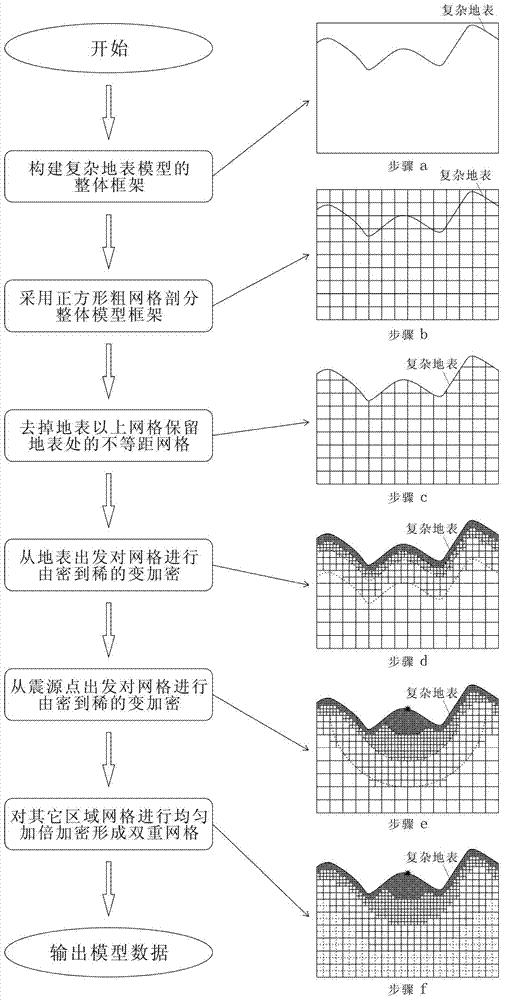
Subregion local variable-density non-equidistant dual mesh division method for complex mountainous region
A technology of grid division and grid refinement, which is applied in seismic signal processing, test sample preparation, instruments, etc., to achieve the effect of increasing the depth sampling rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
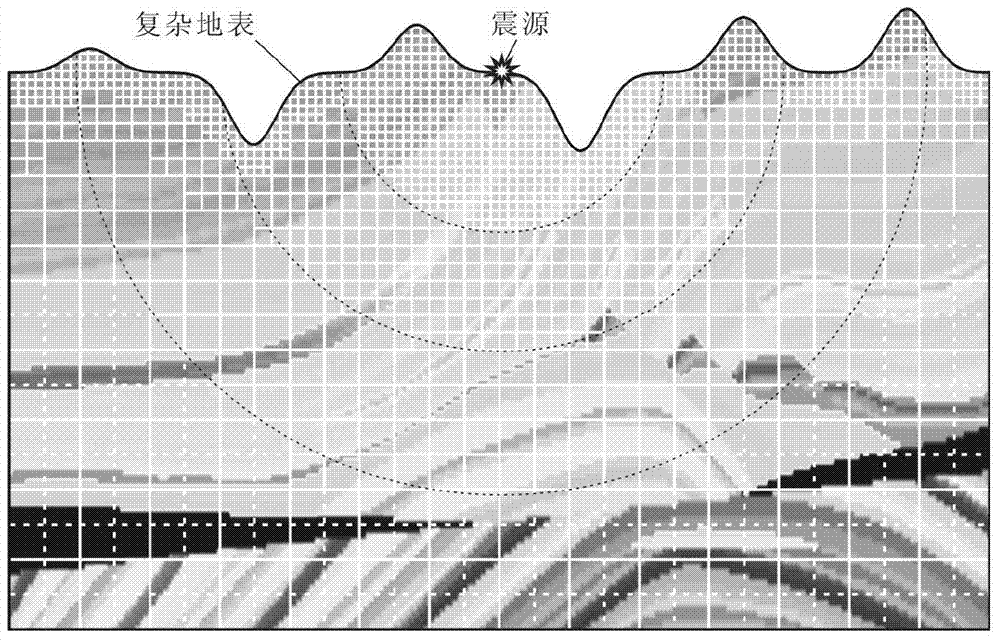
[0031] Such as figure 2As shown in , a complex surface Marmousi model is introduced to the classic Marmousi model after adding surface correction, and the surface fluctuation of this model is relatively severe. When using the grid subdivision technology of the present invention to subdivide it, set the grid spacing of the larger square coarse grid used in step b as h. When performing exponential encryption on the grid near the surface, the maximum index factor is n=4, that is, the distance between the nearest grid to the surface is h / 16, and each exponential encryption factor (respectively n=4, 3, 2) corresponds to The range of the grid densification area starts from the surface and extends downward successively for no more than 1.0h, 1.5h, and 2.0h. When performing exponential refinement on the grid near the seismic source, the maximum exponential factor is n=4, that is, the distance between the grids closest to the seismic source is h / 16, and each exponential refinement fa...
Embodiment 2
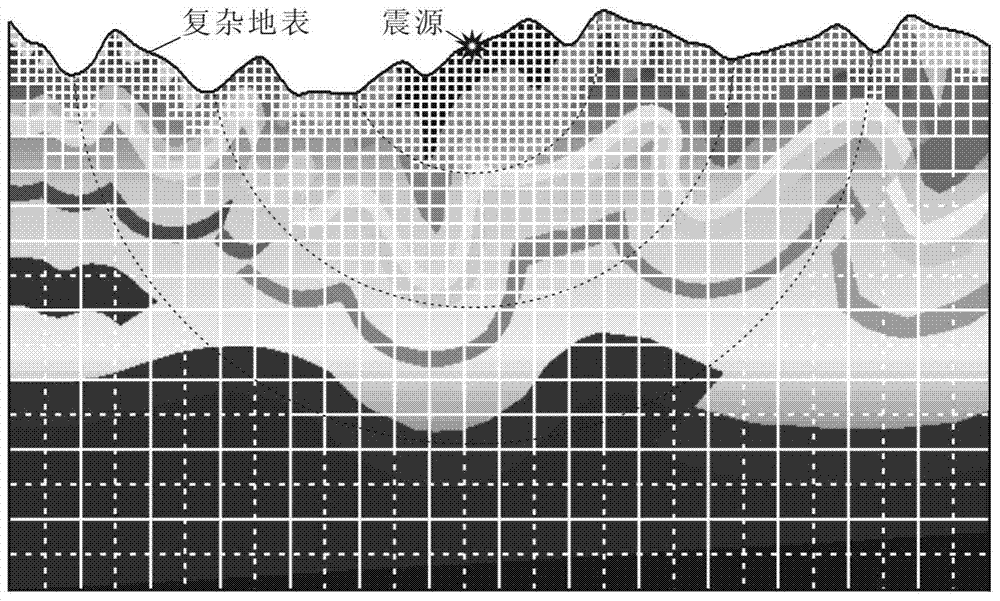
[0033] Such as image 3 As shown, the model is the classic SEG undulating surface Foothill model, and the surface elevation changes in some areas of this model are relatively drastic. Also, when it is subdivided by the grid subdivision technology of the present invention, the grid spacing of the larger square coarse grid used in step b is set to be h. When performing exponential encryption on the grid near the surface, the maximum index factor is n=4, that is, the distance between the nearest grid to the surface is h / 16, and each exponential encryption factor (respectively n=4, 3, 2) corresponds to The range of the grid densification area starts from the surface and extends downward successively for no more than 1.0h, 1.5h, and 2.0h. When performing exponential refinement on the grid near the seismic source, the maximum exponential factor is n=4, that is, the distance between the grids closest to the seismic source is h / 16, and each exponential refinement factor (respectively...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com