Application of heat shock protein hsp23 gene and dsrna of gypsy moth in pollution-free control
A technology of heat shock protein and gypsy moth, applied in DNA/RNA fragments, applications, genetic engineering, etc., to achieve broad application prospects, weaken vitality, and strong silencing effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Example 1: Full-length cloning of the heat shock protein Hsp23 gene of the gypsy moth
[0021] The gypsy moth heat shock protein Hsp23 gene has a nucleic acid sequence of 750bp, an open reading frame of 600bp, encoding 199 amino acids, a molecular weight of 22.84kDa, and a theoretical isoelectric point PI of 5.50. It is an acidic protein.
[0022] Total RNA was extracted from Gypsy moth, using the reverse transcription kit PrimeScript TM RT reagent Kit (TaKaRa) synthesized the first strand of cDNA, and then used the first strand of cDNA as a template to design primers (forward primer: 5'-CAGTAAACAGTATTCGAAG- 3'; reverse primer: 5'-AGGCGAAAGAAACAAGCACT-3'.
[0023] Reaction system: 5×PrimeScript buffer 2 μL, PrimeScript RT Enzyme Mix I 0.5 μL, Oligo d(T) primer (50 μM) 0.5 μL, Random 6mers (100 μM) 0.5 μL, Total RNA 0.5 μg RNaseFree ddH 2 O to make up 10 μL. , PCR amplification program is as follows: 94°C for 3min; 35 cycles of 94°C for 30s, 60°C for 30s, 72°C for 1m...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Embodiment 2: Synthesis of gypsy moth Hsp23 gene dsRNA
[0025] According to the full length of the gypsy moth Hsp23 gene cloned in Example 1, design and synthesize the Hsp23 gene dsRNA forward primer (5'-ATGTCGTTAATTCCTTACATGTA-3') and reverse primer (5'-CTAATTAGATTCTTCAATTGTCG-3'), and amplify the obtained fragment The length of the sequence is 516bp, and the dsRNA of the Hsp23 gene is obtained through an in vitro dsRNA synthesis kit.
[0026] The specific synthesis process is that a section of T7 promoter sequence of about 20 bp is added to the 5' end of each specific primer, and GFP is used as a control group. The target band was amplified by the PCR method, and the reaction program was: 94°C for 3min; 94°C for 30s, 60°C for 30s, 72°C for 1min, 35 cycles; 72°C for 7min. The amplified product was confirmed by electrophoresis and used as a template to synthesize dsRNA ( Refer to the MEGAscript RNAi Kit kit instructions), detect the concentration of dsRNA with a UV sp...
Embodiment 3
[0027] Example 3: Detection of silencing effect of Gypsy moth Hsp23 gene
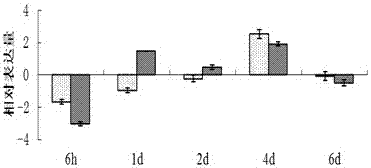
[0028] The dsRNA (1 μg) of the Hsp23 gene and GFP gene synthesized in Example 2 was microinjected into the 3rd instar larvae of the gypsy moth, and the active 3rd instar larvae were selected at 6, 24, 48, 96, and 144 hours respectively, and the RNeasy Mini animal tissue aggregates were used to collect the dsRNA. RNA extraction kit (Qiagen) was used to extract total RNA, using PrimeScript TM The first strand of cDNA was synthesized by RT kit (TaKaRa) and used as a template to detect the expression level of Hsp23 gene after injection by fluorescent quantitative RT-PCR. The expression level of Hsp23 gene in the 3rd instar larvae injected with dsRNA was as follows: figure 2 shown. The results showed that the injection of dsRNA of exogenous control gene GFP into gypsy moth larvae would affect the expression of Hsp23 gene. Compared with the control GFP gene, the effect of Hsp23 gene silencing was higher ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com