Method for evaluating corrosivity of transformer station soil to galvanized steel grounding grid
An evaluation method and substation technology, applied in soil material testing, material inspection products, etc., can solve the problems of illiquidity, unevenness, and inability to evaluate soil corrosion performance in time and seasonality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
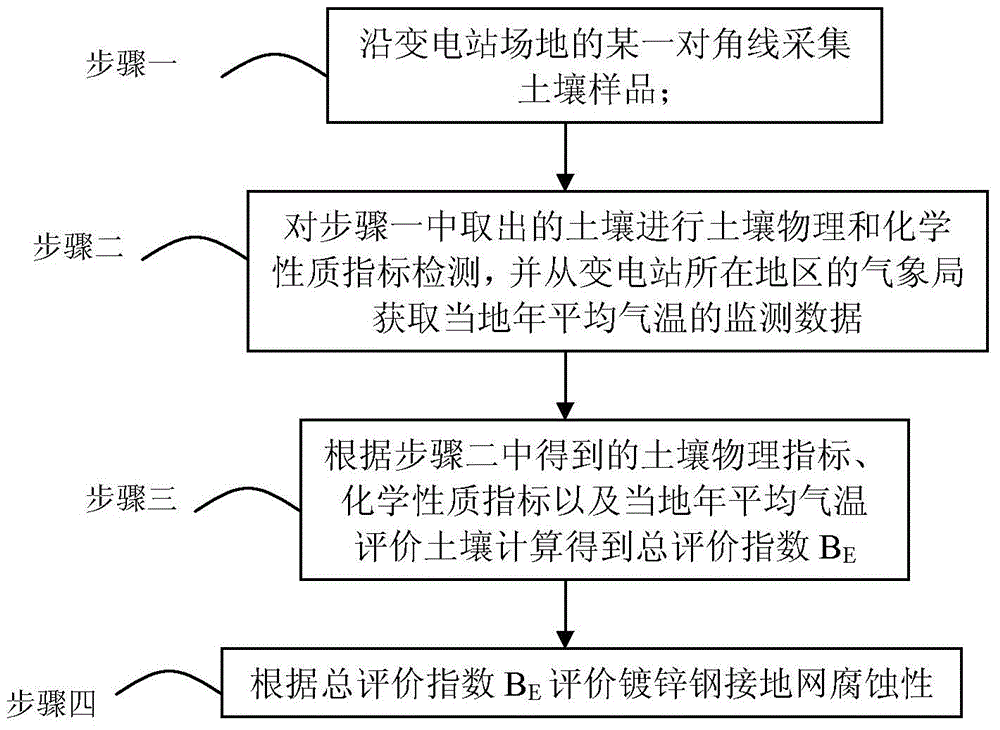
[0018] Specific embodiment one: the substation soil of the present embodiment is specifically prepared according to the following steps to the evaluation method of the corrosion of galvanized steel grounding grid:
[0019] Step 1, collecting soil samples along a certain diagonal line of the substation site; wherein, selecting a suitable area along the substation site without buildings, electrical equipment and solid ground;
[0020] Step 2. Perform soil physical and chemical property index detection on the soil taken out in step 1, and obtain local annual average temperature monitoring data from the Meteorological Bureau in the area where the substation is located; wherein, the physical indicators include soil type, water content and air capacity; Chemical property indicators include resistivity, pH value, soluble Cl - content, soluble SO 4 2- content and redox potential;
[0021] Step 3. Calculate the total evaluation index B according to the soil physical index, chemical ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0026] Specific implementation mode two: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one is: in step one, the soil samples collected along a certain diagonal line of the substation site are specifically:
[0027] (1) Select a certain diagonal line of the substation site, and dig four test pits with a diameter of 0.8-1.0m along the diagonal direction; among them, the distance between each test pit is 10m-11m, and the depth of the test pit is the same as the grounding grid of the substation. The actual buried depth is the same;
[0028] (2) Take about 2kg-2.5kg of soil samples from each test pit. Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0029] Specific implementation mode three: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one or two is that in step two, the soil taken out in step one is carried out for soil physical and chemical property index detection according to the "Material Soil Corrosion Test" written by the National Soil Corrosion Test Website Method", according to the correlation between the corrosion degree of galvanized steel grounding grid and the physical and chemical properties of the soil, the substation soil samples were collected, and the soil type, resistivity, pH value, water content, soluble Cl - content, soluble SO 4 2- Content, air capacity and redox potential were detected. Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com