rope clamp and rope technology, which is applied in the field of rope clamps, can solve the problem that the safety brake cannot meet the actual use needs of elevator safety protection, and achieve reliable and fast pinch brake, realize safe brake, and realize the protection function Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
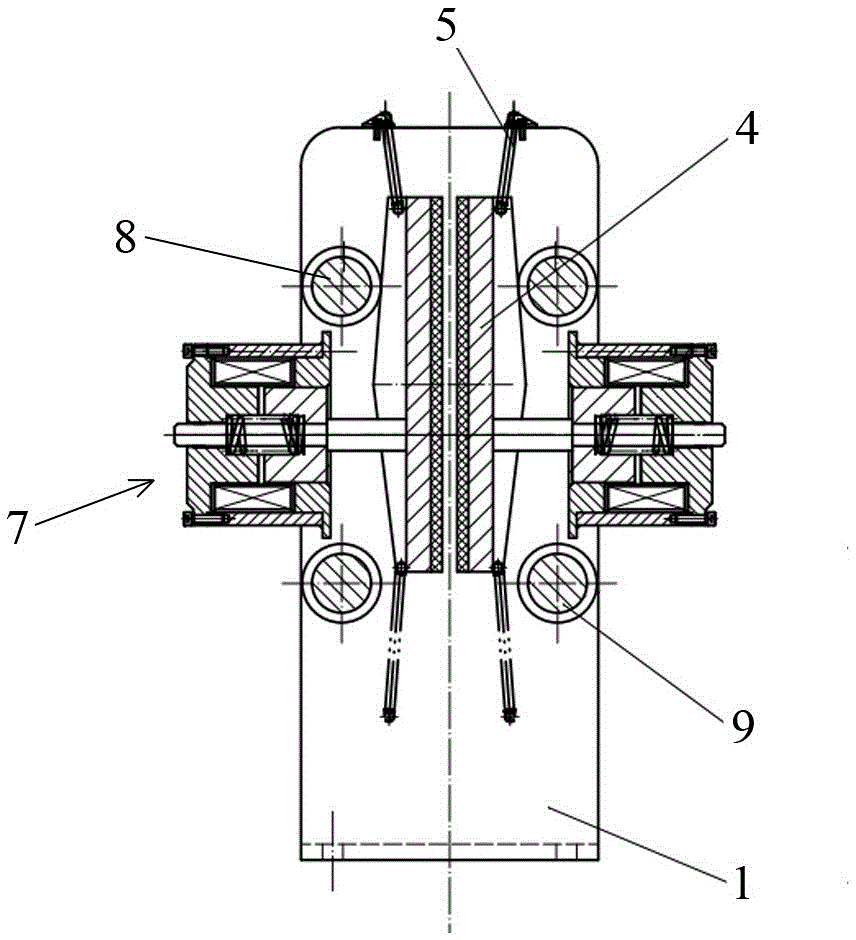
[0032] Such as figure 1 , figure 2 , image 3As shown, the frame 1 is a plate-frame three-dimensional structure surrounded by two end plates and two side frame plates, and two brake clips are arranged in the frame 1, and the clamping of the two brake clips A rope channel 2 is formed between the faces. Both brake clips are movable clips 4, and the structure of the two movable clips 4 is the same, and they are upright and symmetrically arranged in the frame 1 ( figure 1 ). The opposite surfaces of the two movable clamping blocks 4 are clamping surfaces, and the clamping surfaces of the two movable clamping blocks 4 are parallel to each other, and friction plates 3 are arranged on the clamping surfaces of each movable clamping block 4 . The gap between the clamping surfaces of the two movable clamping blocks 4 is the rope channel 2 for passing through the steel wire rope, and the steel wire rope 10 travels up and down in the frame 1 of the rope clamp ( image 3 ). figure 1...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the structure of this embodiment is basically the same as that of Embodiment 1, and the frame 1 is also equipped with double movable clamping blocks. Similarly, two brake trigger mechanisms are correspondingly installed on the frame 1 . The two brake triggering mechanisms all include a brake electromagnet 7, a compression spring 74, a brake push rod 75, etc., and the brake electromagnet 7 adopts an electromagnetic brake triggered by power failure. The front ends of the brake push rods 75 in the two brake trigger mechanisms respectively abut against the longitudinal chute 6 on the back side of the movable clamp block 4 on each side to perform the trigger operation of the safety brake.
[0044] The difference is that four upper horizontal shafts 8 and four lower horizontal shafts 9 are arranged on the frame 1, that is, two parallel horizontal shafts are arranged at each horizontal shaft setting position, and two parallel horizontal shafts are a...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Such as Figure 6 As shown, the basic structure of this embodiment is roughly the same as that of Embodiment 1, the main difference being the two brake clips arranged in the frame 1, one is the movable clip 4, and the other is the fixed clip 11 . The fixed clamping block 11 is fixedly installed in the frame 1, and there is no need to set a brake trigger mechanism to trigger and brake it. Therefore, in this embodiment, only the frame end plate on the side of the movable clamping block 4 is provided with The brake trigger mechanism applies a positive brake trigger extrusion force to the movable clamp block 4 .
[0047] In the present embodiment, the upper cross shaft 8 and the lower cross shaft 9 arranged on the frame 1 are a double-shaft arrangement structure as in embodiment 2, and the two cross shafts in each group are connected with the movable clamp block 4 The oblique position corresponding to the inclination of the slope is set to form a continuous limit to the m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com