A dynamic and semi-static joint scheduling method in LTE system
A semi-static scheduling and joint scheduling technology, applied in electrical components, wireless communication and other directions, can solve the problems of blocking data packet transmission, waste of resources, and delay of not considering grouping, saving signaling resources and realizing secondary allocation. , the effect of bit rate simplification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0069] The specific embodiment of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with accompanying drawing:
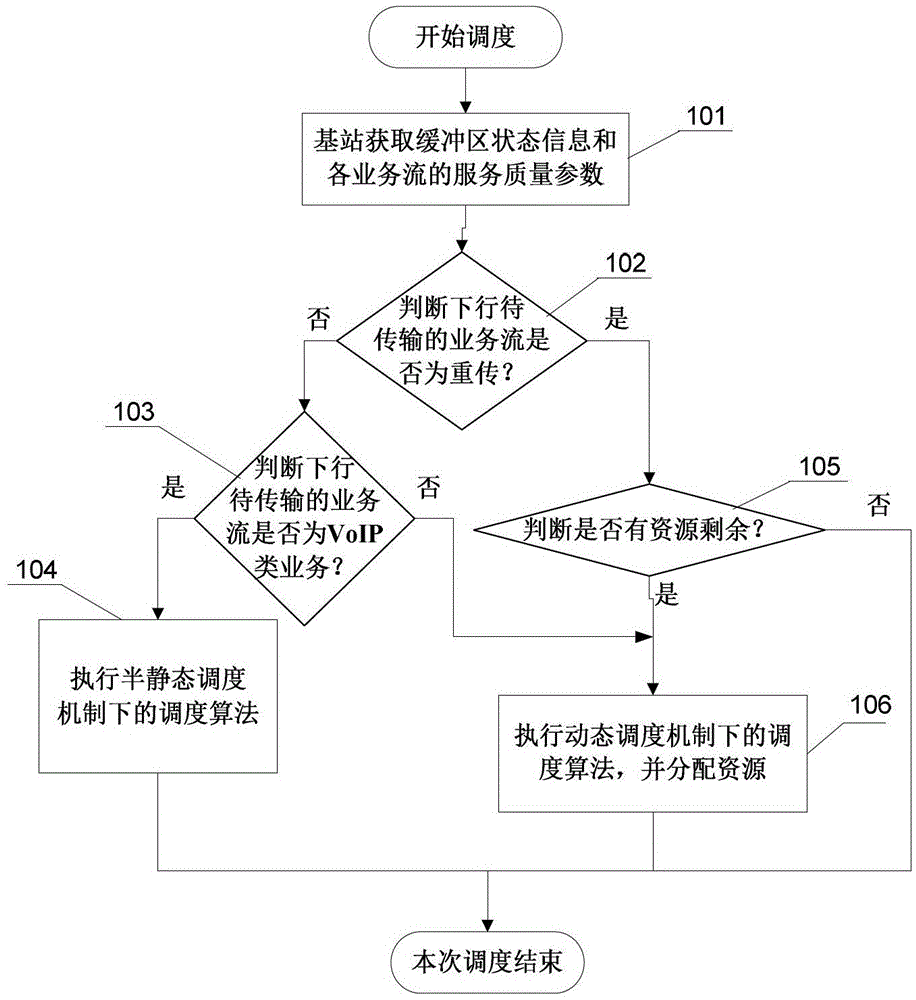
[0070] refer to figure 1 , a dynamic and semi-static joint scheduling method in an LTE system, comprising the following steps:
[0071] 101. The base station acquires buffer status information and service quality parameters of each service flow;
[0072] In each current transmission time interval TTI (denoted as t), it is assumed that the base station side has an infinite buffer size, and the base station obtains the status information of the buffer and the QoS parameters of each service flow;
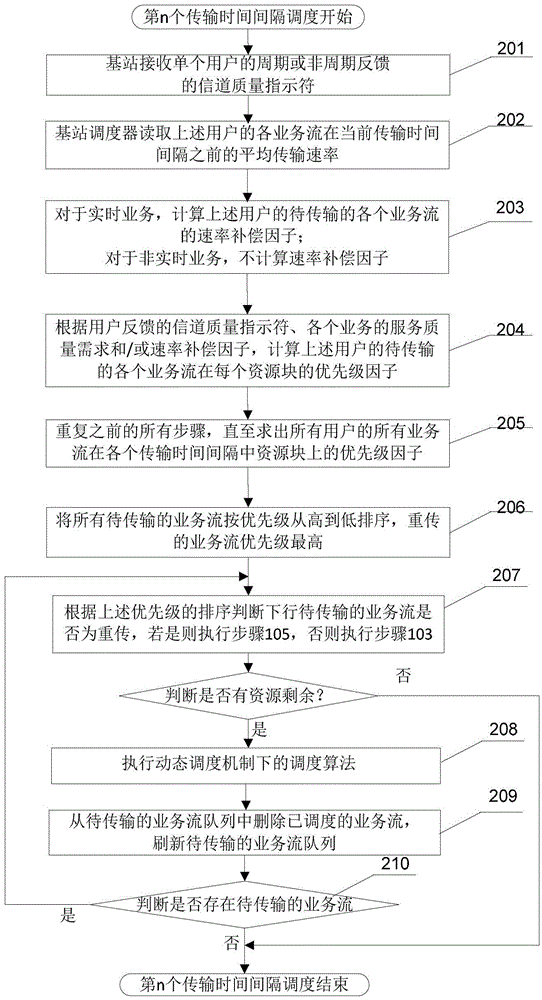
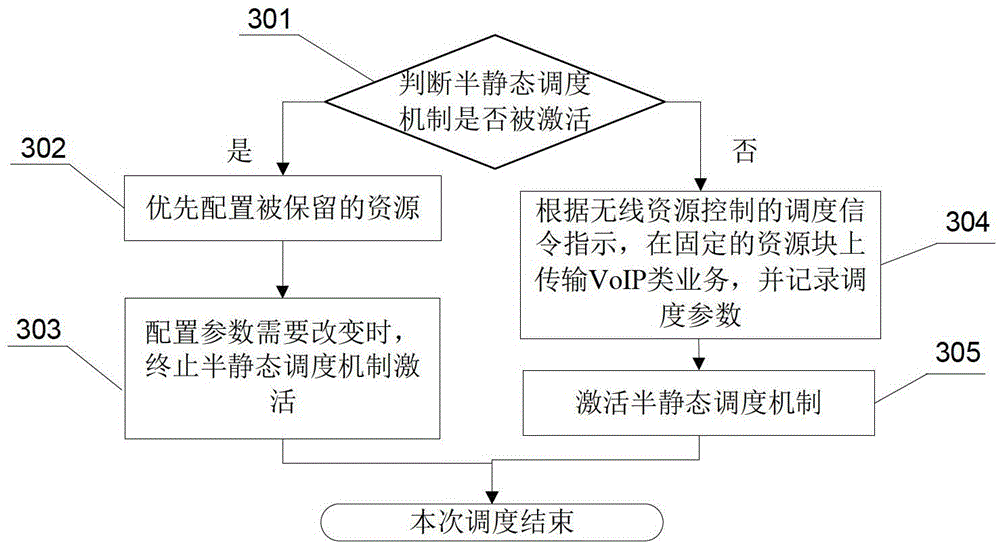
[0073] 102. According to the state information and parameters obtained above, determine whether the downlink service flow to be transmitted is retransmission, if yes, perform step 105, and if not, perform step 103;
[0074] The specific implementation manner in this step is: the scheduler learns whether there is retransmission by checking the indication ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com