A method for preparing tin-iron coarse alloy powder from tin-containing iron ore
A crude alloy and iron ore technology, applied in the field of iron and steel metallurgy, can solve the problems of high energy consumption, high production cost, environmental pollution and other problems in high-temperature roasting, and achieve the effects of low equipment requirements, large loss rate and low recovery rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
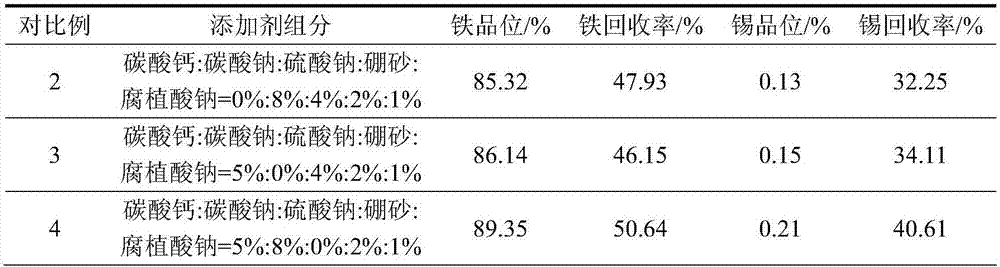
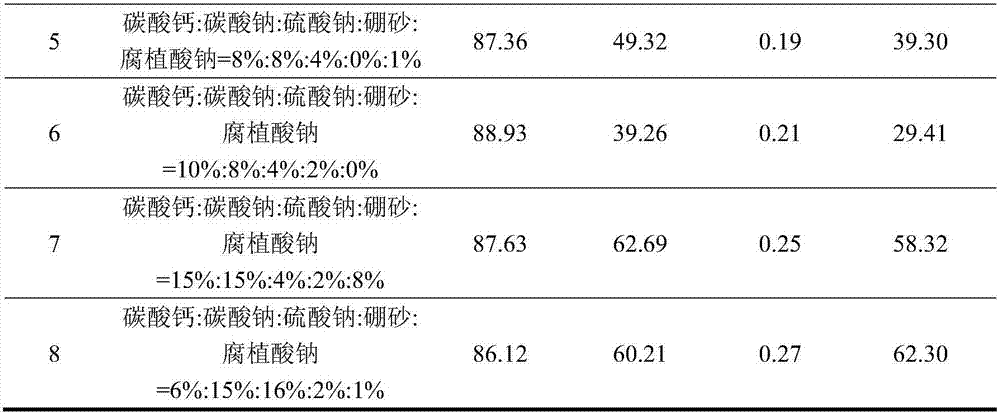
[0024] The tin-bearing iron ore with a TFe grade of 32.11% and a Sn content of 0.18% is 80% after crushing and grinding to -0.074mm; according to the mass fraction of tin-bearing iron ore 10%, 10%, 3%, 1%, 2% Add additives calcium carbonate, sodium carbonate, sodium sulfate, borax, and sodium humate respectively, mix well and pelletize in a disc pelletizer; dry pellets with excess lignite as reducing agent, reduction temperature 1050°C, reduction time 60min ; The reduced roasted product is cooled and ground to -0.074mm, accounting for 85%, and magnetically separated at a magnetic separation intensity of 1000Gs. The iron grade in the obtained tin-iron coarse alloy powder is 90.11%, the iron recovery rate is 92.19%; the tin grade is 0.52%, and the tin recovery rate is 92.10%.
Embodiment 2
[0026] The tin-bearing iron ore with a TFe grade of 32.11% and a Sn content of 0.18% accounts for 85% after crushing and grinding to -0.074mm; according to the mass fraction of tin-bearing iron ore 6%, 12%, 5%, 2%, and 1% Add additives calcium carbonate, sodium carbonate, sodium sulfate, borax, and sodium humate respectively, mix well and pelletize in a disc pelletizer; dry pellets with excess bituminous coal as reducing agent, reduction temperature 900°C, reduction time 120min ; The reduced roasted product is cooled and ground to -0.074mm, accounting for 87%, and magnetically separated at a magnetic separation intensity of 800Gs. The iron grade in the obtained tin-iron coarse alloy powder is 89.23%, the iron recovery rate is 93.19%; the tin grade is 0.50%, and the tin recovery rate is 90.31%.
Embodiment 3
[0028] The tin-bearing iron ore with a TFe grade of 32.11% and a Sn content of 0.18% accounts for 83% after crushing and grinding to -0.074mm; according to the mass fraction of tin-bearing iron ore 5%, 8%, 3%, 1.5%, 1.6% Add additives calcium carbonate, sodium carbonate, sodium sulfate, borax, and sodium humate respectively, mix well and briquette; add excess lignite as reducing agent to the dry mass, reduce temperature at 1000°C, and reduce time for 100 minutes; reduce the roasted product and cool it Post-grinding to -0.074mm accounts for 81%, and magnetic separation is performed at a magnetic separation intensity of 1500Gs. The iron grade in the obtained tin-iron coarse alloy powder is 88.81%, the iron recovery rate is 94.00%; the tin grade is 0.50%, and the tin recovery rate is 91.67%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| magnetic flux density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com