Non-spore curtobacterium and application thereof
A spore-free and short technology, applied in the field of fermented tea, can solve the problems of poor retention and poor brown color formation, and achieve the effect of good brown color formation and high content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Example 1: Isolation and Screening of Bacterial Strains
[0038] 1) Processing of raw materials (naturally fermented tea)
[0039] Weigh 5 g of Duosuike natural fermented tea obtained by fermentation by the conventional method of our laboratory in a sterile Erlenmeyer flask, add 50 mL of sterile water, and shake for 30 min to obtain 10 -1 Diluent; then use 1mL pipette to draw 10 -1 Dilute 1 mL, transfer it into a test tube filled with 9 mL of sterile water, oscillate, let the bacteria liquid mix evenly, and serve as 10 -2 Diluent; and so on, serially diluted to make 10 -3 、10 -4 、10 -5 Wait for a series of dilutions.
[0040] 2) Isolation and cultivation of dominant microorganisms in naturally fermented tea
[0041] Number the media plates and pipette 10 -3 、10 -4 、10 -5 Inoculate 0.2mL of each diluted bacterial solution on potato dextrose agar (PDA) medium with different dilution numbers (20% potato, 2% glucose, 2% agar, natural pH), and then spread the bacter...
Embodiment 2
[0080] Embodiment 2: the identification of bacterial strain
[0081] 1) Colony characteristics:
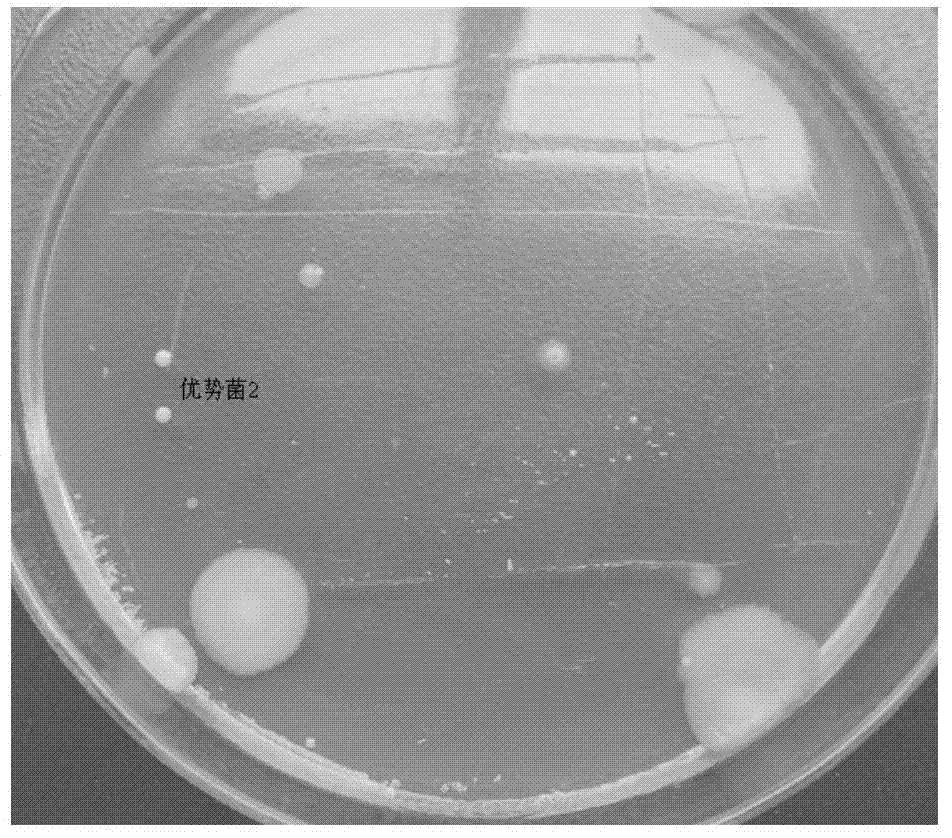
[0082] Streak the dominant bacteria 2 onto sugar agar (PDA) medium (20% potato, 2% glucose, 2% agar, natural pH), then invert the plate, culture at 28°C for 2 days, observe and record the growth of colonies on the plate . figure 1 The characteristics of the colonies showing dominant bacteria 2 are generally as follows: round colonies, milky yellow, moist surface, no jagged edges, and small colony diameter.
[0083] 2) Gram stain: rod-shaped, stubby, red, Gram-negative bacteria.
