Inter-operator interference coordination method
一种干扰协调、网络间的技术,应用在网络规划、分布式分配、电气元件等方向,达到提高干扰协调效率、提升网络性能的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
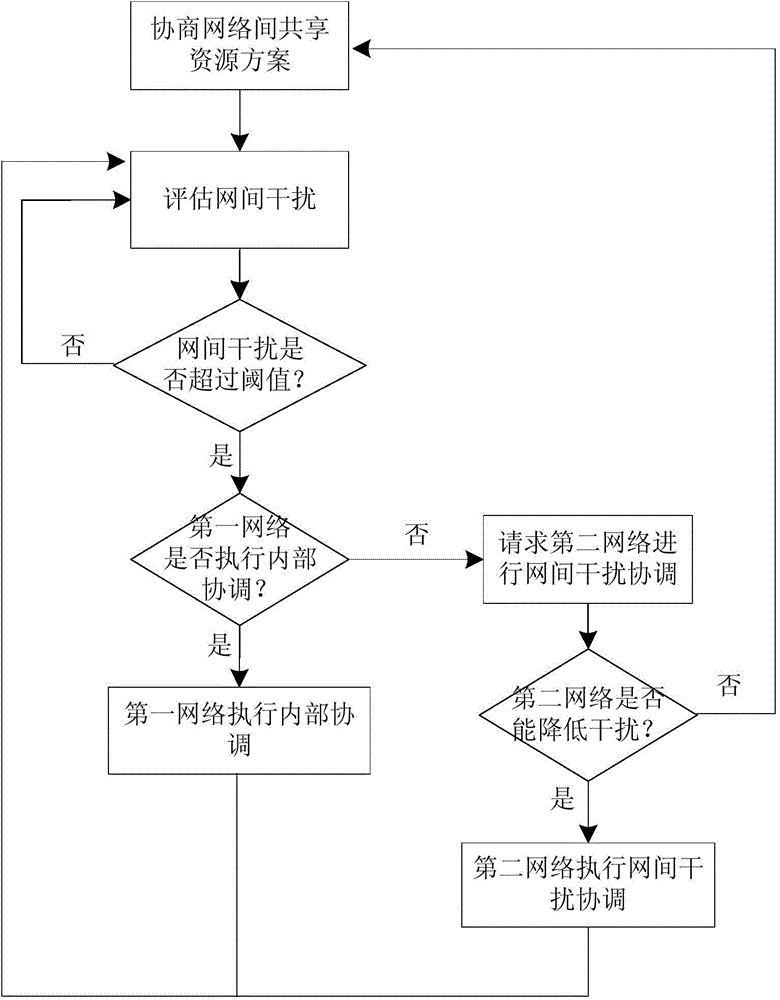
[0037] like figure 1 As shown, the overall solution of the first embodiment includes the following steps:
[0038] Negotiate resource sharing schemes between networks;
[0039] Evaluate network interference;
[0040] The first network judges whether to perform internal coordination, if it judges to perform internal coordination, then the first network performs internal coordination, and returns to the step of evaluating inter-network interference; if it judges not to perform internal coordination, then requests inter-network interference coordination, and proceeds to the next step ;
[0041] The second network judges whether to perform internal coordination, and if internal coordination is performed, the second network performs internal coordination and returns to the step of evaluating inter-network interference; if not performing internal coordination, returns to the step of negotiating a resource sharing scheme between networks.
[0042] To simplify the description, this...
no. 2 example
[0128] To briefly introduce the second embodiment of the present invention, only the differences from the first embodiment are described here.
[0129] Image 6 The network-level inter-network interference of each carrier in the shared spectrum pool of the second embodiment is shown. with the first embodiment Figure 4 Different, the network-level inter-network interference value in the first embodiment is non-quantified, and the network-level inter-network interference value in the second embodiment is quantized, which is divided into high interference, medium interference and low interference, and its signaling The format is as follows. Wherein, the "signaling content" of the second embodiment is different from that of the first embodiment, which is the description of the interference level (it is a quantized value).
[0130]
no. 2 example 3
[0131] Specifically, the second embodiment has three modes:
[0132]
[0133] The second embodiment is the same as the first embodiment, as Figure 4 As shown, for each carrier in the shared spectrum pool, according to the cell-level inter-network interference reported by all the cells assigned to the carrier, the operator management node calculates the average value of the inter-network interference, and obtains the corresponding The average value of inter-network interference received.
[0134] like Image 6 As shown, based on the average cell-level inter-network interference received by the network on each carrier, N operator interference thresholds are selected to quantify the average interference, which corresponds to the average inter-network interference received by the network on each carrier The level has N+1 levels, and the quantified result is used as an indication of network-level interference between networks.
[0135]
[0136] Same as the alternative in th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com