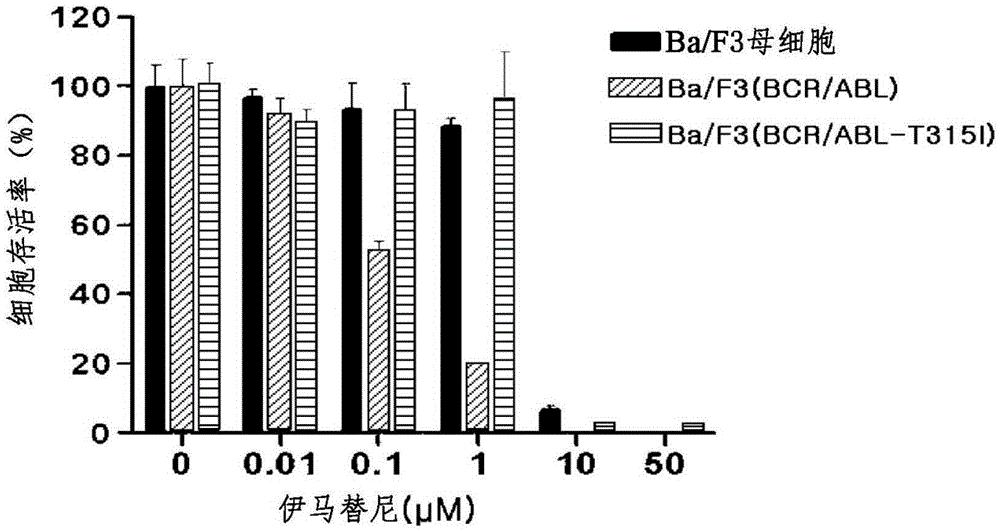
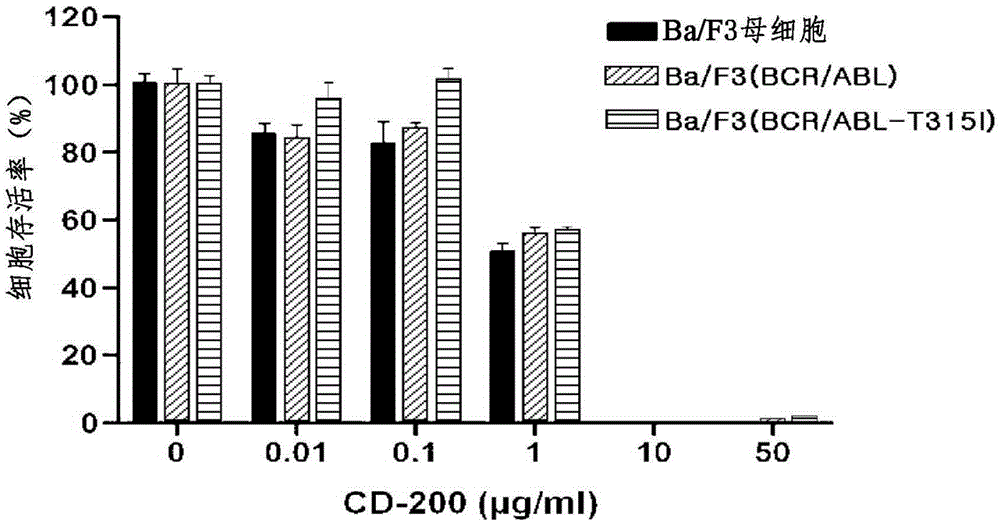
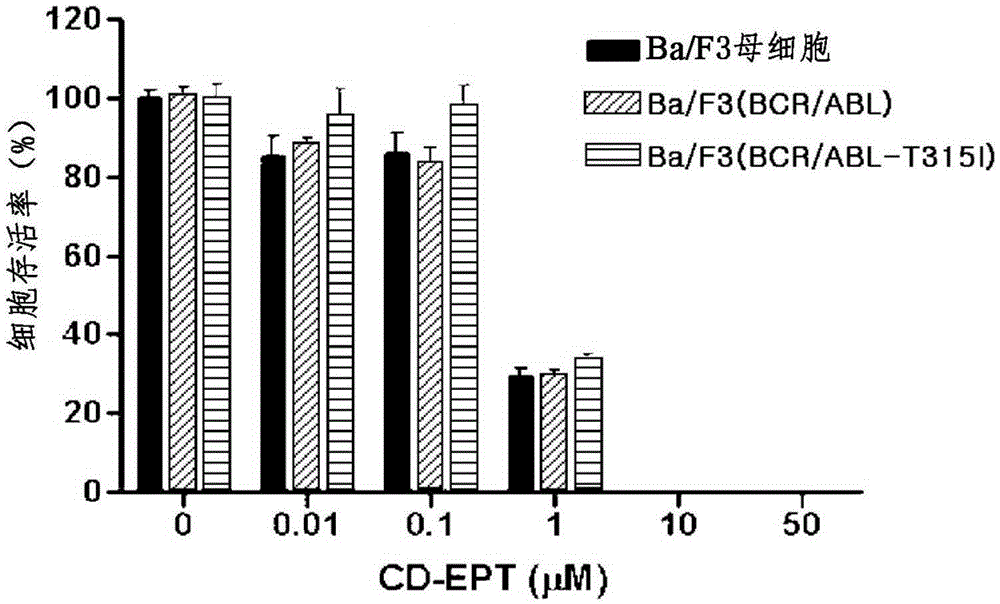
Pharmaceutical composition containing liriodendron tulipifera l. extract for treating chronic myelogenous leukemia
A technology of myeloid leukemia and composition, applied in the field of T315I enzyme variant
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example 1
[0059] (Preparation Example 1) Preparation of the extract (CD-200) from the bark of Liriodendron tulipifera
[0060] 1. Solvent extraction step
[0061] 200 g of chopped and dried bark of Liriodendron tulipifera (3-5 years old) was stirred and extracted with 2000 ml of ethyl acetate for 24 hours at room temperature. The primary extract was obtained after concentration and filtration of the extracted mixture under reduced pressure. The resulting primary extract was further mixed and extracted with 500 ml butanol for 2-4 hours at room temperature. Then, the butanol soluble material was removed by separating and removing the butanol layer. After concentrating the remaining mixture, 12.54 g of crude extract was finally obtained.
[0062] 2. Purification steps
[0063] After 12.54 g of the obtained crude extract was dissolved in 200 ml of 70% ethanol, 200 ml of n-hexane was added to the crude extract mixture and stirred. After separating and removing the n-hexane layer, a 70% ...
preparation example 2
[0064] (Preparation Example 2) Preparation and separation of epituliprolactone fraction (CD-EPT) as the main component of CD-200 from the bark of Liriodendron tulipifera
