Classifier generation method using combination of mini-classifiers with regularization and uses thereof
A technology of classifiers and main classifiers, applied in applications, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as limited performance evaluation and small scale of available sample sets
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0084] Generation of CMC / D classifiers from mass spectrometry
[0085] Data obtained from human samples
[0086] ( Figure 1-Figure 11 )
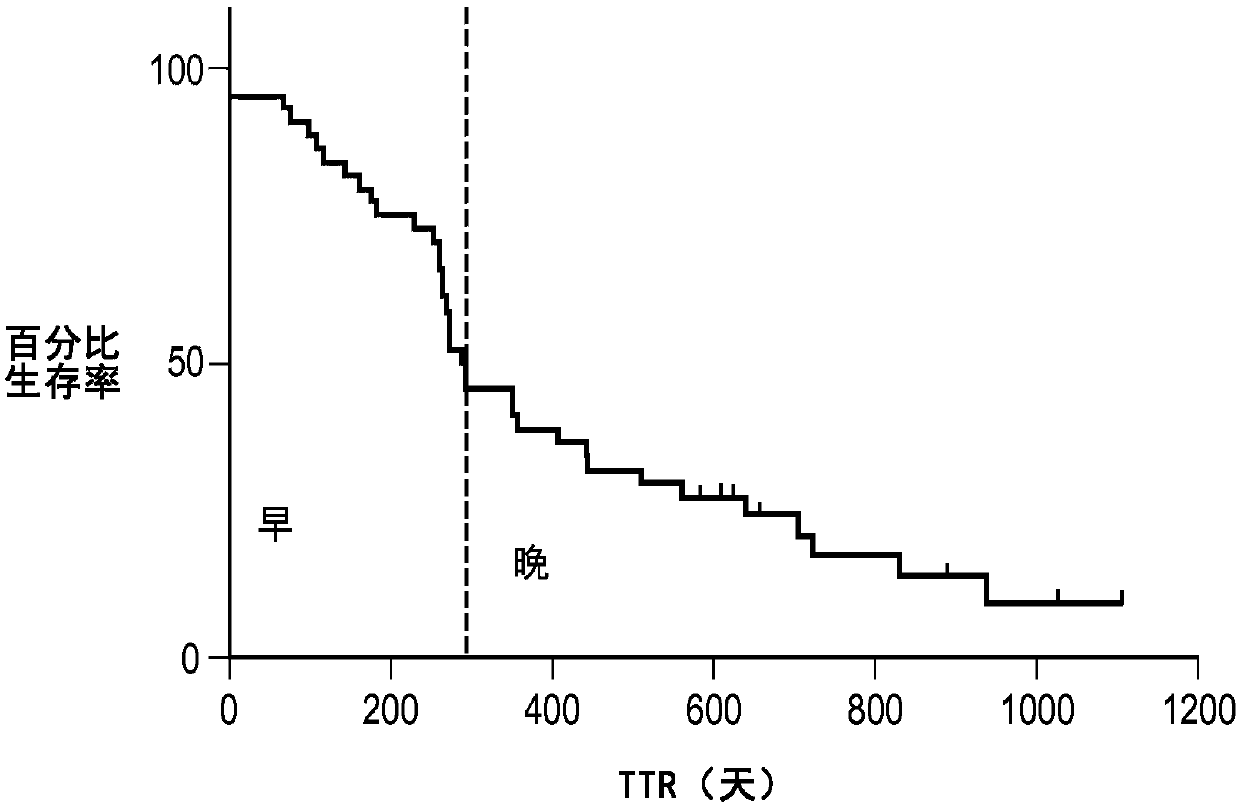
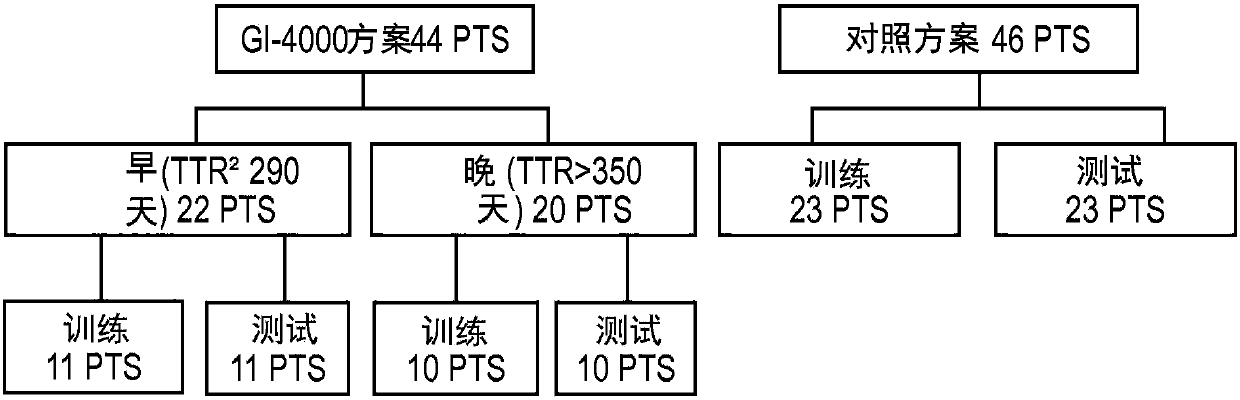
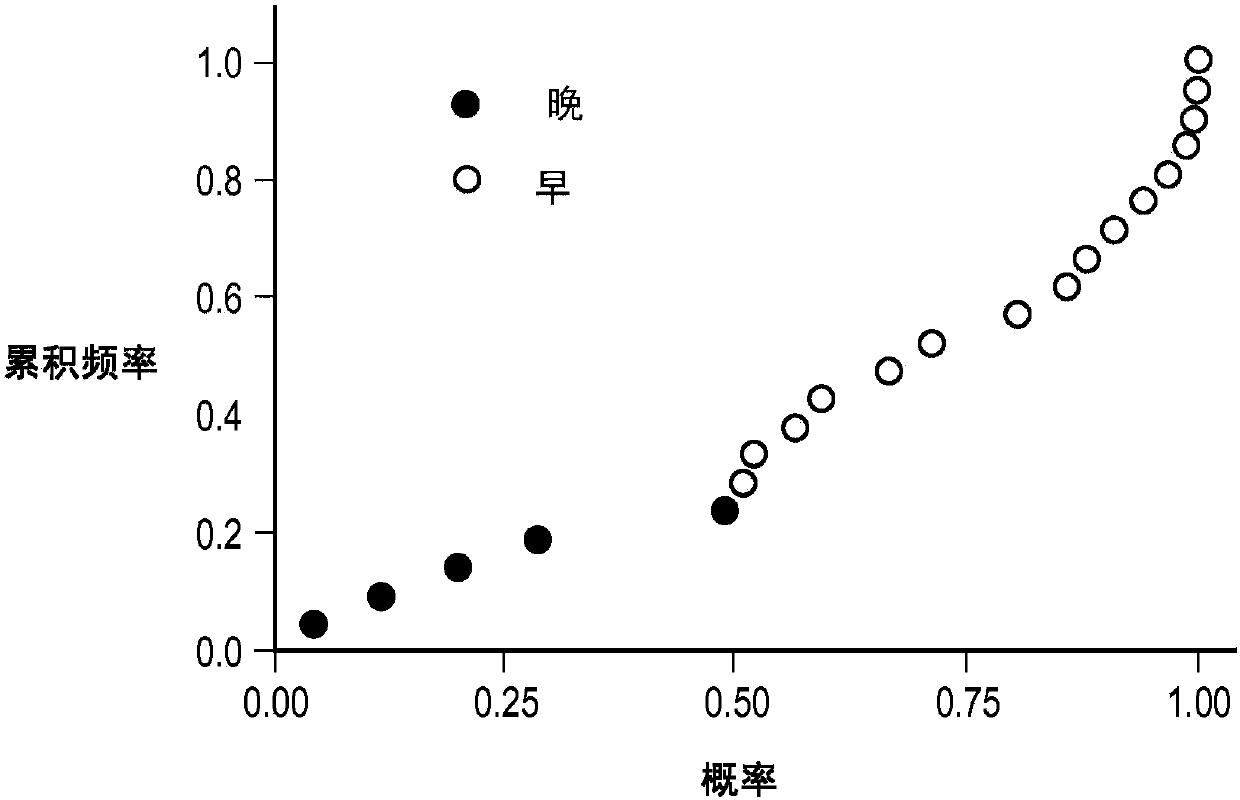
[0087] This section of the paper will illustrate a practical example of performing the CMC / D classifier development method in the context of a sample set in the form of blood-based samples subjected to mass spectrometry and resulting in a data set used in the classification, The dataset was in the form of 100 features (peaks) at different m / Z positions, which were used as the set of features from which to select the features for the mini-classifier. The above samples were obtained from pancreatic cancer patients participating in a clinical trial of the drug GI-4000. The goal of the classifier generation exercise was to demonstrate whether it is possible to construct a classifier (test) operating on the mass spectrum of a blood-based sample that accurately predicts whether a pancreatic cancer patient associated with that sample is likely ...
example 2
[0176] Classifier generation system and sample test system
