Method for producing fermented milk, and dairy product
A manufacturing method and technology for fermented milk, which are applied in the directions of dairy products, milk preparations, and applications, can solve the problems of excess, complicated heating conditions, and taste deterioration of yogurt, and achieve the effect of preventing deterioration of taste.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
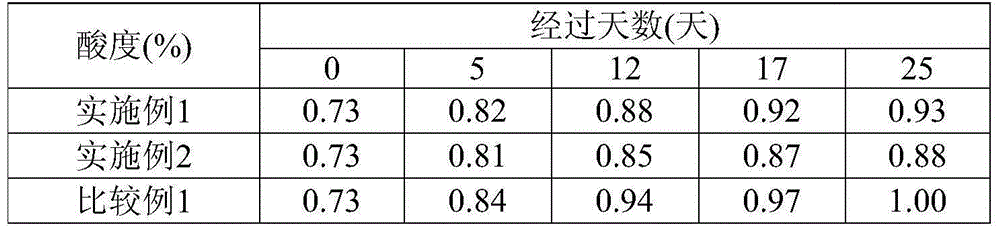
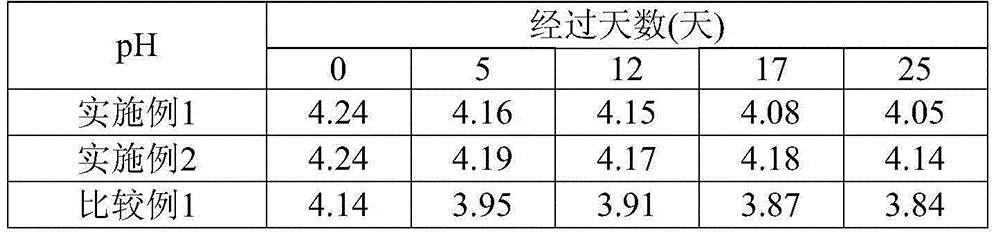
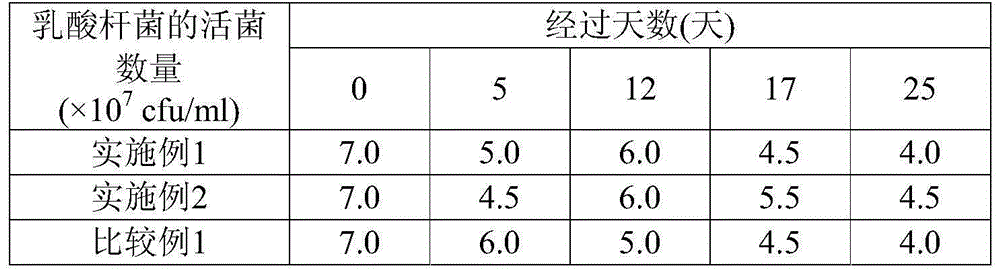
[0060] From the time when the preparation of the final product is completed (specifically, when the final product is fermented milk, it is the time when the fermentation process of fermented milk is completed; when the final product is a dairy product other than fermented milk, it is the time of the dairy product When the fermented milk obtained by the present invention or a dairy product containing the fermented milk (hereinafter also referred to as "fermented milk, etc. of the present invention") is stored at a temperature of 10° C. The range of increase of the acidity (%) in the 25 days (in other words, the acidity value after 25 days minus the value of the acidity value after 0 days) is preferably 0.25% or less, more preferably 0.23% or less, more preferably 0.20% or less, particularly preferably 0.18% or less. The lower limit of this value is not particularly limited, and the smaller the better, it is usually 0.10%.
[0061] In addition, when the fermented milk of the pr...
Embodiment 1
[0072] [Example 1; case of carrying out fermentation at high temperature (45° C.) (laboratory-scale experiment)]
[0073] 705 g of skimmed milk powder and 4195 g of tap water were mixed to prepare fermented milk raw materials (yoghurt mixture), heat-sterilized at 95°C for 10 minutes, and then cooled to 45°C. Next, inoculate 100 g of a mixed starter of Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus isolated from "Meiji Bulgarian yoghurt" (trade name; manufactured by Meiji Dairy Co., Ltd.), in a tank at 45° C. Fermentation was carried out, and when the fermentation time was 5 hours, the acidity reached 1.20% due to the generation of lactic acid, and the fermentation process was terminated, followed by cooling to 10° C. or lower to obtain fermented milk. In addition, as fermentation time, this 5 hours was the same as the case of the comparative example 1 which fermented at the conventional optimum temperature mentioned later.
[0074] The obtained fermented milk was hom...
Embodiment 2
[0075] [Example 2; case of carrying out fermentation at high temperature (47° C.) (laboratory-scale experiment)]
[0076] 705 g of skimmed milk powder and 4195 g of tap water were mixed to prepare a fermented milk raw material (yoghurt mixture), which was heat-sterilized at 95°C for 10 minutes, and then cooled to 47°C. Next, inoculate 100 g of the mixed starter in the same manner as in Example 1, and ferment in the tank at 47°C. When the fermentation time is 5.5 hours, the acidity reaches 1.20% due to the generation of lactic acid, and the fermentation process is completed, followed by cooling. to below 10°C to obtain fermented milk. In addition, as fermentation time, this 5.5 hours is almost the same as the case of the comparative example 1 which fermented at the conventional optimum temperature mentioned later.
[0077] About the obtained fermented milk, it carried out similarly to Example 1, and obtained the fermented milk product (drinking type yoghurt) which is a final p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com