Methods for classifying pleural fluid
A technology for pleural fluid and exudate, which is used in biochemical equipment and methods, pharmaceutical formulations, emulsion delivery, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
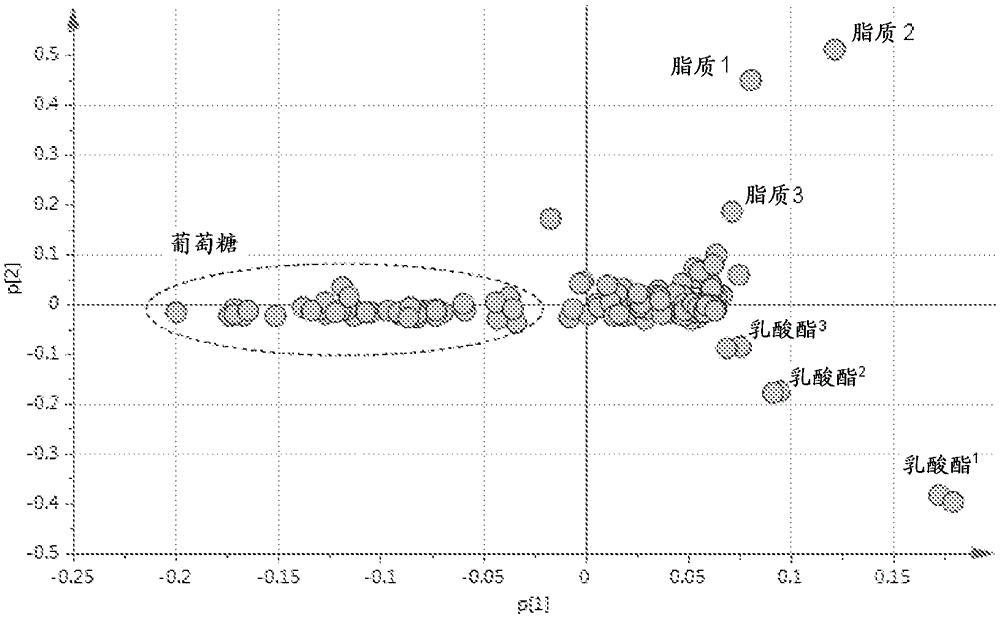
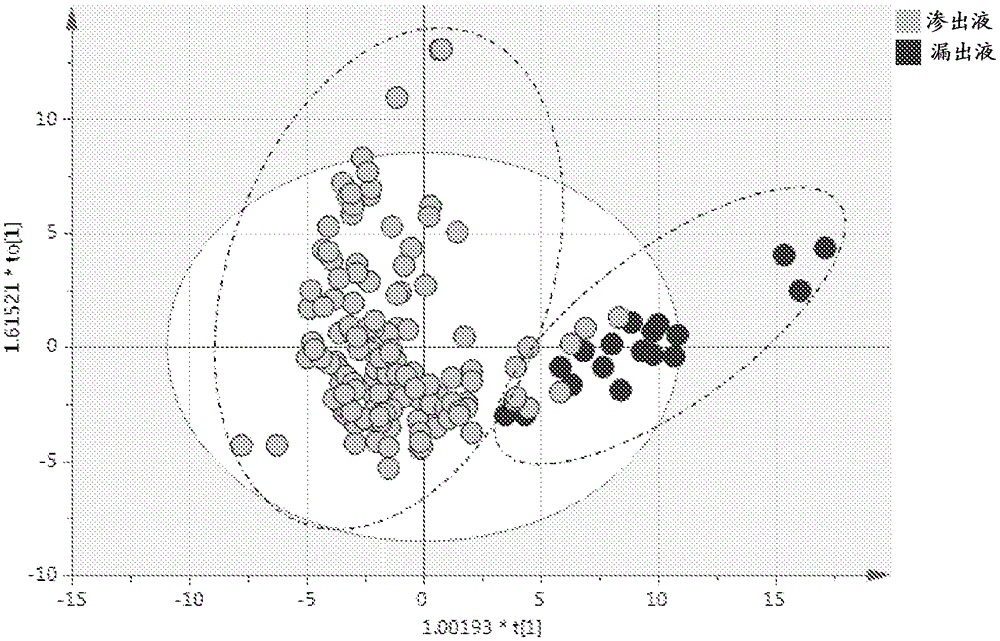
[0105] Pleural effusion NMR signals of lipid particles as biomarkers of exudative pleural effusions
[0106] Materials and methods
[0107] Sample Preparation
[0108] Samples were collected into sterile regular bottles, followed by centrifugation at 3000 rpm for 10 minutes at 4°C to obtain a clear supernatant. At the time of analysis, mix 480 μL sample with 120 μL buffer solution (in 100% D 2 1.5MKH in O 2 PO 4 )mix. Samples were pooled and 550 μL of each were freshly transferred to 5 mm NMR tubes for NMR analysis.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com