[0177] The CMC / D classifier development method described above can be implemented as a tangible classifier development system in the form of a mass spectrometer (or other detection instrument) used to extract samples from multiple samples (e.g., Classifier development set of samples) to obtain mass spectral (or other) data; the general purpose computer has a processing unit that executes code for implementing the CMC / D classification method. In particular, the computer includes a machine-readable memory (such as a hard disk) for storing detection data. The computer also stores executable code that performs preprocessing of the detection data, such as background subtraction, spectral calibration and normalization (as described above), and stores integrated intensity values at specific features for classification, e.g. Example 1 Integrated intensity values for the features listed in Appendix B.
[0178] The compute...
example 3
[0205] EGFR-I Drug Selection (VS2.0) for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Patients Generating CMC / D Classifiers by Mass Spectrometry of Patient Blood-Based Samples
[0206] Another example of generating a CMC / D classifier and using it to guide the treatment of NSCLC patients is described in this section. The generation of the classifier largely followed that described in Example 1 above and in Example 2 above for Figure 11 method described in the Discussion. However, in this example, the processing of the test samples for prediction with the CMC / D classifier utilized the reference spectra, and the spectral Additional adjustments made by processing. The generation of the final classification labels for the tested samples also exploits the feature-dependent noise properties and the following will combine Figure 12 Other techniques are described in more detail. However, this section will show yet another example of generating a CMC / D classifier from mass spectrometry data...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com