Microorganism electrochemical device for in-situ remediation of polluted water and bottom mud and method for in-situ remediation of polluted water and bottom mud
A technology of microbial electrochemistry and in-situ remediation, applied in chemical instruments and methods, biological water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve problems such as high maintenance costs, high cost, and cumbersome sediment, Achieve environmental protection and safety cost, increase the speed of removal, and increase the effect of the scope of action
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
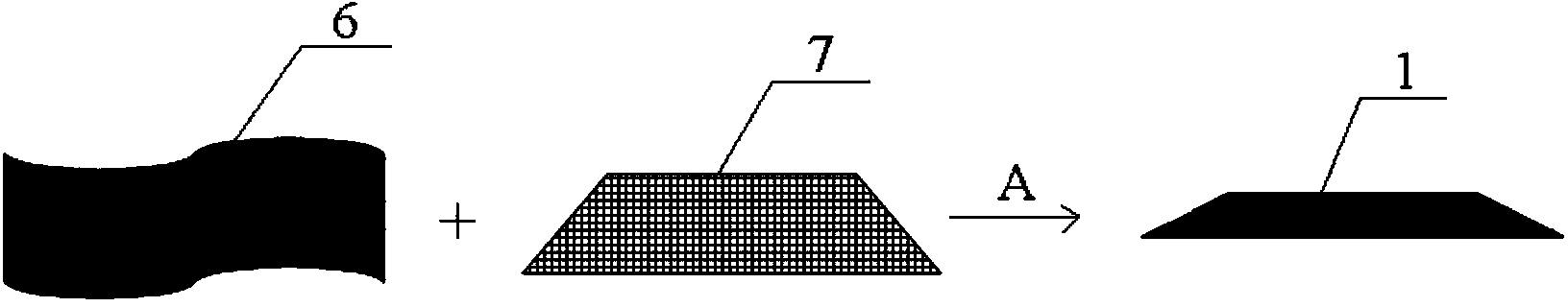
[0027] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 , this embodiment is a microbial electrochemical device for in-situ restoration of polluted water and sediment, which includes a cathode 1, an anode 2, a first wire 3, a second wire 4 and a charging and discharging device 5;
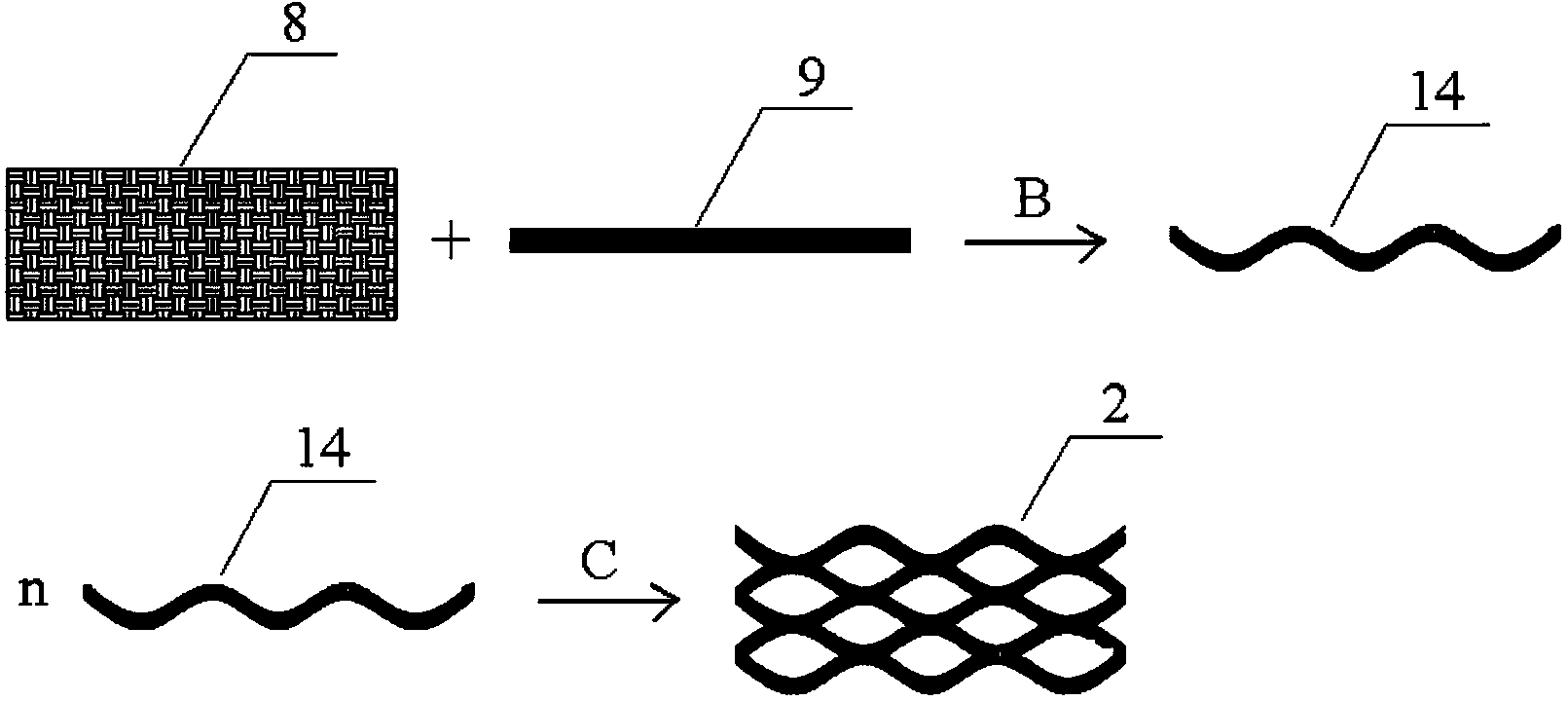
[0028] The cathode 1 is formed by pressing the cathode catalytic layer 6 and the stainless steel mesh 7 by rolling; the anode 2 is bonded to the surface of the support material 9 by the carbon fiber cloth 8, and then the carbon fiber cloth 8 and the support material 9 are bonded together by titanium wire. Fixing to obtain the support material 14 fixed by the titanium wire; every two support materials 14 fixed by the titanium wire are pressed at intervals of 19 cm to 21 cm to obtain the anode 2;
[0029] The cathode 1 is connected to the negative pole of the charging and discharging device 5 through the first wire 3 , and the anode 2 is connected to the positive pole of the charging and discharging...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0041] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the anode 2 is honeycomb-shaped. Other steps are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0042] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is: the rolling method is specifically completed according to the following steps: 1. Preparation of adhesive: polytetrafluoroethylene solution and conductive Carbon black is ultrasonic 30min under the condition of power 100W, obtains adhesive; Wherein, described polytetrafluoroethylene solution concentration is 60%; The mass ratio of the volume of described polytetrafluoroethylene solution and conductive carbon black is 1mL: 9g;
[0043] 2. Coating: the binder is coated on the surface of the cathode catalytic layer 6, and the coating thickness is 0.4 mm to 0.5 mm, and then the stainless steel mesh 7 is placed on the cathode catalyst layer 6 coated with the binder to obtain cathode. Other steps are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com