Method for recognizing circuit switching on and failures through specific short window integral value of directional traveling waves
A technology of short-window integration and directional traveling waves, which is applied in the direction of the fault location, can solve the problems that the protection cannot operate correctly, the fault is difficult to identify, and the circuit breaker is not considered to be closed at the same time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1 Embodiment 1
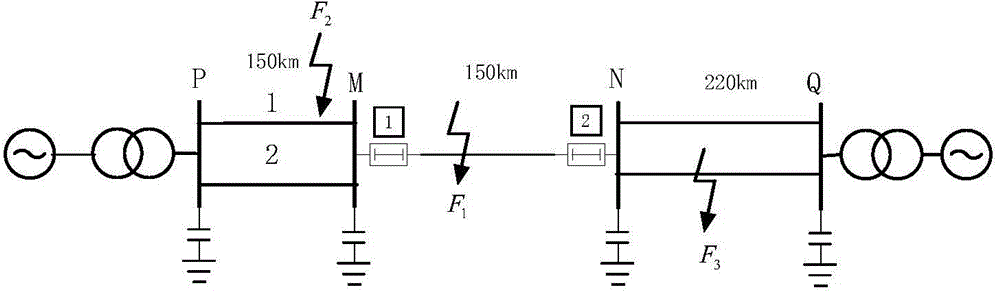
[0041] Embodiment 1 Embodiment 1: as figure 1 The simulation system model of 500kV transmission line shown, the line to be protected is MN, and the line length is L PM = 150km, L MN = 150km, L NQ =220km, the sampling rate is 1MHz. Assume that the A-phase circuit breaker at the N-end of the protected line is in the disconnected state, and the A-phase circuit breaker at the M-end of the protected line’s measurement end performs the closing operation, assuming that there is no fault in the line MN and an AG metallic ground fault occurs 149km away from the M-end , the transition resistance is 0Ω, and the initial phase angle is 90°.
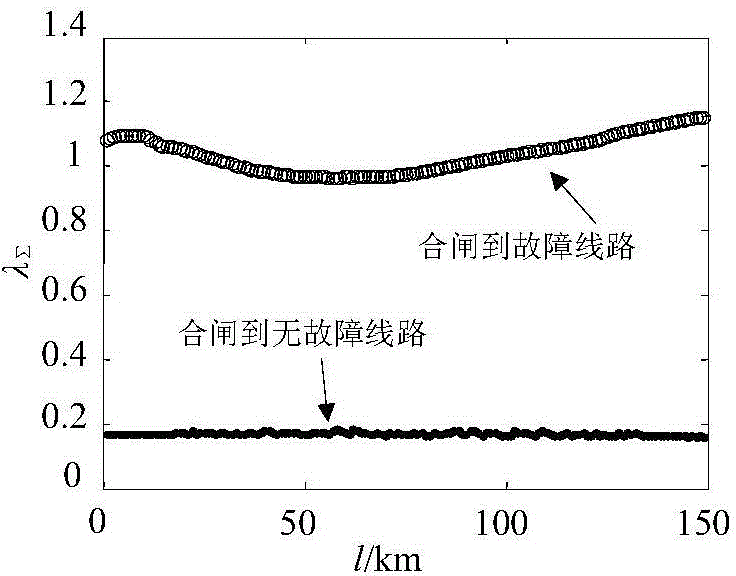
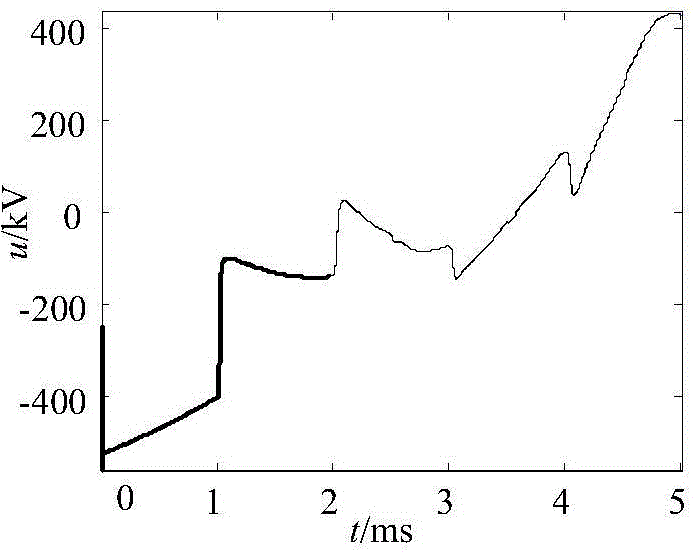
[0042] After a single-phase ground fault occurs on the protected line, the faulty phase is disconnected. At this time, the circuit breaker of the faulty phase at the M terminal of the protected line performs the closing operation, and the circuit breaker at the N terminal at the other end of the protected line is in the disconnected state. The thr...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Embodiment 2: as figure 1 The simulation system model of 500kV transmission line shown, the line to be protected is MN, and the line length is L PM = 150km, L MN = 150km, L NQ =220km, the sampling rate is 1MHz. Assume that the A-phase circuit breaker at the N terminal is in the open state, and the A-phase circuit breaker at the M terminal performs the closing operation. Assume that there is no fault in the line MN and a BG metallic ground fault occurs 60km away from the M terminal, the transition resistance is 10Ω, and the initial phase angle 90°. The three-phase current traveling wave and the three-phase voltage traveling wave generated by the closing measurement terminal M of the line are collected. The three-phase voltage and three-phase current traveling waves are transformed into phase-mode using equations (1) and (2), and three line-mode voltage components Δu are extracted α , Δu β and Δu γ and the current component Δi α , Δi β and Δi γ , and select the ...
Embodiment 3
[0056] Embodiment 3: as figure 1 The simulation system model of 500kV transmission line shown, the line to be protected is MN, and the line length is L PM = 150km, L MN = 150km, L NQ =220km, the sampling rate is 1MHz. Assume that the A-phase circuit breaker at the N terminal is in the open state, and the A-phase circuit breaker at the M terminal performs the closing operation. Assume that there is no fault in the line MN and a CG metallic ground fault occurs 90km away from the M terminal. The transition resistance is 10Ω, and the initial phase angle 90°. The three-phase current traveling wave and the three-phase voltage traveling wave generated by the closing measurement terminal M of the line are collected. The three-phase voltage and three-phase current traveling waves are transformed into phase-mode using equations (1) and (2), and three line-mode voltage components Δu are extracted α , Δu β and Δu γ and the current component Δi α , Δi β and Δi γ , and select the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com