Image foreground extracting method based on Gaussian variation model
A foreground extraction and image technology, applied in the field of image processing, can solve the problems of recognition accuracy and precision need to be improved
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
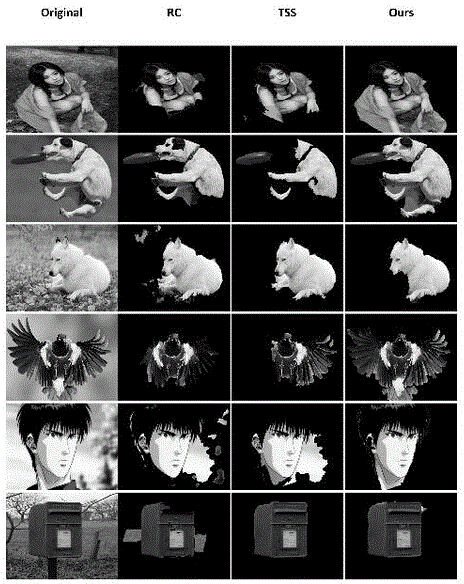
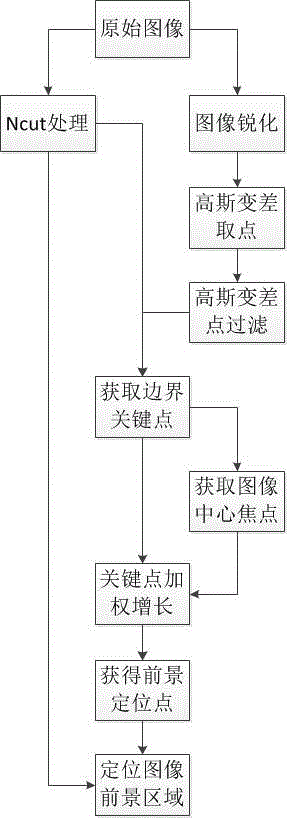
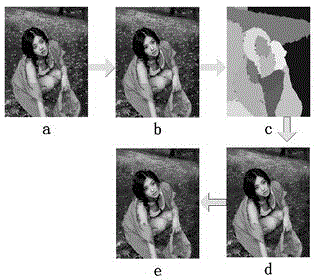
[0024] Step 1, use the Ncut technology to perform region segmentation on the target image, and obtain the region segmentation map of the target image.
[0025] Step 2: Perform sharpening processing on the original target image to obtain a sharpened image, perform Gaussian variation model foreground extraction on the sharpened image in RGB space, and obtain Gaussian variation points.
[0026] We perform Gaussian convolution on each pixel in the image, as shown in the following formula (1), G is the Gaussian function, I is the pixel in the image, and we let the pixels in the image be convolved with the Gaussian function. L is the matrix obtained after convolution. σ is the scale of the Gaussian function, and our value for σ is 1.6.
[0027] L(x,y,σ)=G(x,y,σ)*I(x,y) (1)
[0028] In formula (2), we get the Gaussian variation D, which represents the difference between the Gaussian convolution of the original image at different scales.
[0029] D(x,y,σ)=L(x,y,kσ)-L(x,y,σ) (2)
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com