Double crankshaft self-balancing internal combustion engine and driving unit thereof
A driving unit and self-balancing technology, which is applied in the direction of machines/engines, transmissions, mechanical equipment, etc., to achieve the effects of convenient manufacture, increased power, and good carrying capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
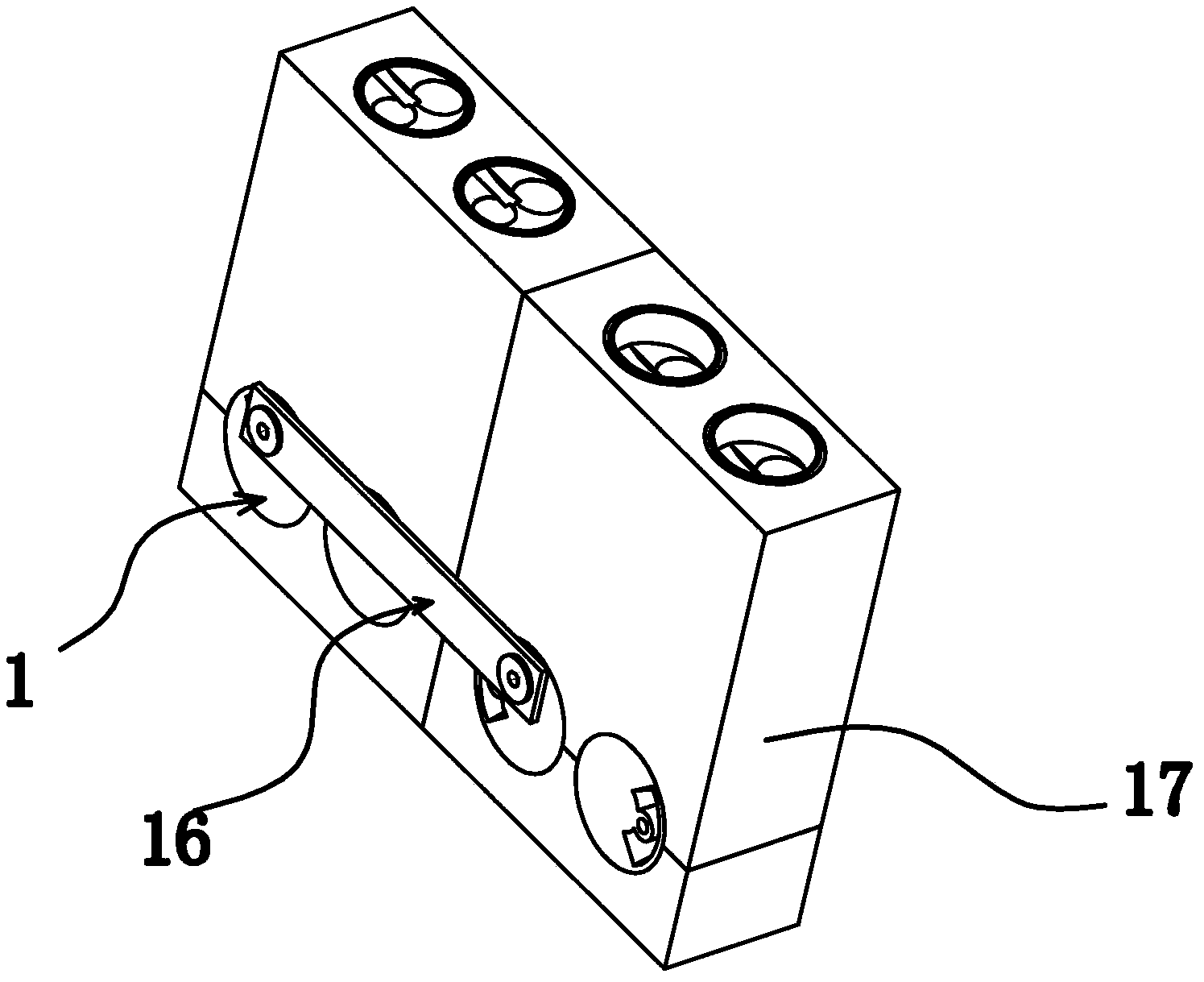
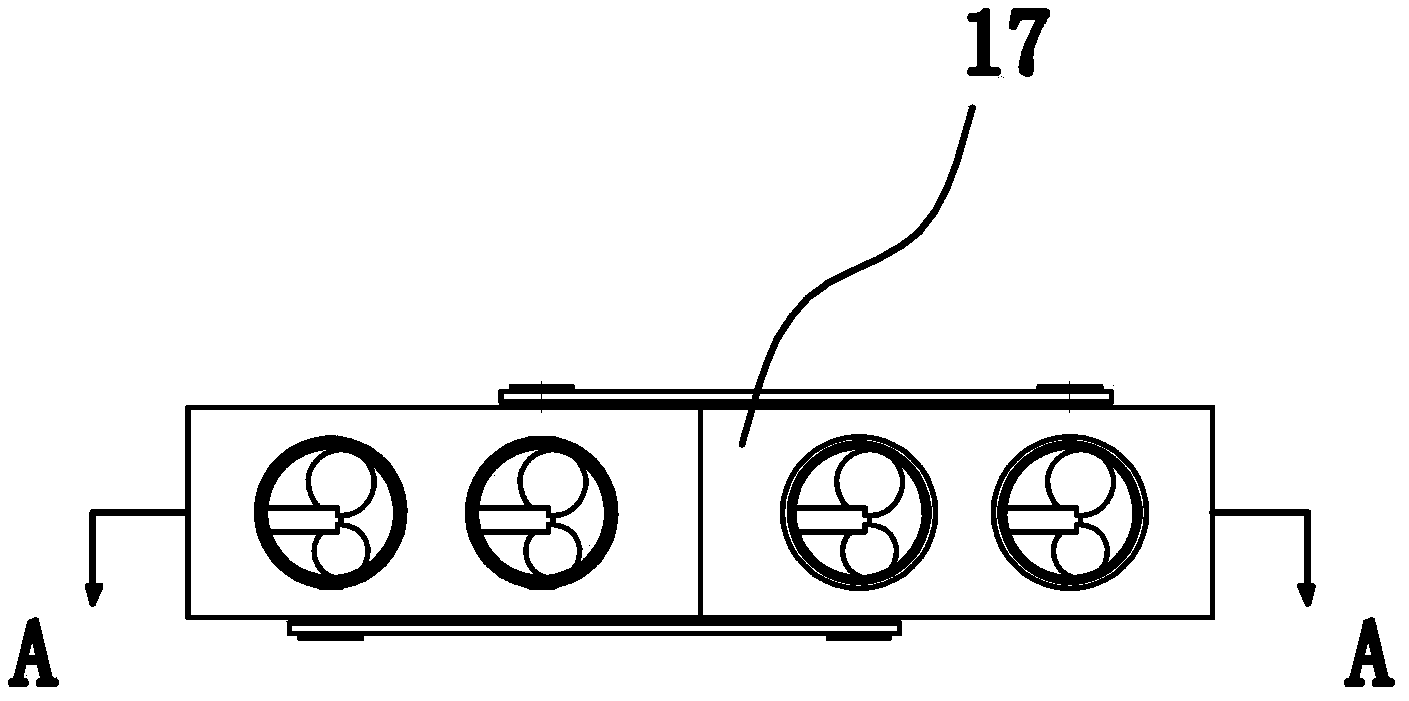
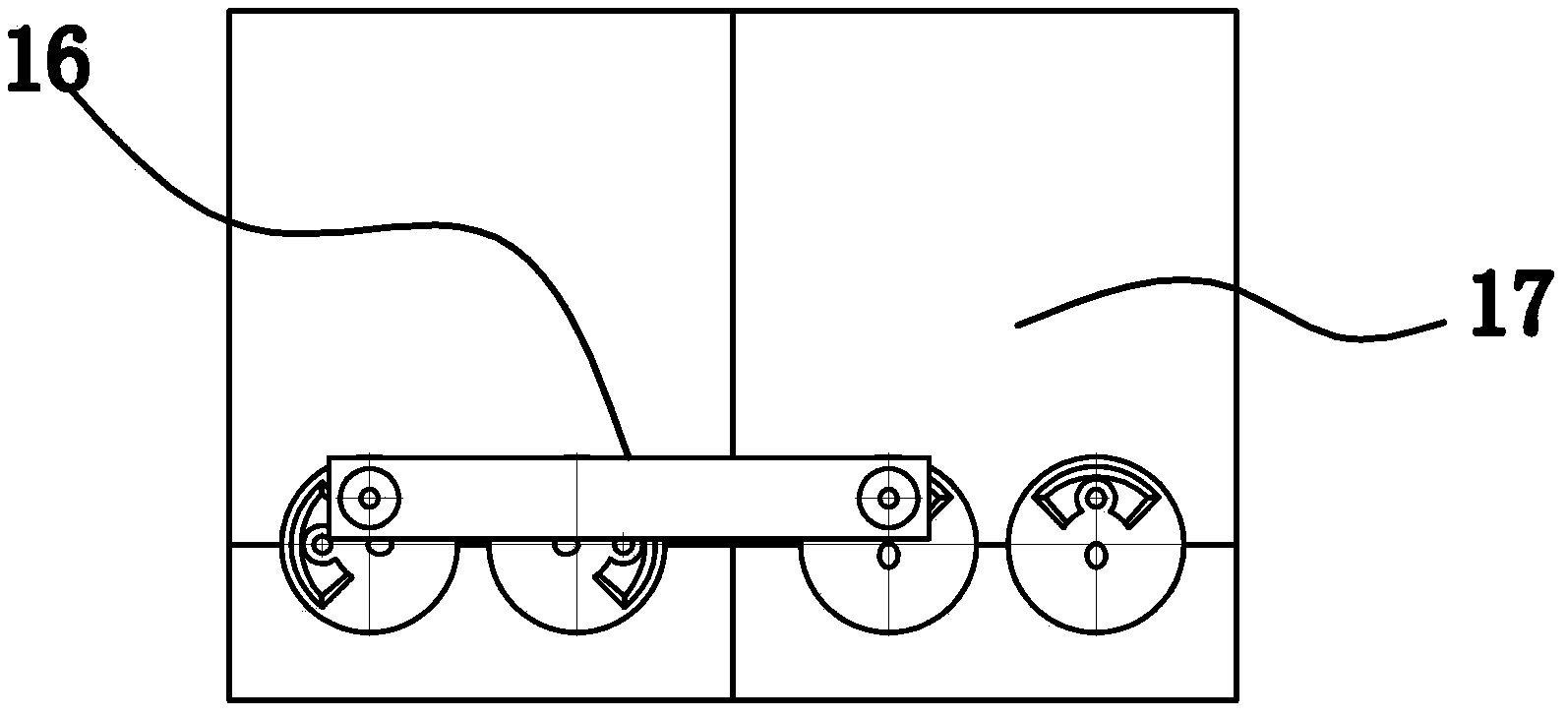
[0057] Such as Figure 1-Figure 7 As shown, the double crankshaft self-balancing internal combustion engine includes a casing 17, and several drive units 1 are arranged in the casing 17. As a preferred solution, the drive unit 1 includes a pair of identical cylinders 2 and a pair of identical crankshafts 3, each Each cylinder 2 has a piston 4 and each crankshaft 3 has a journal 5 . The advantage is that the mass of the crankshaft 3 is too large. After segmentation, one cylinder 2 corresponds to a lower crankshaft 3, and the shape and weight of a single crankshaft 3 become smaller, which is easy to process. A crankshaft 3 for transmission corresponds to a multi-cylinder body. A present crankshaft 