Electric vehicle charging management method based on urban infrastructure and system
A technology for electric vehicle and charging management, applied in electric vehicle charging technology, electric vehicles, secondary battery charging/discharging, etc., can solve problems such as equipment not running, resource waste, and low load utilization rate of substations, and achieve less site, delaying construction investment, and solving the effect of grid load pressure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
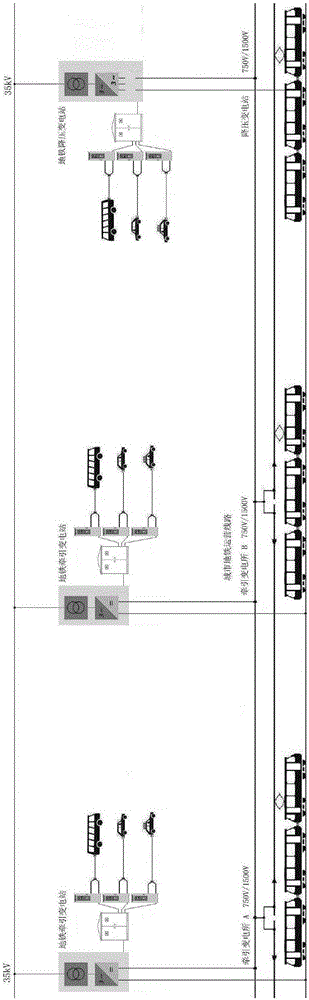
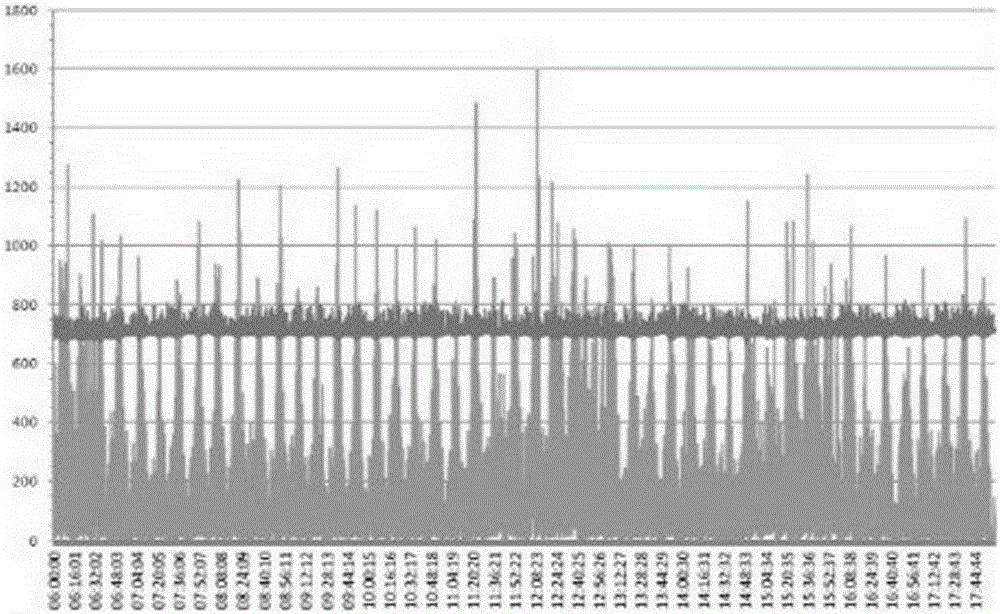
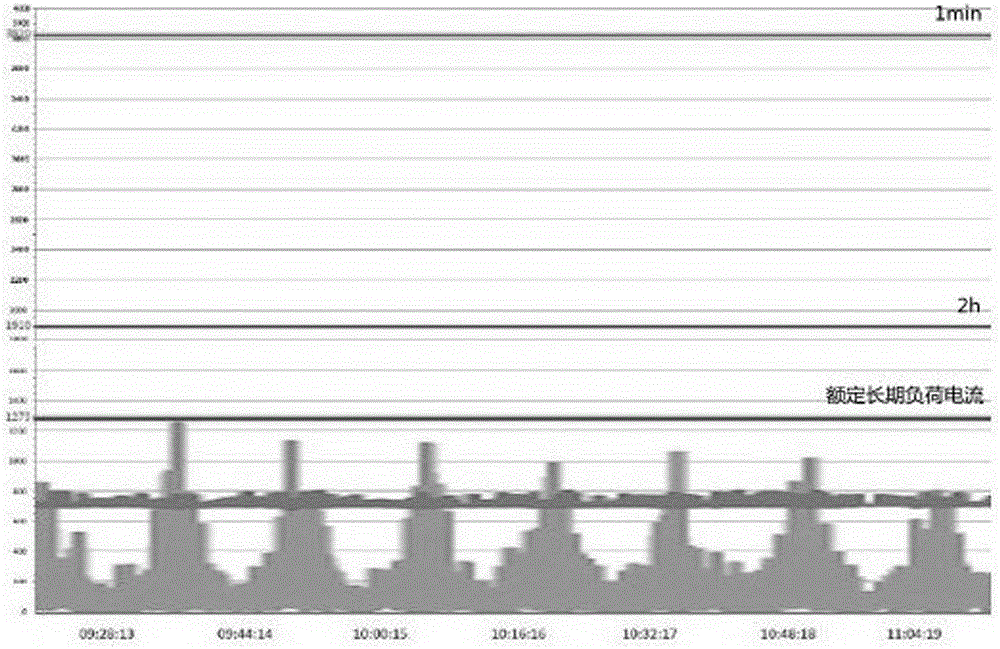
[0039] Such as image 3 As shown, this invention utilizes the abundant power of the existing urban basic smart grid and several substations electrically connected to the urban basic grid, and transforms it on this basis, and appropriately increases some substations according to the station conditions Fast charging devices and energy storage batteries not only solve the load pressure on the power grid brought about by the large-scale development of electric vehicles, but also are used for peak shaving and valley filling, spinning reserve, new energy access, and improve the flexibility, reliability and energy utilization efficiency of power grid power supply , Delay investment in power grid construction.
[0040]Specifically, the system includes an urban basic smart grid, several substations electrically connected to the urban basic grid, a bidirectional power supply electrically connected to the substation, an energy storage battery connected to the bidirectional power supply, ...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Such as Figure 4 As shown, this embodiment is roughly the same as Embodiment 1, the difference is that the urban basic smart grid described in this embodiment is the catenary of urban trams, and the traction substation of urban trams receives power from the urban power supply network. The traction substation outputs 800V (650V) alternating current from the 10kV / 20kV power grid through the traction rectifier transformer, and outputs 750V (600V) traction power through the 12-phase or 24-phase rectifier, and takes power from the DC traction power supply 750V (600V) after transformation. The two-way power supply, the energy storage battery, the substation fast charging device and the power dispatching software management system are connected.
Embodiment 3
[0054] Such as Figure 5 As shown, this embodiment is roughly the same as Embodiment 1. The difference is that the urban basic smart grid described in this embodiment is an urban supercapacitor tram catenary, and the traction power supply of the urban supercapacitor tram takes power from 380V and is rectified by traction. After the transformer is stepped up, it outputs 520 AC power, outputs 600-720V traction power through a 12-phase rectifier, takes power from 600-720V DC traction power, and respectively connects to the bidirectional power supply, the energy storage battery, and the substation fast charging device And power scheduling software management system.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com