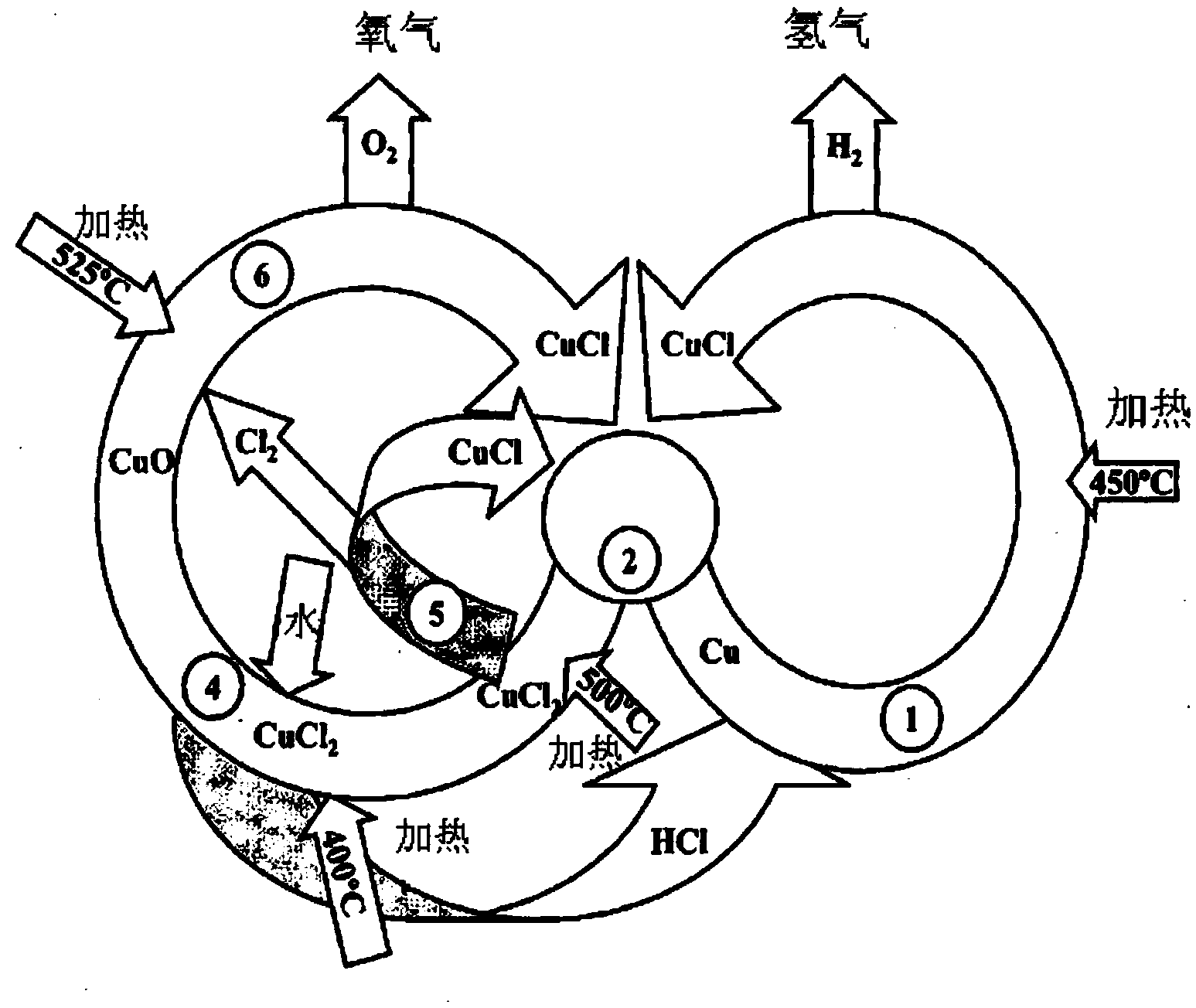
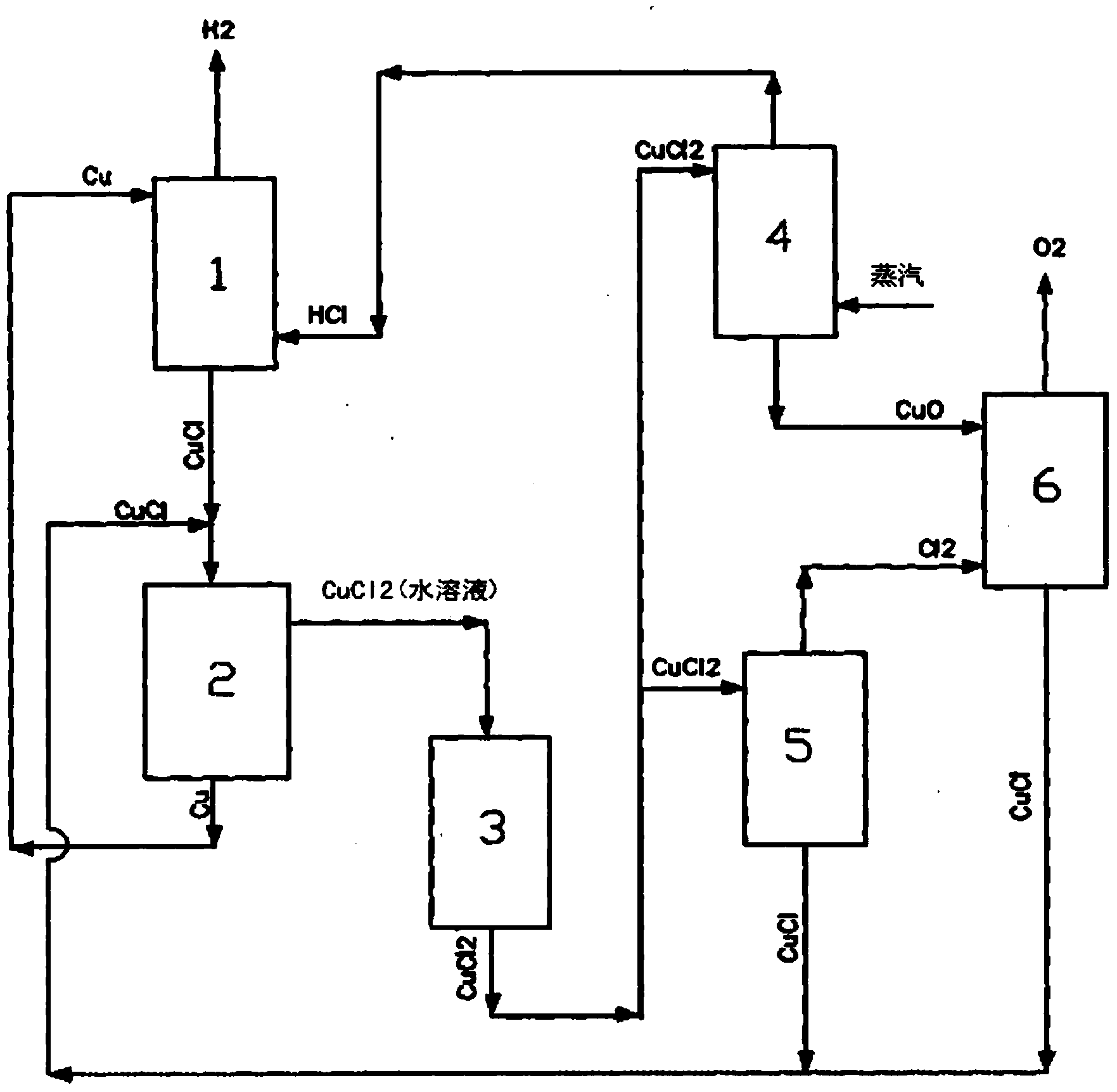
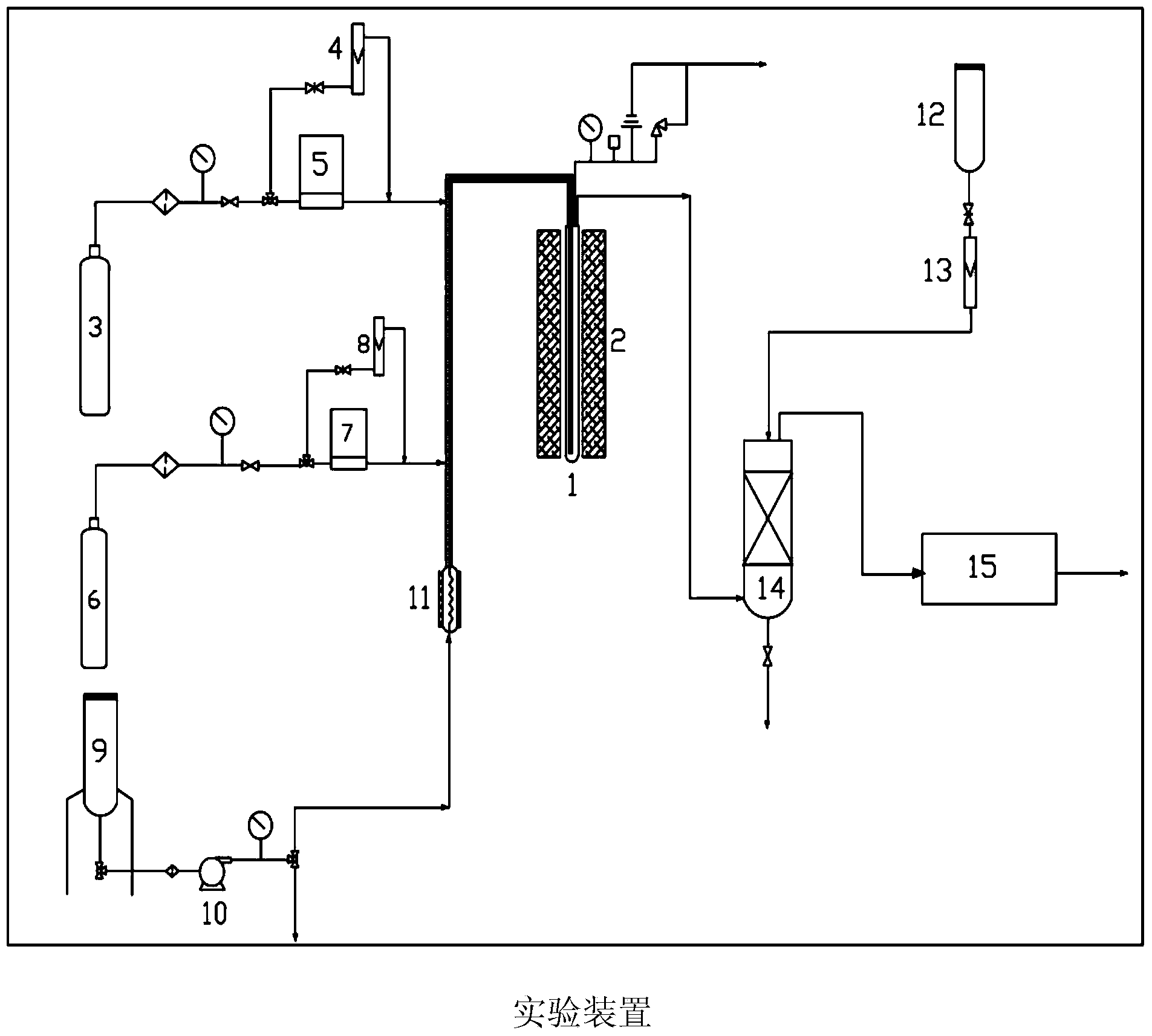
Hydrogen production method by multi-step copper-chlorine thermochemical cycle
一种热化学、氯化氢的技术,应用在化学仪器和方法、氢/合成气生产、氢的生产等方向
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-5
[0127] According to the above disclosure of the present invention, the following experiments were carried out in a quartz microreactor. The reaction was carried out as a fixed bed reactor type. The dry hydrogen chloride gas required for the reaction was supplied into the reactor through a mass flow controller through a quartz tube extending to the bottom of the reactor. The reaction is carried out under atmospheric pressure. Dry hydrogen chloride gas is introduced into the reactor at the desired flow rate. The results are shown in Table 1. The reaction is carried out under the following operating conditions:
