Alumite and Iron Removal Process in Zinc Hydrometallurgy Process
A hydrometallurgical zinc smelting and process technology is applied in the application field of the oxidant in the process of removing iron from heavy alum, which can solve the problems of high sulfur and ferrous content, energy loss, etc., and achieves low cost, reduced power consumption, and improved electrolysis current efficiency. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Fe in supernatant of heavy alum 2+ The content is 0.6~1.34g / l, adjust PH=4.0, temperature: 70°C, add H equal to 1.6 times the theoretical amount from the bottom of the sinking alum supernatant 2 o 2 solution, the reaction time is 40min, and the iron removal rate is shown in Table 6:
[0048]
Embodiment 2
[0050]The addition of manganese powder is 60% of the theoretical addition, H 2 o 2 When the amount of oxidant added is 1.1 to 1.3 times the theoretical amount 2 o 2 Oxidant industrial test data, the reaction conditions are: PH value of supernatant of heavy alum: 4.0, temperature: 70°C, H 2 o 2 The solution is industrial hydrogen peroxide. The results are shown in Table 7:
[0051]
Embodiment 3
[0053] The amount of manganese powder added is 30% of the theoretical addition, H 2 o 2 The amount of oxidant added is 1.8 to 2.0 times of the theoretical amount added, and the reaction conditions are as follows: PH value of supernatant of heavy alum: 4.0, temperature: 70°C, H 2 o 2 The solution is industrial hydrogen peroxide. The results are shown in Table 8:
[0054]
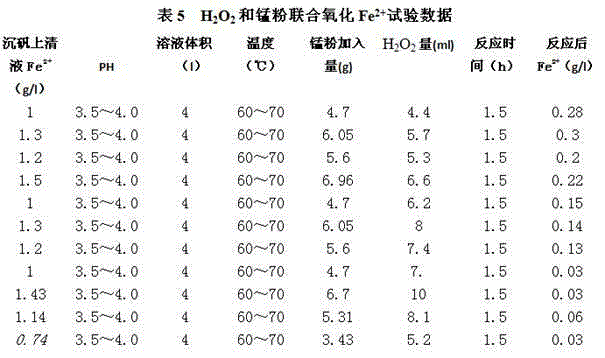
[0055] As can be seen from Table 7 and Table 8, when the addition of manganese powder in the oxidation tank is 60% of the theoretical addition, H 2 o 2 When the amount of oxidant added is 1.0 to 1.3 times of the theoretical amount, the flow rate of oxidizing liquid is 220m 3 / h, heavy alum supernatant Fe 2+ 1g / l, calculated as cathode zinc 340t / d, H 2 o 2 The unit consumption of oxidant is 19.18㎏ / t.Zn, combined oxidant to Fe 2+ The oxidation rate is 92%; when the addition of manganese powder in the oxidation tank is 30% of the theoretical addition, H 2 o 2 When the amount of oxidant added is 1.8...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com