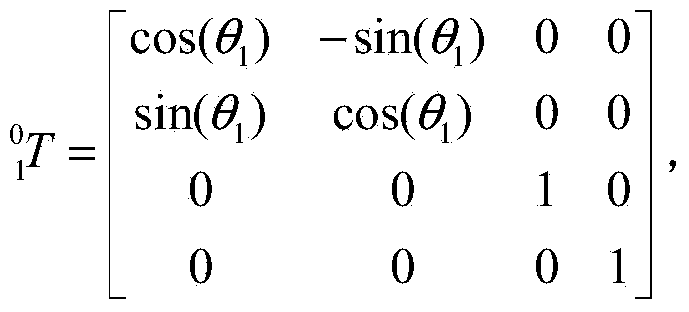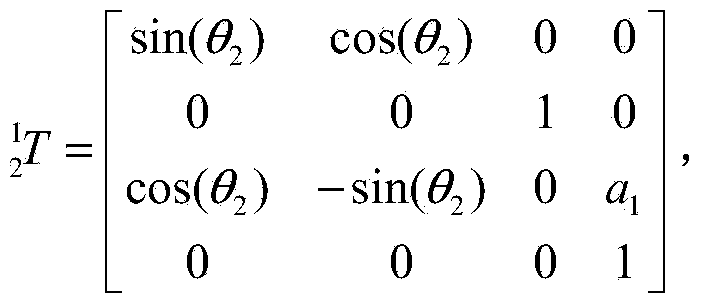Quantitative analysis method of influence of joint centralization error on locating precision of multi-freedom-degree mechanical arm tail end
A positioning accuracy, robotic arm technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problems of statistical difficulties in distribution, difficult compensation and correction, lack of
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0048] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
[0049] A quantitative evaluation method of the influence of joint centering errors on the positioning accuracy of the end of a multi-degree-of-freedom mechanical arm is mainly aimed at a six-degree-of-freedom mechanical arm. At present, the application of the six-degree-of-freedom manipulator is very extensive, and the more joints the manipulator has, the more obvious the impact of the centering error on the positioning accuracy of the end of the manipulator, and the more necessary the analysis of the centering error, so for the six-degree-of-freedom It is especially important to evaluate the manipulator. In specific applications, mechanical arms with other degrees of freedom can also be implemented with reference to the present invention.
[0050] Such as Figure 11 Shown, in specific application examples, the detailed steps of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com