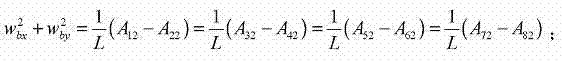Six-dimensional acceleration acquisition method
An acquisition method and acceleration technology, which is applied in multi-dimensional acceleration measurement, acceleration measurement using inertial force, etc., can solve problems such as the complexity of the six-dimensional acceleration acquisition method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
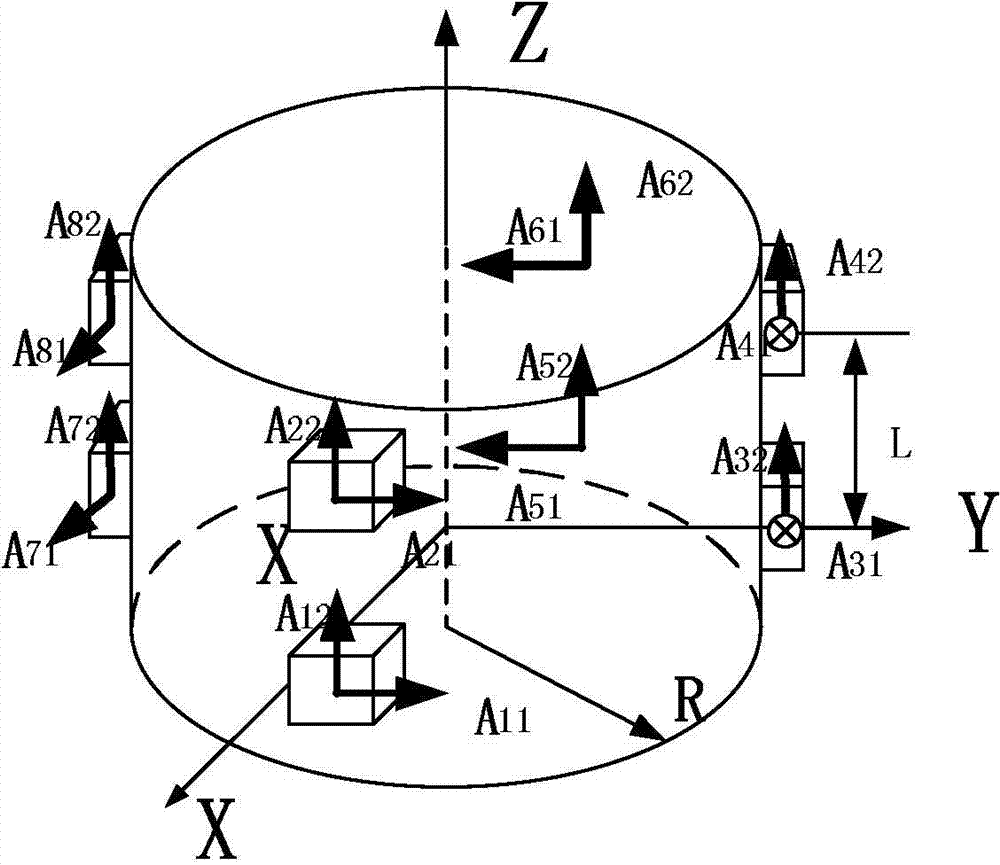
[0027] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 Describe this embodiment, a kind of six-dimensional acceleration acquisition method described in this embodiment, described acquisition method is realized based on 8 two-axis accelerometers, and described method comprises the following steps:
[0028] Step 1: Establish a 16 accelerometer detection space model:
[0029] The model is in the form of a cylinder, four two-axis accelerometers are arranged at 90 degrees to each other and form the top surface of the cylinder; the other four two-axis accelerometers are arranged at 90 degrees to each other and form the cylinder The bottom surface of the bottom surface; the positions of the four two-axis accelerometers on the top surface and the four two-axis accelerometers on the bottom surface correspond to each other, and the distance between the top surface and the bottom surface is L, and the radius of the cylinder is R; each two The directions of the two sensitive axes of t...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0032] Specific Embodiment 2: This embodiment is a further limitation of the six-dimensional acceleration acquisition method described in Specific Embodiment 1. The direction of any one of the two sensitive axes of the two-axis accelerometer is the same as the Z axis. .
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0033] Embodiment 3: This embodiment is a further limitation of the six-dimensional acceleration acquisition method described in Embodiment 1.
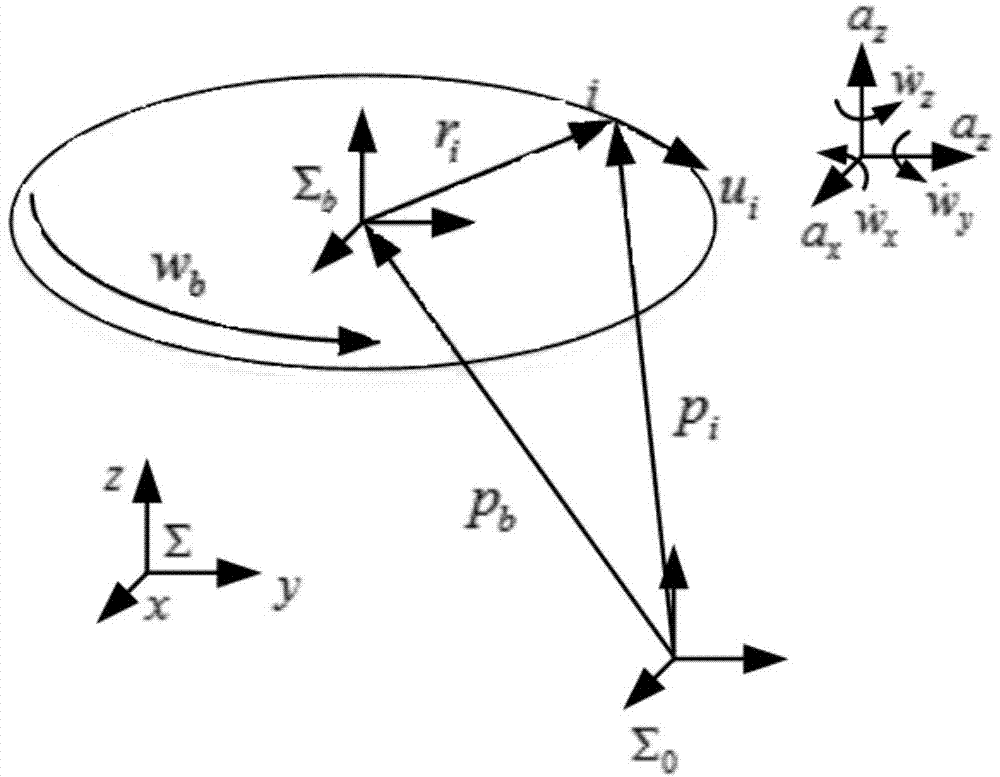
[0034] In step 3, the method of using the 8 two-axis accelerometers to measure the linear acceleration and angular acceleration of the end of the robot to be tested in the carrier coordinate system is:
[0035] p · · bx = 1 2 ( A 71 - A 31 )
[0036] p · · by = 1 2 ( A 11 - A 51 ) ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com