[0065] The high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) Alliancee 2695 system of WATERS was used to separate the epituliprolactone fraction from the extract CD-200 from the bark of Liriodendron tulipifera. The conditions of HPLC analysis were as follows: using a reversed-phase column Kromasil C18, loading 5 mg / ml of the sample, and measuring the amount of the eluate with a UV wavelength of 215 nm (flow rate: 1.0 ml / min). In addition, mobile phase (water and methanol) gradient conditions were employed. Finally, the epituliprolactone fraction was isolated from the fraction with retention time = ~31 minutes. This extract was named CD-EPT.
preparation example 3
[0066] (Preparation Example 3) Isolation and Identification of Epituliprolactone (CD-EPT)
[0067] After loading and passing both the samples of the above fractions and the epi-lipidolide standard through the HPLC column, the epi-lipidolactone in the obtained fractions was identified by comparing the retention times. Then, since the retention time of both the obtained site and epi-lipidolide was measured to be the same, it was confirmed that the component of the obtained site was mainly composed of epi-lipidolactone. In addition, the specific rotation of epituliprolactone was measured. The measured value of epituliprolactone from CD-200 ([α]D=+74) was almost in agreement with the reported value of epituliprolactone ([α]D=+76). Therefore, the presence of epituliprolactone was confirmed by stereochemistry.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com