Probabilistic-routing-oriented DTN (delay-tolerant network) congestion avoiding method
A delay tolerant network and congestion avoidance technology, applied in the field of delay tolerant network, can solve the problems of node congestion, not considering the success rate of data transmission, not considering the number of copies of data packets, etc., to achieve the effect of avoiding congestion.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
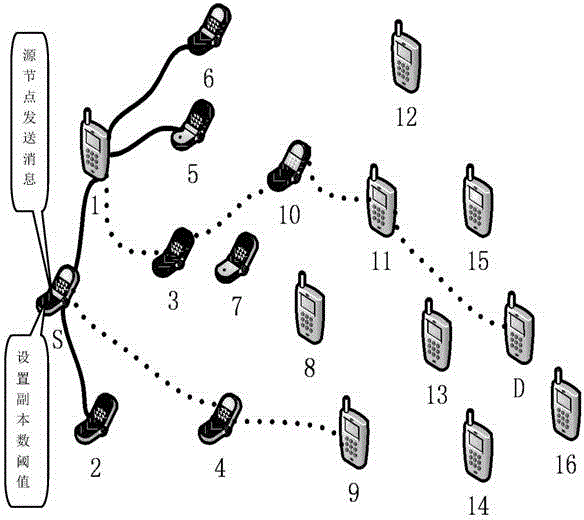
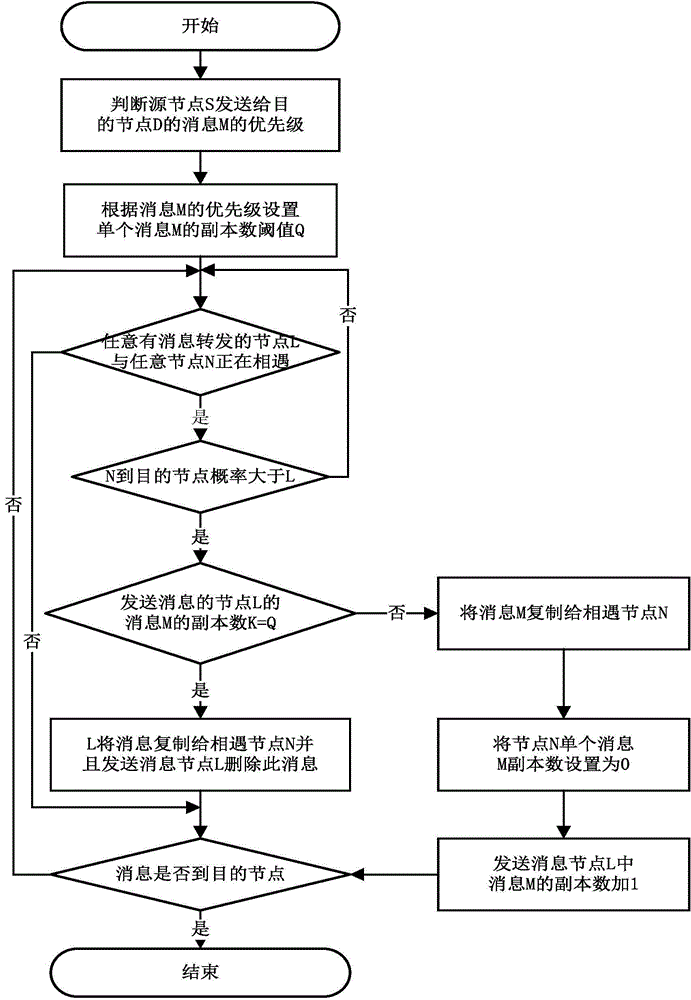
[0025] Step 1: The source node S sends a message M to the destination node D. Messages are prioritized according to the message prioritization method.
[0026] Step 2: For messages with a determined priority, use the message copy number threshold allocation method to set the copy number threshold Q that can be generated by a single message.
[0027] Step 3: Determine whether any node L that has message forwarding is meeting any node N, if yes, go to step 4; otherwise, go to step 8.
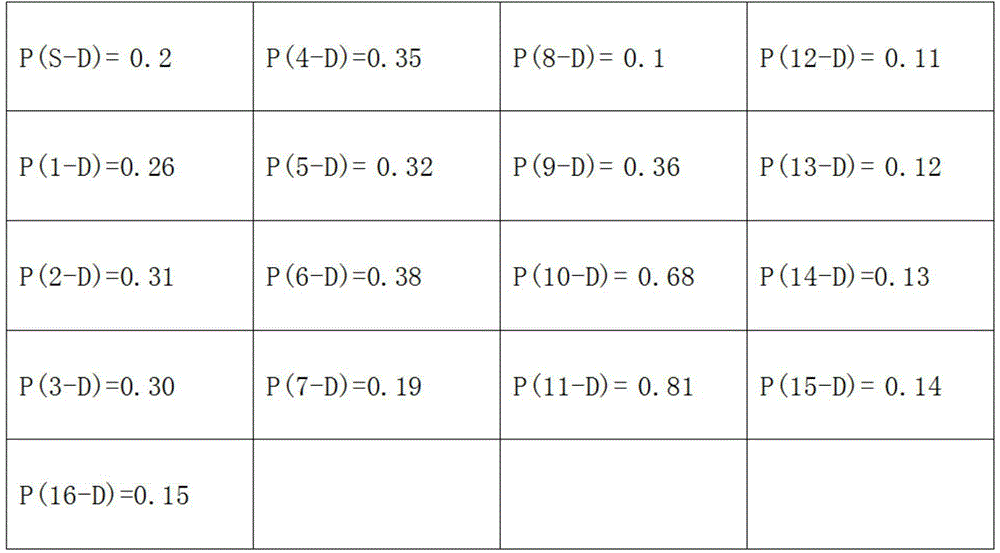
[0028] Step 4: Determine whether the probability of N reaching the destination node D is greater than L, if yes, perform step 5; otherwise, return to step 3.
[0029] Step 5: Determine whether the copy number K of the message M sent by the message sending node L is equal to the threshold Q, if not, go to step 6; otherwise, go to step 7.
[0030]Step 6: L copies the message to the meetin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com