Human error probability calculating method and human error probability calculating device
A human error probability and calculation method technology, applied in the field of information science and human factors engineering, can solve the problem that the human error probability cannot be quantitatively and effectively evaluated
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
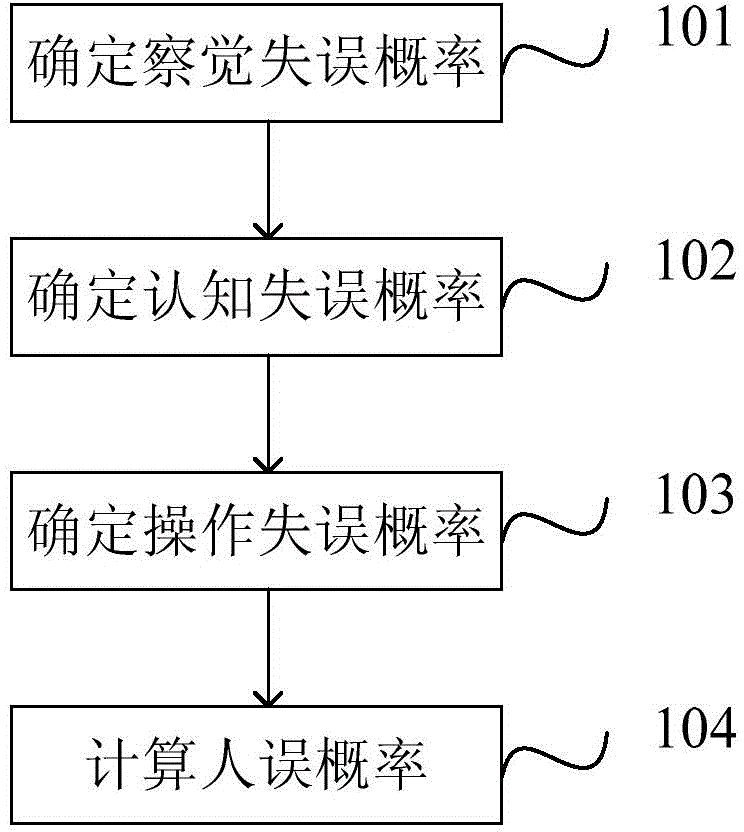
[0069] refer to figure 1 , a preferred embodiment of the present invention provides a method for calculating the probability of human error, including:
[0070] Step 101, determine the detection error probability p det .
[0071] After the accident, the operator in the main control room may fail to detect the accident. If the detection fails, it may lead to the inability to recognize the accident in time, resulting in the failure of the operation. Therefore, the detection error probability is the failure The probability of successfully detecting an accident.
[0072] Furthermore, when an accident occurs under normal working conditions, the detection error probability p det =10 -5 ;
[0073] When an accident occurs during the accident handling process, the detection error probability p det =0.
[0074] Specifically, the calculation of the detection error probability of an accident is divided into the following two situations:
[0075] (1) Accidents occur under normal wo...
Embodiment 2
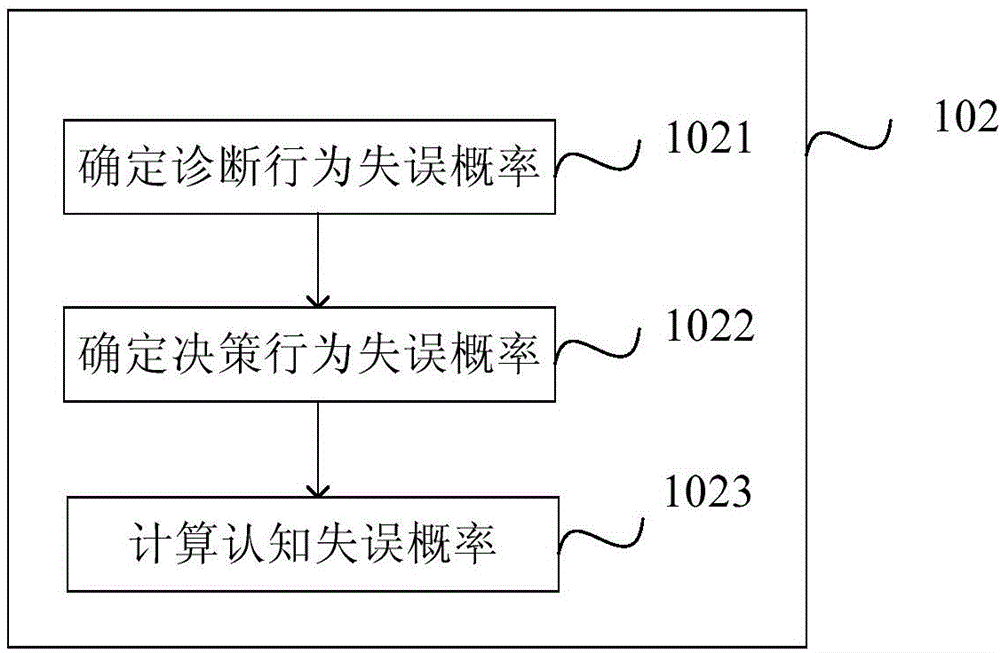
[0087] refer to figure 2 , Embodiment 2 is a supplementary description based on Embodiment 1, wherein step 102 includes:
[0088] Step 1021, determine the error probability p of diagnostic behavior diag .
