Estimation Method of Body Mount Dynamic Stiffness Based on Mobile Multilevel Bandwidth Estimation Model
A technology of bandwidth estimation and dynamic stiffness, applied in the field of dynamic stiffness estimation, to achieve the effect of reducing the number, strong engineering applicability, and strong application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
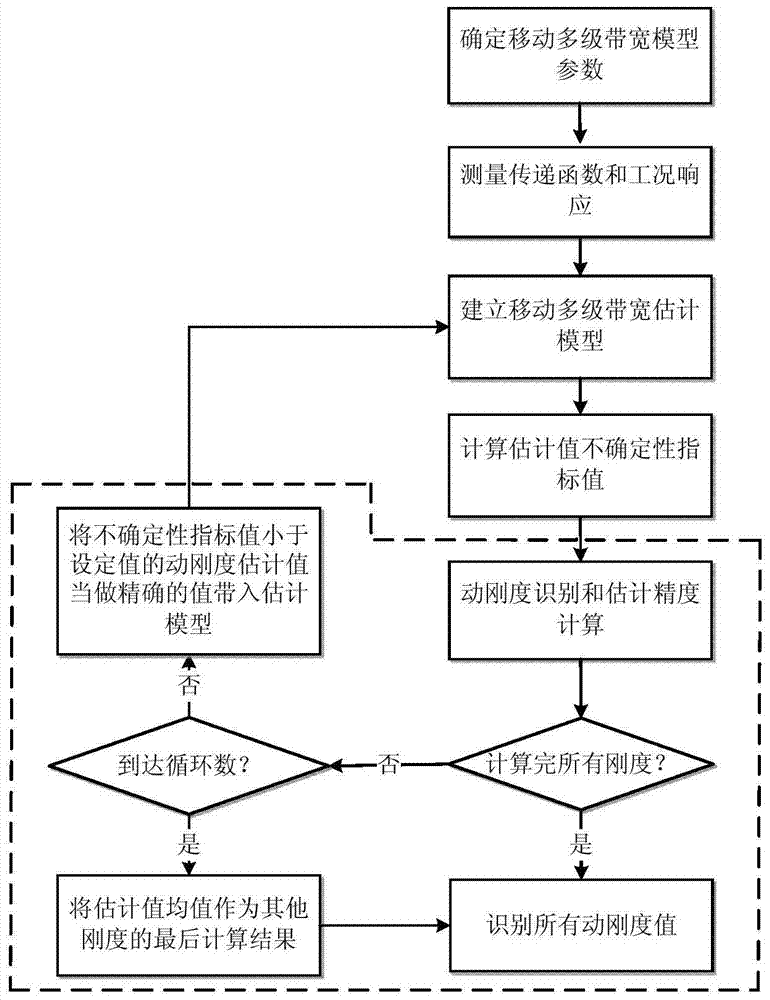
[0037] Such as figure 1 and Figure 4 As shown, this embodiment includes the following steps:
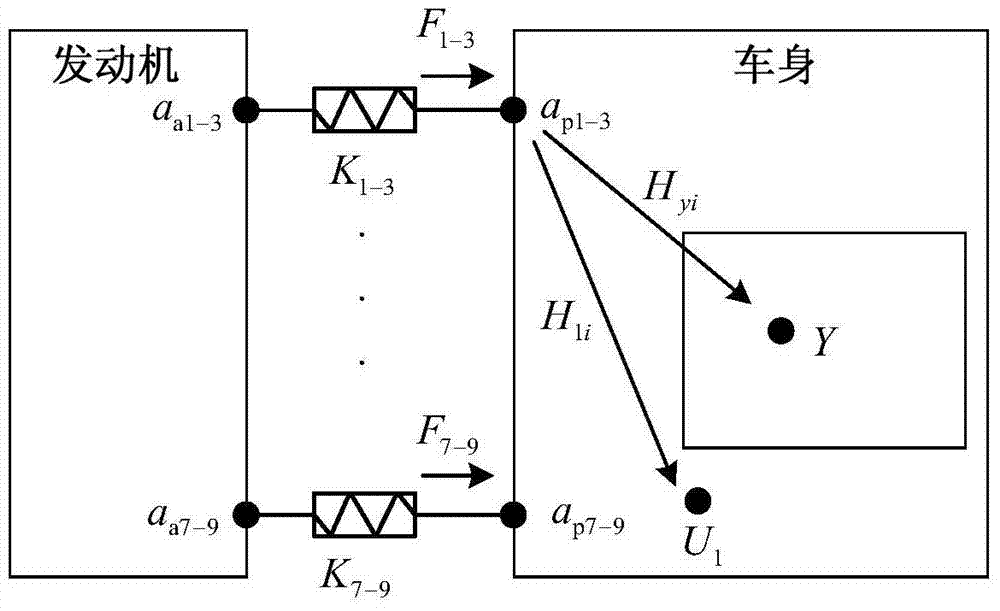
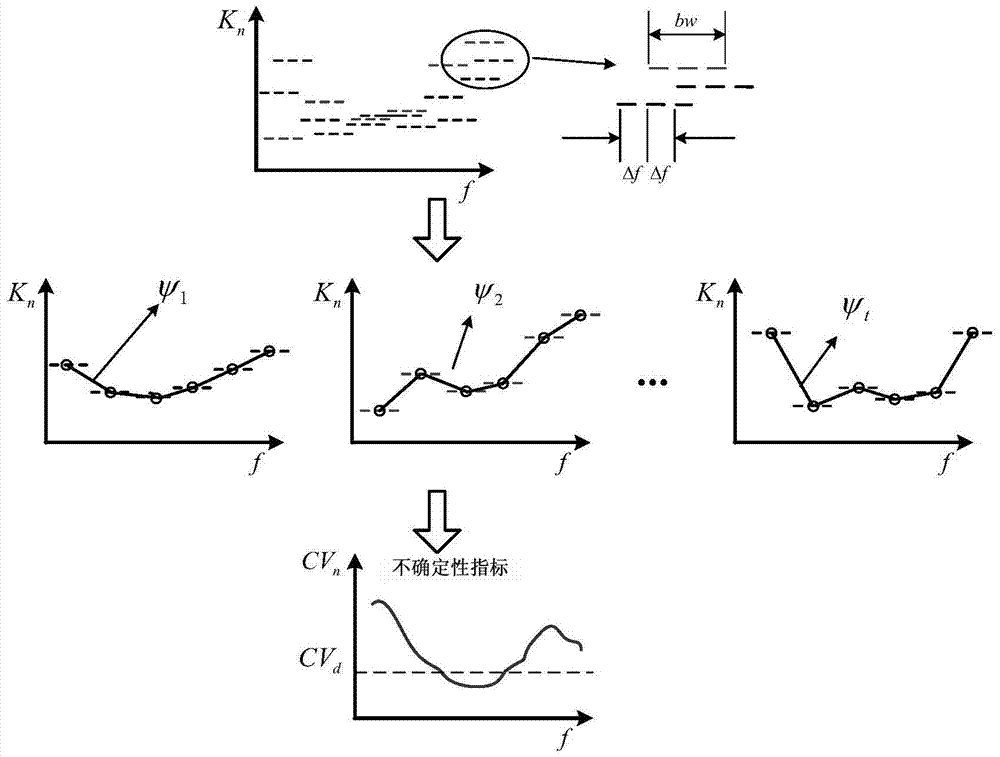
[0038] Step 1. Determine the parameters of the multi-level bandwidth estimation model for the engine mount movement: the engine system has three mounts: left mount, right mount and rear mount. Each mount only considers the dynamic stiffness in the translational direction (X, Y, Z three directions), so there are 9 dynamic stiffnesses of transmission paths, the analysis frequency range is 10‐190Hz, and 10 order slice data are used. According to the empirical formula of the mobile multi-stage bandwidth estimation model: n=9, m=10, fr=191Hz, bw=32Hz, Δf=4Hz, and the implementation condition can be satisfied when the number of reference points is 1, that is, v=1.
[0039] Establish a transfer path analysis model, such as figure 2 shown.
[0040] Step 2. Measure the operating condition response and transfer function:
[0041] 2.1) Under working conditions, measure on the vehicle bod...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com