Method for producing surface-treated glass substrate
A glass substrate and surface treatment technology, which is applied in the field of chemically strengthened glass manufacturing, can solve the problems of film peeling, poor adhesion between the glass substrate and the functional film, etc., and achieve the effects of less warping, excellent transmittance, and improved productivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment A1
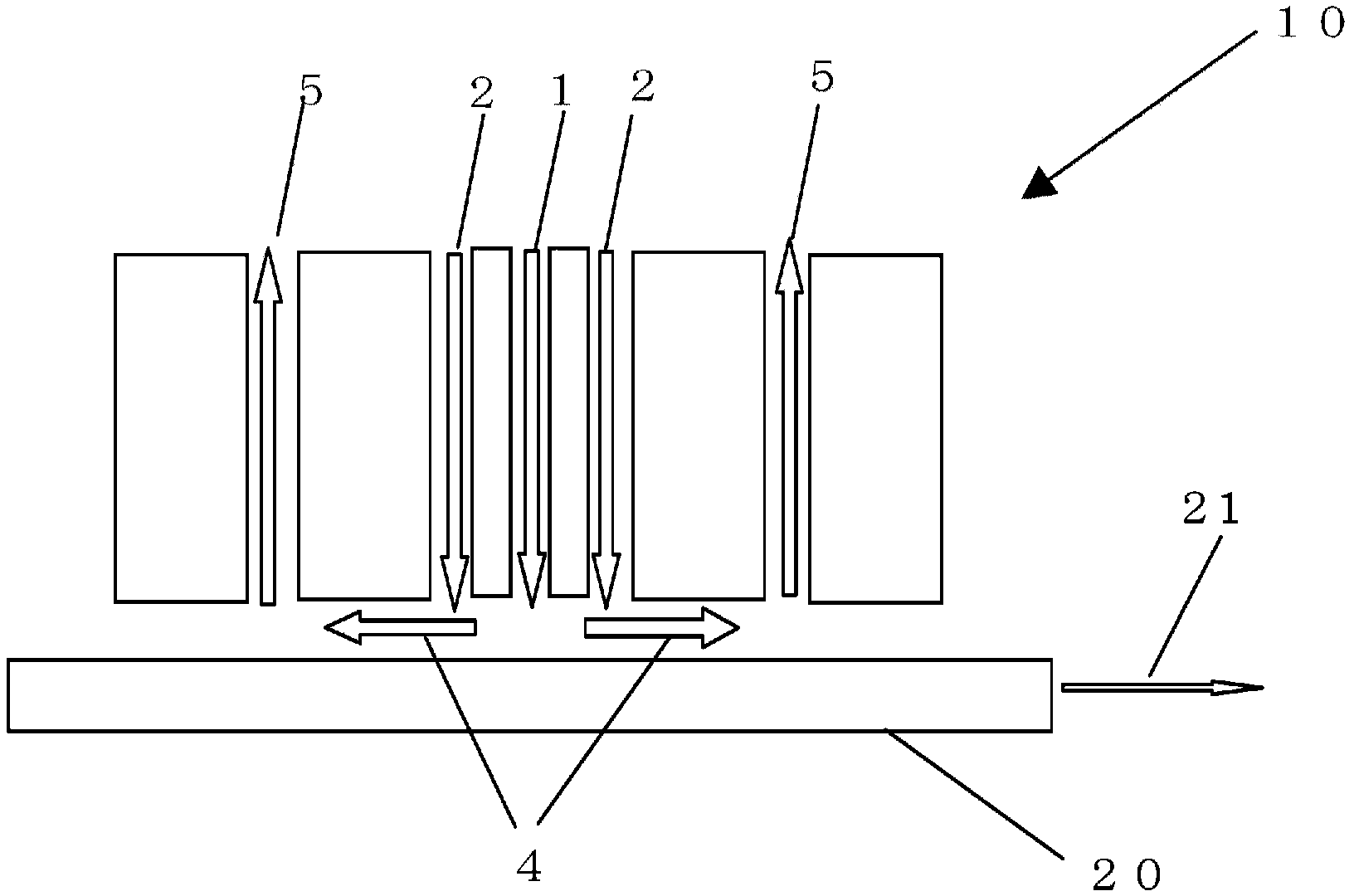
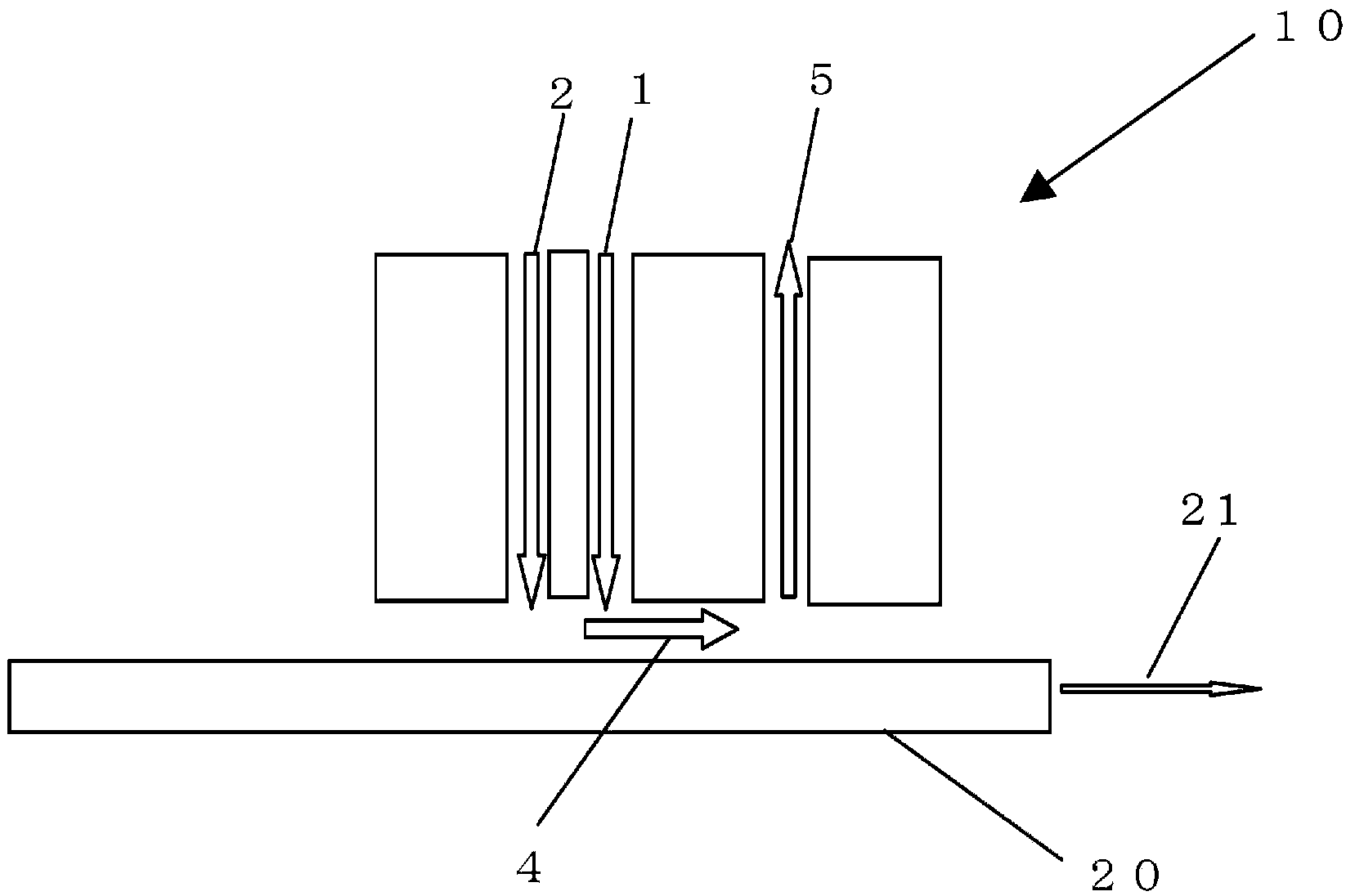
[0074] Using the twin-fluid injector 10 used in the atmospheric pressure CVD method, such as figure 1 As shown in the schematic diagram, a gas containing hydrogen fluoride was brought into contact with the surface of the glass substrate of the original plate A shown in Table 1. The surface contacting the hydrogen fluoride-containing gas serves as a molten metal bath non-contact surface of the glass substrate produced by the float method.
[0075] That is, mix HF0.56SLM (in terms of gas in the standard state, liters per minute) and nitrogen (N 2 ) The gas obtained by 9SLM is heated to 150°C, at a flow rate of 64cm / s from figure 1 The central slit 1 is shown spraying towards the glass substrate and 245.5 SLM of N from the outer slit 2 onto the glass substrate 2 . The gas flows on the substrate 20 through the channel 4 , and the gas in an amount twice the jet flow rate is discharged through the exhaust slit 5 . The temperature and flow velocity of the gas were measured using ...
Embodiment A2、A3 and A4
[0077] Except that the temperature of the glass substrate in Example A1 is set to 560°C (Example A2), 400°C (Example A3) or 620°C (Example A4), the surface of the glass substrate is carried out in the same manner as in Example A1. deal with.
Embodiment A5
[0079] The surface treatment of the glass substrate was performed in the same manner as in Example 1A except that the amount of HF in the central slit 1 was set to 1.12 SLM.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com