[0089] The diagnostic action consists of a paired cycle of monitoring and status evaluation. When the state of DCS changes, the operator needs to determine the current state level of DCS by monitoring the changes of system parameters. Assume that at time t, the system provides N parameters to represent the state of DCS, and the operator monitors these parameters in sequence according to the electronic procedures. Every time the operator observes a parameter, he will update his state model according to the meaning of the parameter. For example: the operator observes parameter 1 at time t1, interprets the meaning of the parameter through his mental model, and obtains state model 1. State model 1 drives the operator to transfer to parameter 2 at time t2. The same process o...
Embodiment 3
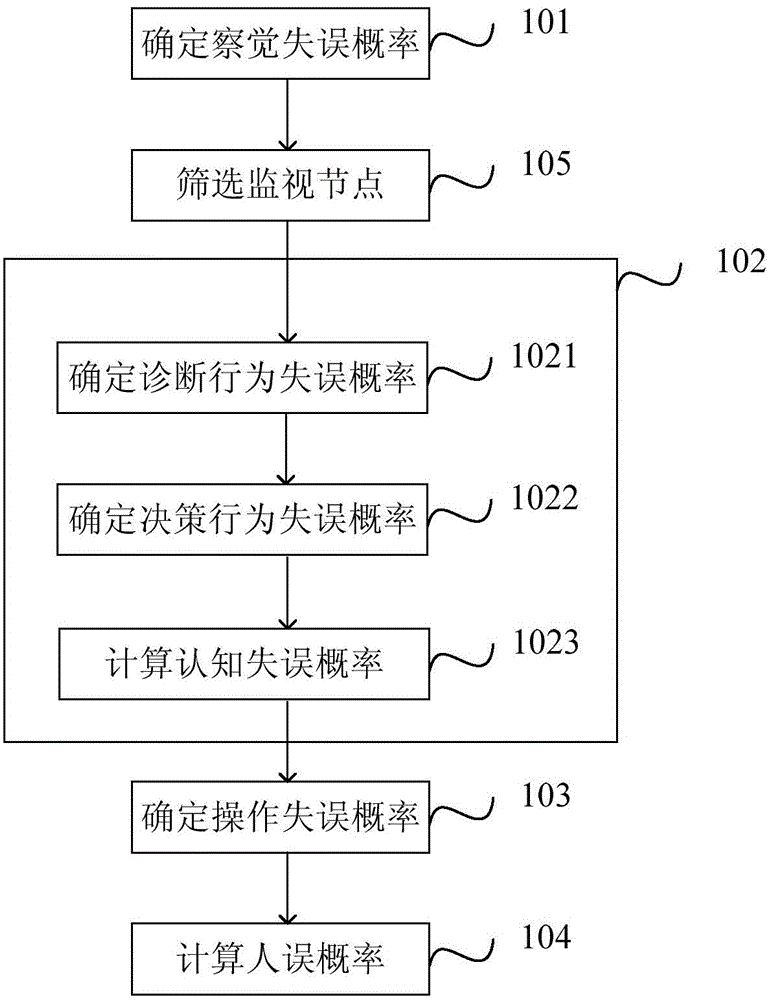
[0095] This embodiment is a supplementary description based on the above embodiments.
[0096] refer to image 3 , in determining the detection error probability p det After that, determine the diagnostic behavior error probability p diag Before, it also includes step 105, screening monitoring nodes, and the screening method is:
[0097] Exclude monitoring nodes that the system can handle automatically;
[0098] For monitoring nodes with alarm signal assistance, if the monitoring node fails, the monitoring node will be excluded;
[0099] Exclude monitoring nodes that do not pose a significant impact;
[0100] The selected monitoring nodes can provide necessary and sufficient information for diagnosing the current accident, that is, the selected monitoring nodes can provide neither redundant nor indispensable information for diagnosing the accident, and the information that is more serious than the current accident can be excluded. An accident, an accident that is more sev...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com