Light emitting device
一种发光装置、发光元件的技术,应用在发光材料、节能措施、园艺等方向,能够解决驱动电路复杂化、部件个数增加、成本变高等问题,达到培育效率提升的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
[0050] Before describing the first embodiment of the light-emitting device of the present invention, cultivation of plants will be briefly described. Light functions as a stimulus and information source for germination, flowering, stem elongation, and the like. Photosynthesis of plants is carried out through the absorption of light by chlorophyll. There are two wavelength regions in which the absorption of light by chlorophyll peaks. The first region is in the range of wavelength 400nm to 500nm (more specifically, near the wavelength of 450nm), and the second region is in the wavelength range of 600nm to 700nm (more specifically, near the wavelength of 660nm).
[0051] The light in the first region (blue light) is light required for normal morphological formation of leaves and the like, and the light in the second region (red light) is light required for photosynthesis. In addition, when plants are irradiated with mixed light, far-red light is required for pitch elongation and...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
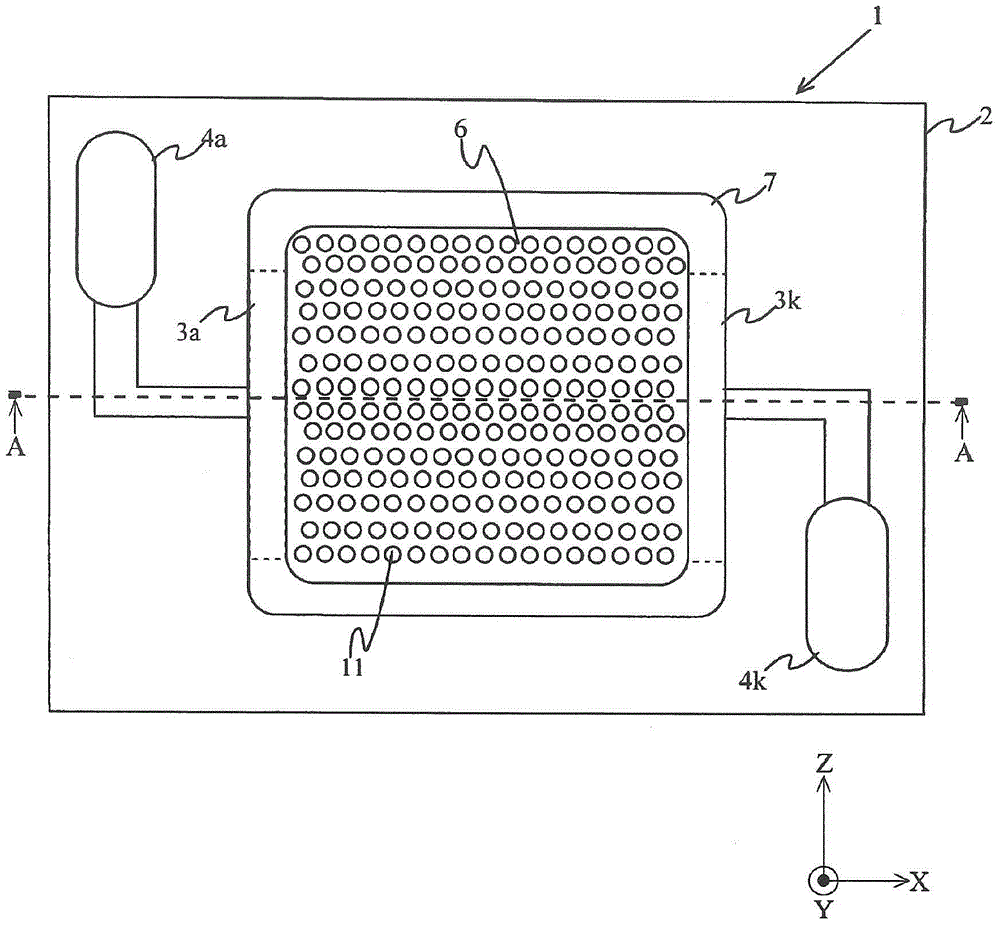
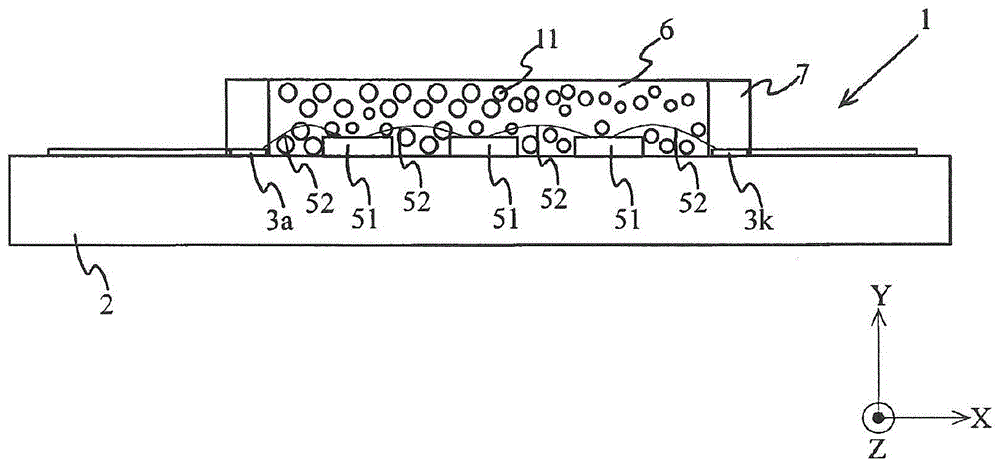
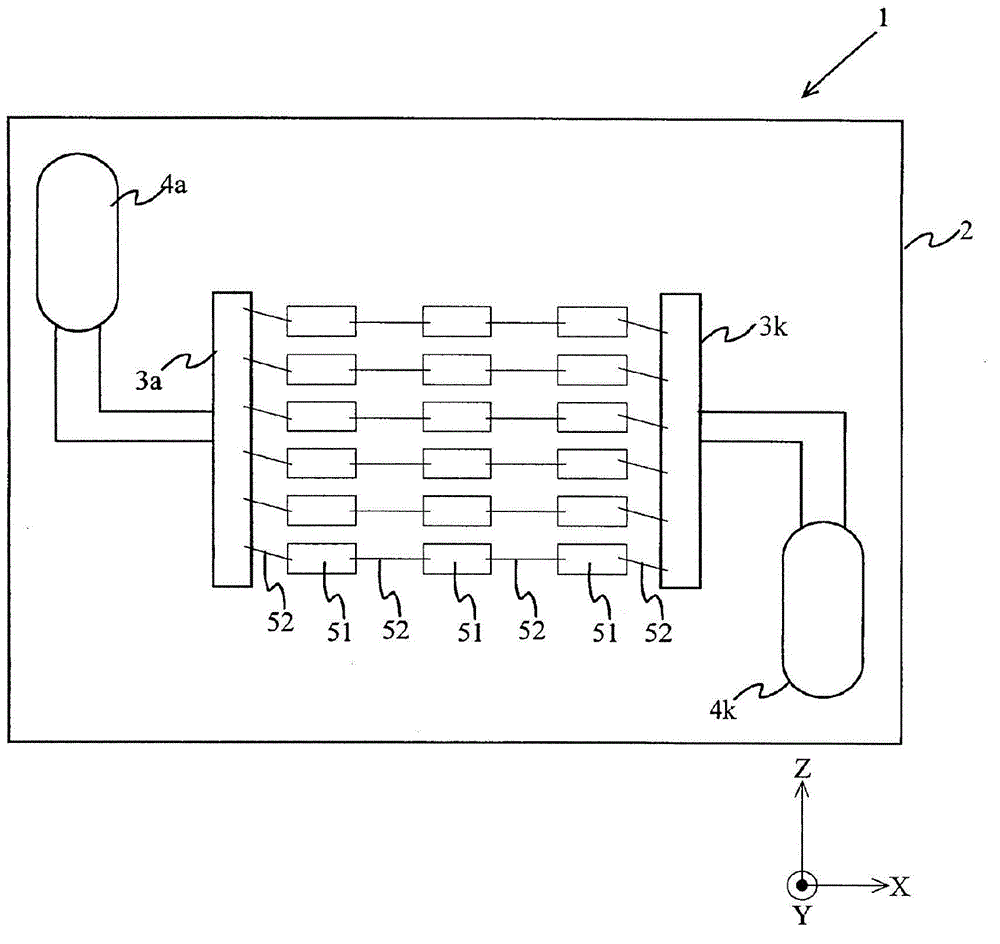
[0074] Figure 5 It is a top view showing the light emitting device of the second embodiment. Figure 6 yes Figure 5 Side view under XY section at A-A of the light-emitting device shown. Since the LEDs mounted on the board are the same as those in the first embodiment, illustration is omitted. In addition, a part of description will be omitted about the part whose structure is the same as that of 1st Embodiment.
