Plasmid with tracing property and capable of degrading atrazine, gene engineering bacteria and application thereof
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and atrazine, applied in the field of atrazine-degrading plasmids, engineering bacteria and degradation, can solve problems such as in-situ real-time detection difficulties, to prevent environmental ecological risks, promote formation and scale expansion , The effect of stable biological treatment efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1 pUC18- atzA-gfp Construction of recombinant plasmids.
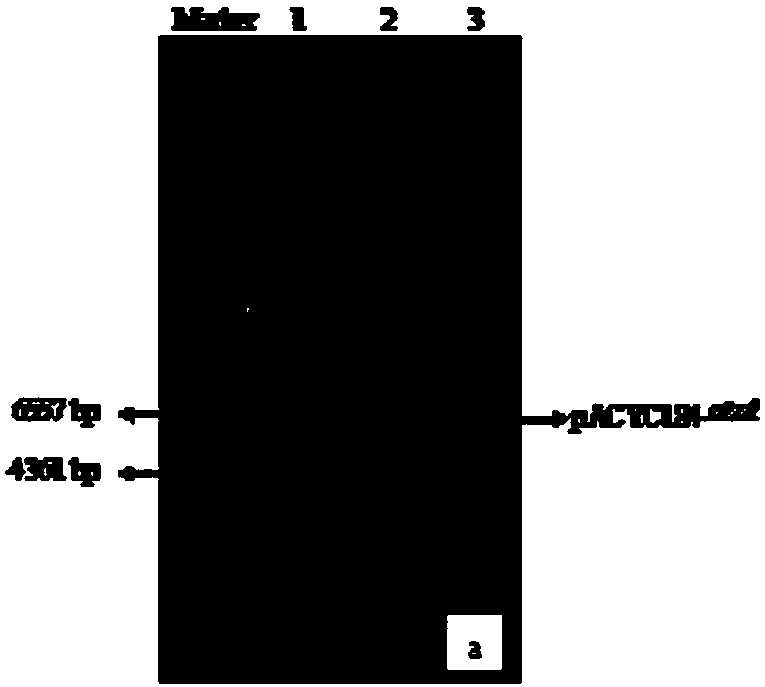
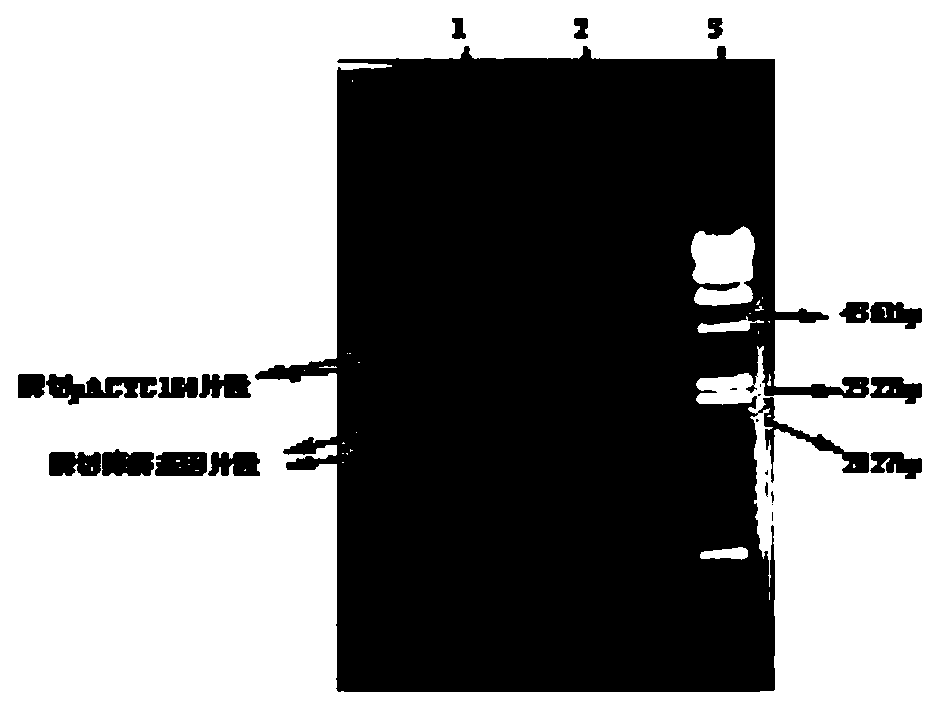
[0037] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention constructs a recombinant plasmid through plasmid pACYC184 and plasmid pUC18. Plasmid pACYC184 contains atzA gene and resistance to chloramphenicol, and its size is about 6500bp. The plasmid map is as follows figure 2 As shown, the gel electrophoresis Figure 4 ; Plasmid pUC18 contains the gfp gene, is resistant to ampicillin, and is about 2600bp in size. The plasmid map is as follows image 3 As shown, the gel electrophoresis Figure 6 shown. Both plasmids contain restriction endonuclease Eco88I restriction sites, therefore, the two plasmids were respectively digested with Eco88I to obtain linear atzA Fragment and linear pUC18- gfp Fragment, then use T 4 Ligase was used for connection, and recombinant plasmids were obtained after screening.
[0038] The electrophoresis pattern of restriction endonuclease Eco88Ⅰ after digestion of plasmid...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2 The acquisition of genetically engineered bacteria
[0042] The recombinant plasmid pUC18- atzA-gfp Transformation into Escherichia coli DH5α to obtain genetically engineered bacteria, and carry out antibiotic resistance, gfp gene expression and atzA DNA Testing.
[0043] 1. Antibiotic resistance detection
[0044] The genetically engineered bacteria were cultured on the medium containing ampicillin and chloramphenicol respectively, and the results were as follows: Figure 9 As shown, only colonies appear on the medium containing ampicillin, but no colony grows on the medium containing chloramphenicol, indicating that the genetically engineered bacteria are only resistant to ampicillin, and have no resistance to chloramphenicol. The results were consistent with the antibiotic resistance of the recombinant plasmid pUC18-atzA-gfp.
[0045] 2. Green fluorescent protein gene ( gfp gene) expression detection
[0046] Cultivate the genetically engineered ba...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Example 3 Degradation of Atrazine
[0050] Under the same conditions, the genetically engineered bacteria obtained in Example 2 (containing the recombinant plasmid pUC18- atzA-gfp ) and the plasmid containing pACYC184- atzA The strain degrades atrazine, the experimental results are as follows Figure 13 shown. It can be seen that the genetically engineered bacteria and the original degradation plasmid (pACYC184) have the same ability to degrade atrazine.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com