3 corresponds to a single cylinder, and multiple pairs of single cylinder drive units 1 are combined to form an engine array, which greatly increases the power of the internal combustion engine. A crankshaft 3 corresponds to the position of a cylinder 2 respectively. There is a piston...
Embodiment 2
[0075]The general content of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1, the difference is that in this embodiment, as another solution, the transmission mechanism 7 includes a piston rod 9, a sliding frame 10 and a sliding block 11, and the middle part of the sliding block 11 is provided with a A mounting hole 12 whose caliber matches the diameter of the journal 5, and the journal 5 is inserted in the mounting hole 12. When the crankshaft 3 rotates, the journal 5 will drive the slider 11 to move synchronously. At the same time, the journal 5 and the inner wall of the mounting hole 12 will rotate, and the force relationship between the journal 5 and the slider 11 will be improved by using the plugging method. Stable without impact.
[0076] The upper end of the piston rod 9 is fixedly connected with the piston 4, and the lower end of the piston rod 9 is fixedly connected with the sliding frame 10. The sliding frame 10 is provided with a chute 18 along the radial direc...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Such as Figure 22 As shown, the general content of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 2, the difference is that in this embodiment, as another solution, each crankshaft 3 corresponds to two cylinders 2, and when in use, both the crankshaft 3 and the cylinder 2 The axis is laid horizontally along the horizontal direction. The two cylinders 2 are located at both ends of the crankshaft 3 and are symmetrically distributed. The piston 4 of each cylinder 2 is fixedly connected to a piston rod 9, and the two pistons corresponding to a crankshaft 3 The rods 9 are fixedly connected to the front and rear ends of the slide frame 10 respectively, and the two piston rods 9 are located on the same axis. In the present embodiment, the piston stroke is 93mm, and the weight of the crankshaft 3 is 55 kilograms. The advantage of this embodiment is that since a crankshaft is provided with a cylinder 2 at the front and rear ends, the piston rod 9 has a force on both ends of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com