A kind of method of industrialized fermentation high-yield l-tryptophan
A tryptophan, high-yield technology, applied in the field of amino acid fermentation, can solve the problems of low production cost in the fermentation cycle, low L-tryptophan acid production rate, etc., to achieve easy operation and maintenance, obvious decolorization effect, and less floor space Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] A method for industrialized fermentation of high-yield L-tryptophan, comprising the steps of:
[0026] Step 1) Fermentation: Escherichia coli (Escherichiacoli) ATCC 27325 (see Appl.Environ.Microbiol.October 1994vol.60no.10, 3724-3731) with tnaA, trpR and tyrR gene knockout or inactivation and glutamic acid rod Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032 (Journal of Biotechnology, V104, September 2003, Pages5-25) was cultured to a concentration of 1×10 7 Each / mL of the bacterial liquid, mixed according to the volume ratio of 1:1 to obtain the mixed bacterial liquid, then inoculated into the fermentation medium (glucose 20g / L, yeast powder 15g / L, magnesium sulfate according to 5% (v / v) inoculum 2.5g / L, Ammonium Sulfate 2g / L, Citric Acid 2.5g / L, Dipotassium Hydrogen Phosphate 9g / L, Ferrous Sulfate 76mg / L, Manganese Sulfate 5mg / L, Sodium Sulfate 20mg / L, Zinc Sulfate 7mg / L , cobalt chloride 6mg / L, copper sulfate 0.9mg / L), temperature 37°C, dissolved oxygen control 20%, tank press...
Embodiment 2
[0034] A method for industrialized fermentation of high-yield L-tryptophan, comprising the steps of:
[0035] Step 1) Fermentation: Escherichia coli (Escherichia coli) CCTCC M 2011316 (see CN201110400855X) and Corynebacterium glutamicum (Corynebacterium glutamicum) ATCC13032 were cultivated to a concentration of 1×10 7 Each / mL of the bacterial liquid, mixed according to the volume ratio of 1:1 to obtain the mixed bacterial liquid, then inoculated into the fermentation medium (glucose 20g / L, yeast powder 15g / L, magnesium sulfate according to 5% (v / v) inoculum 2.5g / L, Ammonium Sulfate 2g / L, Citric Acid 2.5g / L, Dipotassium Hydrogen Phosphate 9g / L, Ferrous Sulfate 76mg / L, Manganese Sulfate 5mg / L, Sodium Sulfate 20mg / L, Zinc Sulfate 7mg / L , cobalt chloride 6mg / L, copper sulfate 0.9mg / L), temperature 37°C, dissolved oxygen control 20%, tank pressure 0.05MPa, pH 7.0, when the glucose in the fermentation medium is exhausted, it will enter the production of sugar supplementation In th...
Embodiment 3
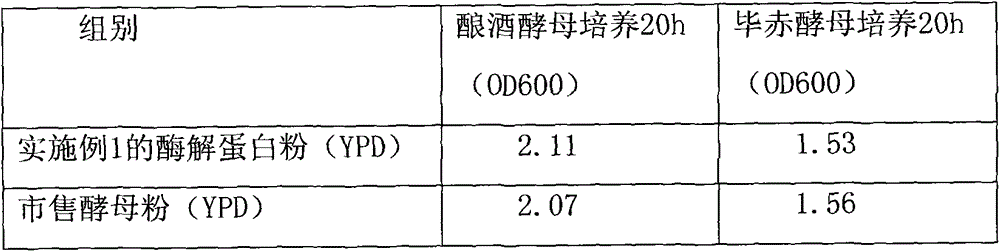
[0043] The bacterial protein powder prepared in Example 1 was used to replace the yeast powder in the standard YPD medium, and the rest of the ingredients were unchanged. Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Pichia pastoris were cultivated under the same conditions, and the culture effect of the product was evaluated by comparing the growth of the cells. See Table 1.
[0044] Table 1
[0045]
[0046] Conclusion: OD600 was used to measure the growth of cells characterized by turbidimetry, indicating that this product can replace commercially available yeast powder products and achieve similar culture effects.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com