Method for monitoring machine with rotating shaft
A technology for machines and rotating parts, applied in the direction of machines/engines, instruments, mechanical equipment, etc., can solve problems such as inability to monitor bearings, impossible to distinguish friction points, etc., to achieve the effect of simple installation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
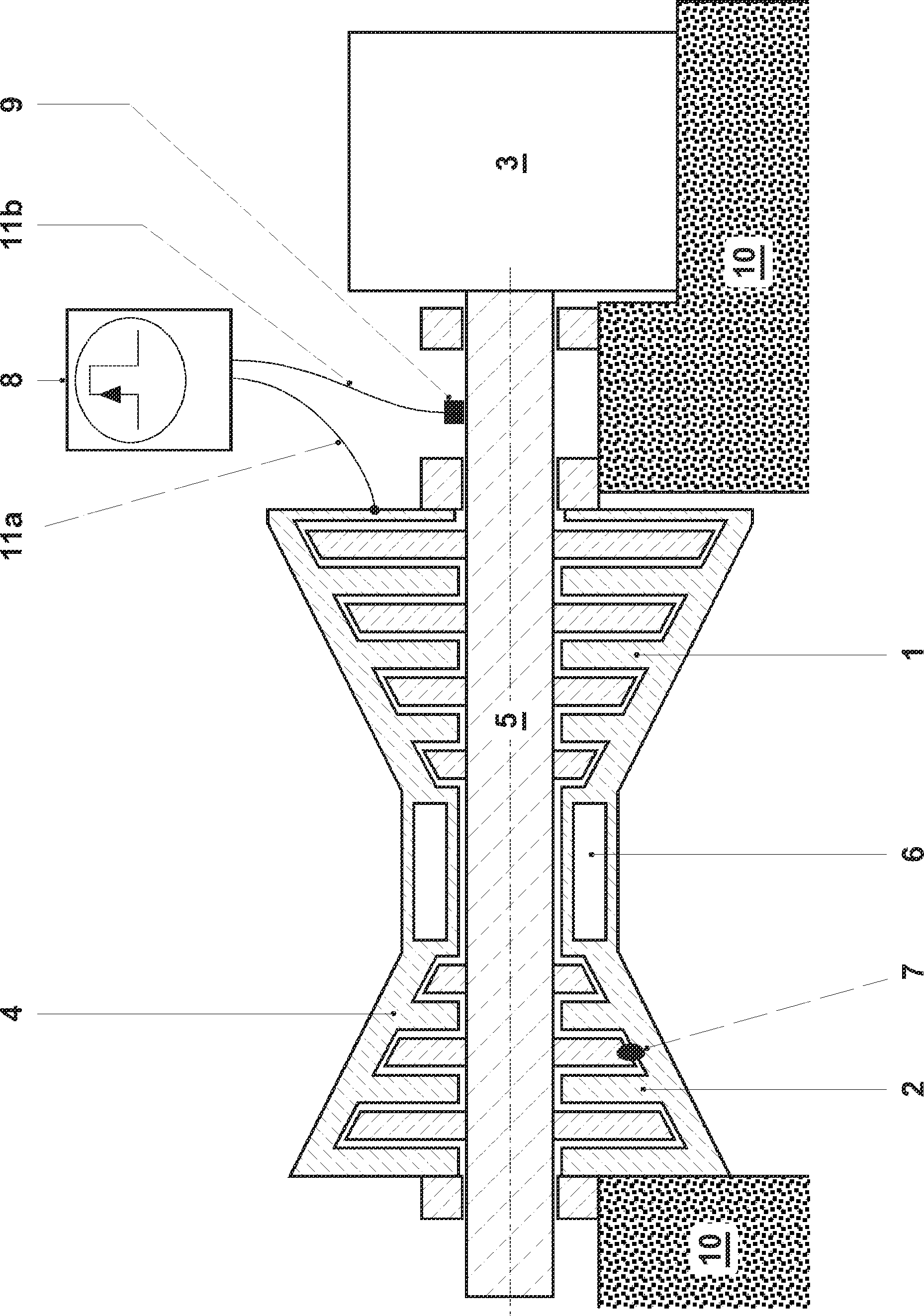
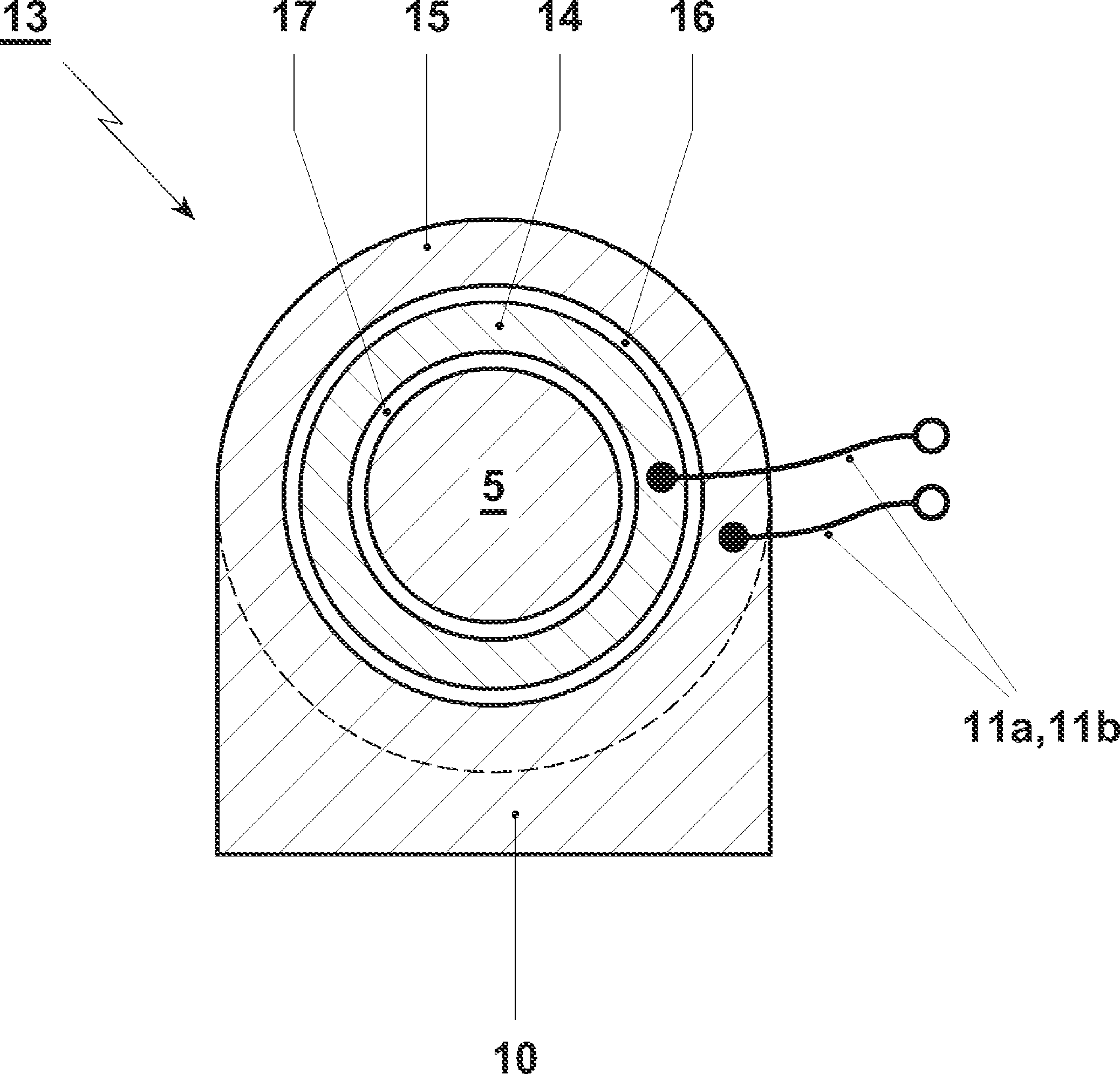
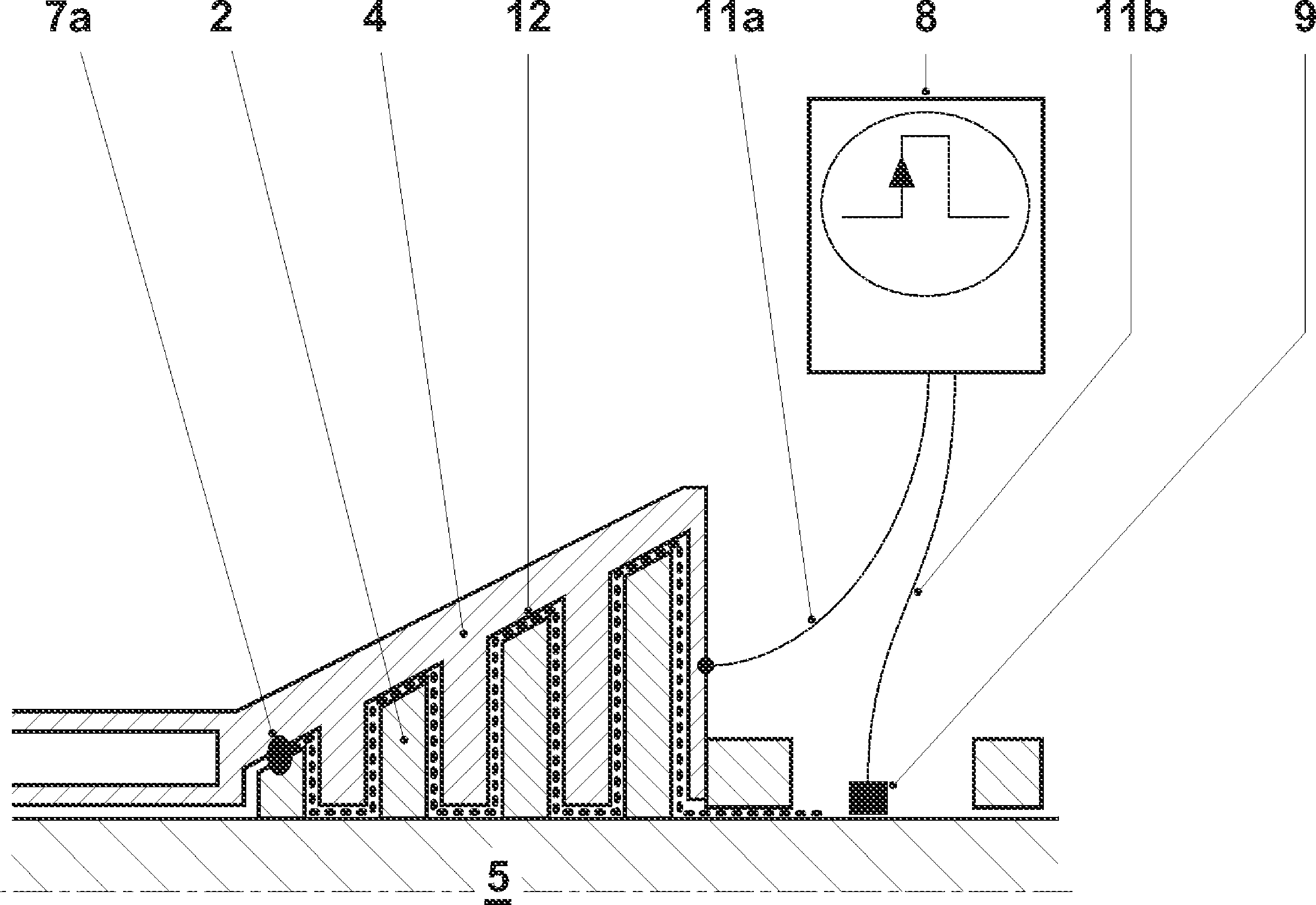
[0037] figure 1A gas turbine train is schematically shown in sectional view in , which essentially consists of at least one compressor 1 , a combustion chamber 6 which is only implied in the figure, a turbine 2 and a generator 3 . Such a group of gas turbines may also be operated by sequential combustion, wherein a first turbine is arranged on the outlet side of a first combustion chamber connected downstream of the compressor, and a second combustion chamber is operated at the outlet side of the first turbine, the combustion The hot gases of the chamber are applied to the second turbine. The point of friction in the turbine is marked as point 7 in the diagram. The measuring device 8 injects said voltage pulses into the coaxial system via the measuring cables 11a, 11b, the contacts on the housing 4 and the shaft contacts 9 and uses these pulses to measure the elapsed time or the transmission characteristic. The always present ground contact is advantageously used as shaft co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com