[0075] The phosphor layer 6 is a resin layer filled inside a resin frame 7 described later so as to cover the LED 5 . Phosphor layer 6 is excited by light (excitation light) emitted from LED 5 to emit light having a peak wavelength in a predetermined range. Phosphor layer 6 is composed of a first phosphor layer 61 and a second phosphor layer 62 . The first phosphor layer 61 is constituted by containing the first phosphor 10 ( Figure 5 The phosphors represented by Δ marks among others), the second phosphor layer 62 is constituted by containing the second phosp...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0092] Figure 7 It is a top view showing the light emitting device of the third embodiment. Figure 8 yes Figure 7 The side view under the XY section at B-B of the light-emitting device shown. Figure 9 It is a top view showing the LED mounted on the board in the third embodiment. Figure 10 It is a schematic diagram showing the positional relationship between the phosphor layer and the LED. in addition, Figure 10 The △ mark indicating the first phosphor 10 and the ◯ mark indicating the second phosphor 11 are omitted for easy understanding of the positional relationship between the phosphor layer and the LED.
[0093] In the second embodiment described above, the absorption of red light by the second phosphor layer 62 is suppressed by laminating the first phosphor layer 61 on the second phosphor layer 62 . In this embodiment, the absorption of red light by the second phosphor layer is suppressed without laminating the first phosphor layer and the second phosphor layer....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com