[0128] Copper (Cu): 0.015 mol (1 gram)
[0129] Molar ratio of HCl / Cu: 5:1
[0130] Copper (Cu) size: 3-5μm
[0131] N 2 Flow rate: 15cm 3 / minute
[0132] Table 1
[0133] Example number
Embodiment 6-8
[0135] According to the above disclosure of the present invention, the following experiments were carried out in a quartz microreactor. The reaction was carried out as a fixed bed reactor type. The dry hydrogen chloride gas required for the reaction was supplied into the reactor through a mass flow controller through a quartz tube extending to the bottom of the reactor. The reaction is carried out under atmospheric pressure. Dry hydrogen chloride gas is introduced into the reactor at the desired flow rate. The results are shown in Table 2. The reaction is carried out under the following operating conditions:
[0136] Copper (Cu): 0.015 mol (1 gram)
[0137] Molar ratio of HCl / Cu: 1:1
[0138] Copper (Cu) size: 3-5μm
[0139] Temperature: 450°C
[0140] Table 2
[0141] Example number
Embodiment 9-11
[0143] According to the above disclosure of the present invention, the following experiments were carried out in a quartz microreactor. The reaction was carried out as a fixed bed reactor type. The dry hydrogen chloride gas required for the reaction was supplied into the reactor through a mass flow controller through a quartz tube extending to the bottom of the reactor. The reaction is carried out under atmospheric pressure. Dry hydrogen chloride gas is introduced into the reactor at the desired flow rate. The results are shown in Table 3. The reaction is carried out under the following operating conditions:
[0144] Copper (Cu): 0.015 mol (1 gram)
[0145] Copper (Cu) size: 3-5μm
[0146] Temperature: 450°C
[0147] N 2 Flow rate: 50cm 3 / minute
[0148] table 3
[0149] Example number
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com