An optimization method for satellite double-difference observation structure under occlusion environment
An optimization method, a technology of double-difference observation, applied in satellite radio beacon positioning systems, measurement devices, radio wave measurement systems, etc., to achieve the effects of reducing ill-posedness, improving the quality of positioning solutions, and improving reliability and stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0040] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
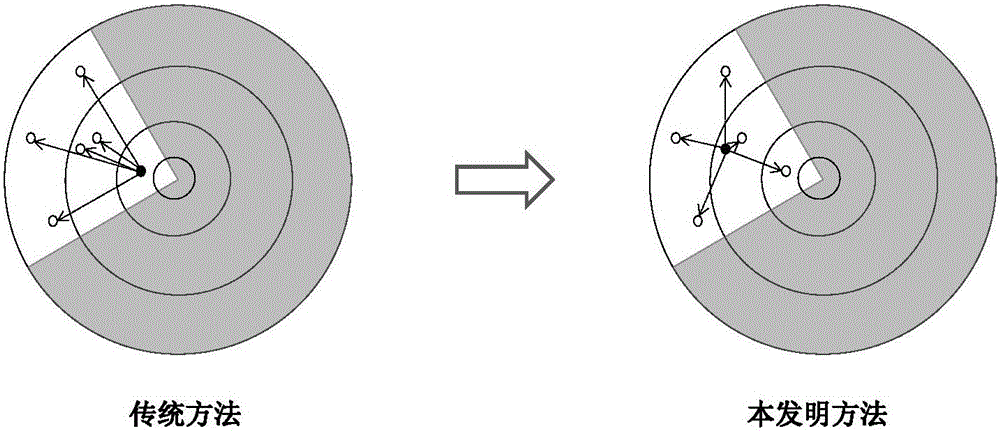
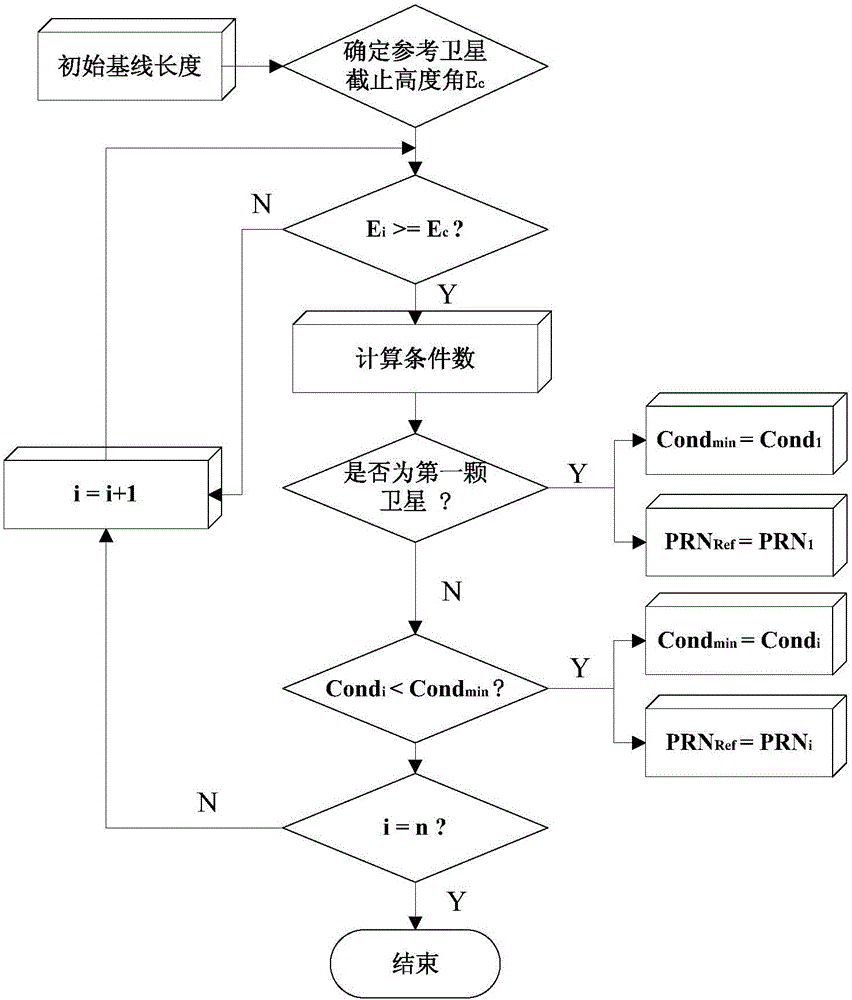
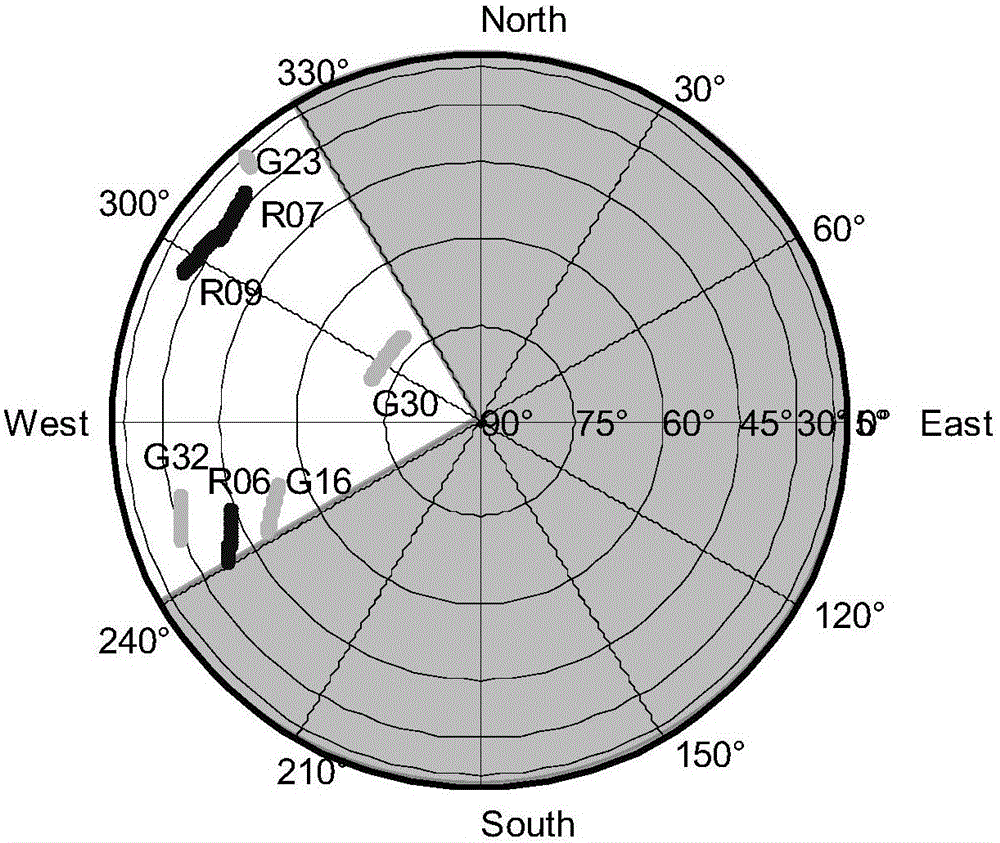
[0041] A method proposed by the present invention to improve the reliability and stability of GNSS positioning in an occlusion environment by optimizing the observation structure, firstly analyzes the influence of the geometric distribution of satellite pairs (reference satellites and non-reference satellites) on the correlation between carrier double-difference observation equations, Clarified the essential relationship between the correlation between the carrier double-difference equations and the second type of ill-conditionedness, and proposed the condition number as the evaluation index of the stability of the carrier double-difference observation structure. On this basis, a new minimum condition based on the cofactor matrix was further proposed Number of reference satellite selection methods.
[0042] A satellite double-difference observation structure provided b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com