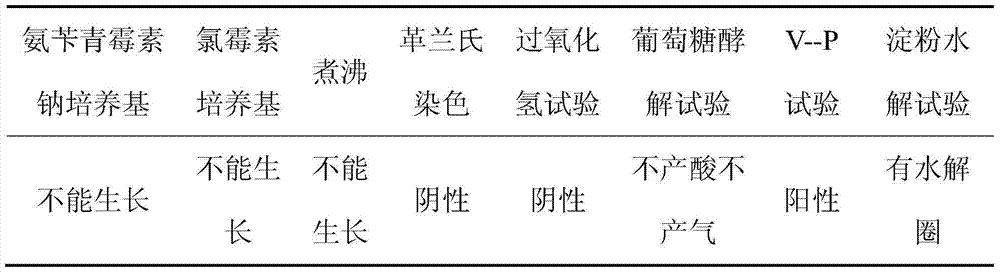
[0084] 3) Physiological and biochemical identification
[0085] (1) Ampicillin sodium medium: add ampicillin sodium at a final concentration of 100 mg / mL to PDA plate medium (potato 20%, glucose 2%, agar 2%, natural pH), inoculate dominant bacteria 2, 28°C Cultivate for 2 days, observe the growth of dominant bacteria 2 on the PDA plate medium supplemented with ampicillin sodium, and identify whether t...
Embodiment 3
[0098] Embodiment 3: the brewing effect of the Duosuike fermented tea fermented by the pure strain of non-spore bacillus 13-13
[0099] Take 5g of the fermented tea and 5g of the original tea (before fermentation) obtained by the pure fermented fermented by the method of 3) in Example 1 using Brevibacterium 13-13, respectively, and brew them with boiling water for 15 minutes, and compare their brown color and Taste.
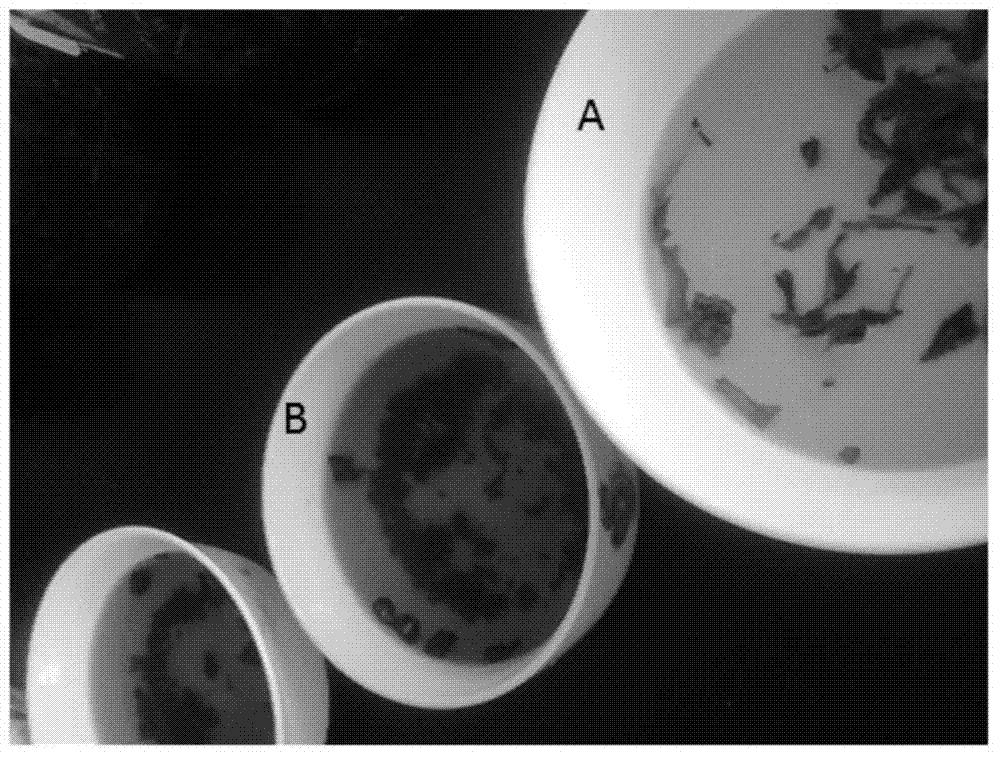
[0100] figure 2 It shows the comparison result of the brown color after brewing of the fermented tea of Polyacae fermented tea produced by the fermentation of Brevibacterium 13-13 of the present invention and the brown color of the original tea (before fermentation). It can be seen that after brewing, the fermented tea of Polyacea The tea color of the tea is brown (B), which is clearly different from the light green (A) of the original tea. The prepared tahoko fermented tea tastes soft and mellow, with the sweetness of tahoko itself.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com