Genetical epilepsy-combining febrile convulsion additional symptom SCN1A gene new mutation
A gene and genome sequence technology, applied in the field of disease-related mutation genes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
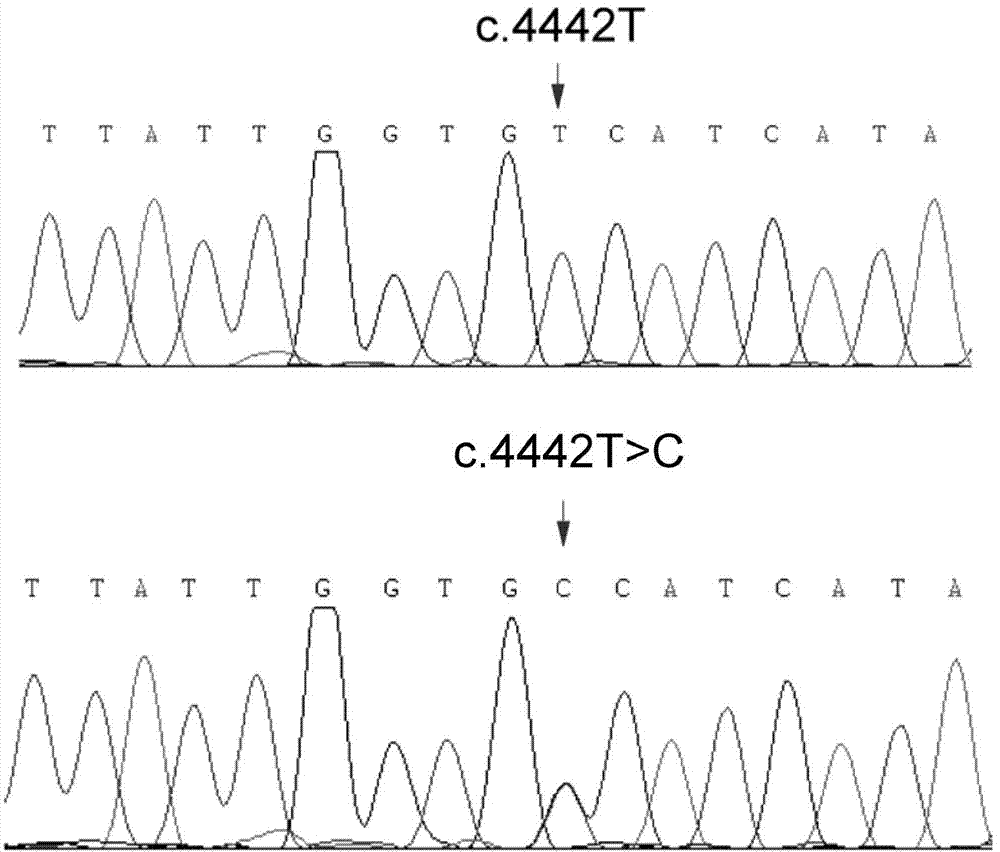
[0045] In this example, a new generation of whole-exome sequencing technology was used to perform high-throughput sequencing of the entire exon region of a GEFS+ family with autosomal dominant inheritance in the Chinese Han nationality. Combining with biological information analysis, it was found that the c on the SCN1A gene The .4442T>C / p.Val1481Ala mutation was associated with GEFS+, and this variation was verified by co-segregation experiments and other methods.
[0046] 1. Sample Collection
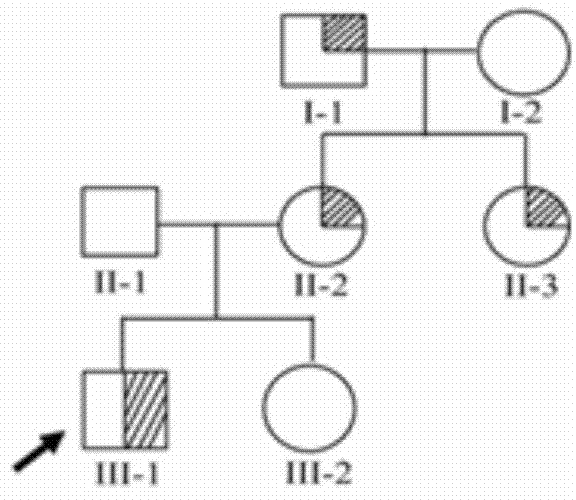
[0047] The GEFS+ family contained 7 members, including 4 patients ( figure 1 ). Two GEFS+ patients in the family were selected as exome sequencing samples (Table 1), and 2ml of peripheral blood samples were collected from each sample, anticoagulated with EDTA, and stored at -80°C. Later, another 2 patients and 3 normal control individuals in the family were collected as secondary verification samples (Table 2). 2 ml of peripheral blood samples were collected from each, anticoagulate...
Embodiment 2
[0089] As a further verification of Example 1, the following examples are provided.
[0090] 1 Sample preparation
[0091] Collect the peripheral blood of 7 samples (4 patients and 3 controls) in the GEFS+ family, extract genomic DNA according to the method of 2.1 in Example 1, and use a spectrophotometer to measure the concentration and purity of DNA. OD260 / OD280 are both between 1.7-2.0, the concentration is not less than 200ng / ul, and the total amount is not less than 30μg.
[0092] 2 Gene detection of disease-causing mutations
[0093] Whole exome sequencing was performed on the 2 samples (both patients) in Table 1 in the family and the SCN1A gene of 7 samples (4 patients and 3 controls in the family, see Table 1 and Table 2 for specific information) The mutation site is detected, and primers are designed for the sequence near the new mutation site detected by the known gene, and the relevant sequence near the deletion site is obtained by PCR amplification, product purif...
Embodiment 3
[0118] Kit 1: a kit for detecting the mutant SCN1A gene, comprising one or more sets of primer pairs, wherein the mutation is the mutation c.4442T>C of the SCN1A gene (ie protein mutation p.Val1481Ala), and the primer pairs are respectively Design on the genomic sequence or cDNA sequence based on a position selected from the following, so that the amplified product covers this position: the 4442nd position of the cDNA sequence of the SCN1A gene, and the kit for detecting the mutant SCN1A gene or protein includes the following primers:
[0119] SEQ ID NO:3 and SEQ ID NO:4.
[0120] Kit 2: a kit for detecting the mutant SCN1A gene, comprising one or more nucleic acid probes, the mutation is the mutation c.4442T>C of the SCN1A gene, and the probe and the mutant SCN1A gene contain Complementary regions on the genome sequence or cDNA sequence: position 4442 of the cDNA sequence of the SCN1A gene.
[0121] The specific steps for detecting the mutant SCN1A gene or protein using the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com