A Method for Predicting the Corrosion Remaining Life of Transmission Line Towers in Coastal Areas
A technology for transmission line and life prediction, which is applied in the field of electric power engineering to achieve the effect of clear physical meaning, strong practicability and high accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
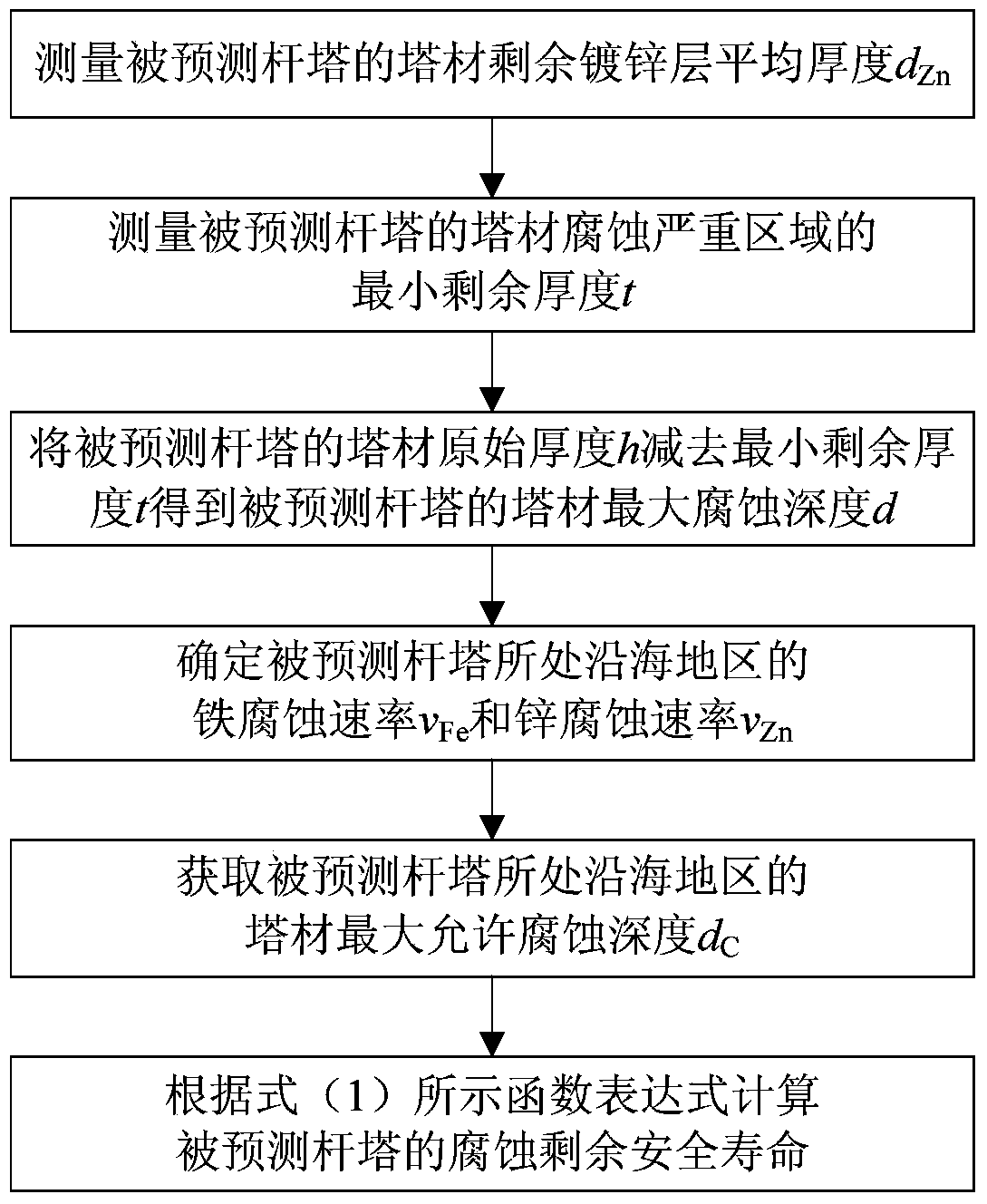
[0033] like figure 1As shown, the steps of the method for predicting the remaining corrosion life of transmission line towers in coastal areas in this embodiment include:
[0034] 1) Measure the average thickness d of the remaining galvanized layer of the tower material to be predicted Zn , unit μm;
[0035] 2) Measure the minimum remaining thickness t of the severely corroded area of the tower material of the predicted tower, and subtract the minimum remaining thickness t from the original thickness h of the tower material of the predicted tower to obtain the maximum corrosion depth d of the tower material of the predicted tower, in mm; In the embodiment, the original thickness h of the predicted tower material is 8 mm, the minimum remaining thickness t is 5 mm, and the maximum corrosion depth d of the tower material is 3 mm;
[0036] 3) Determine the iron corrosion rate v in the coastal area where the predicted tower is located Fe and zinc corrosion rate v Zn ;
[003...
Embodiment 2
[0056] This embodiment is basically the same as the first embodiment, and the main difference is that the implementation methods of step 3) and step 4.1) are different.
[0057] In this embodiment, the detailed steps of step 3) include: first obtain the classification of the corrosion environment in the coastal area where the predicted tower is located, and then query the preset maximum corrosion rate comparison table for the corrosion environment according to the classification of the corrosion environment (see Table 1 for details), Get the iron corrosion rate v of the coastal area where the predicted tower is located Fe and zinc corrosion rate v Zn .
[0058] Table 1: Comparison table of maximum corrosion rate in corrosive environment.
[0059]
[0060] The classification of the corrosive environment in the coastal area where the predicted tower is located can be obtained from the environmental monitoring center or atmospheric corrosion site where the predicted tower ta...
Embodiment 3
[0064] This embodiment is basically the same as the first embodiment, and the main difference is that the implementation methods of step 3) and step 4.1) are different.
[0065] In the present embodiment, the detailed steps of step 3) include: first directly calculate the iron corrosion rate v of the coastal area where the predicted tower is located according to formula (3) Fe , and then according to the predicted iron corrosion rate v in the coastal area where the tower is located Fe Look up the comparison table of the maximum corrosion rate of the preset corrosion environment (see Table 1 for details), and obtain the zinc corrosion rate v of the coastal area where the predicted tower is located Zn ;
[0066] v Fe =1000(h-t)÷T (3)
[0067] In formula (3), v Fe is the iron corrosion rate in the coastal area where the predicted tower is located, h is the original thickness of the tower material of the predicted tower, t is the minimum remaining thickness of the severely cor...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electrical resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com