zoom lens
A zoom lens and lens group technology, applied in the field of zoom lenses, can solve the problem of inability to take into account the freedom of optical design and manufacturing costs, and achieve the effects of good optical characteristics, reduced production costs, and reduced use quantity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
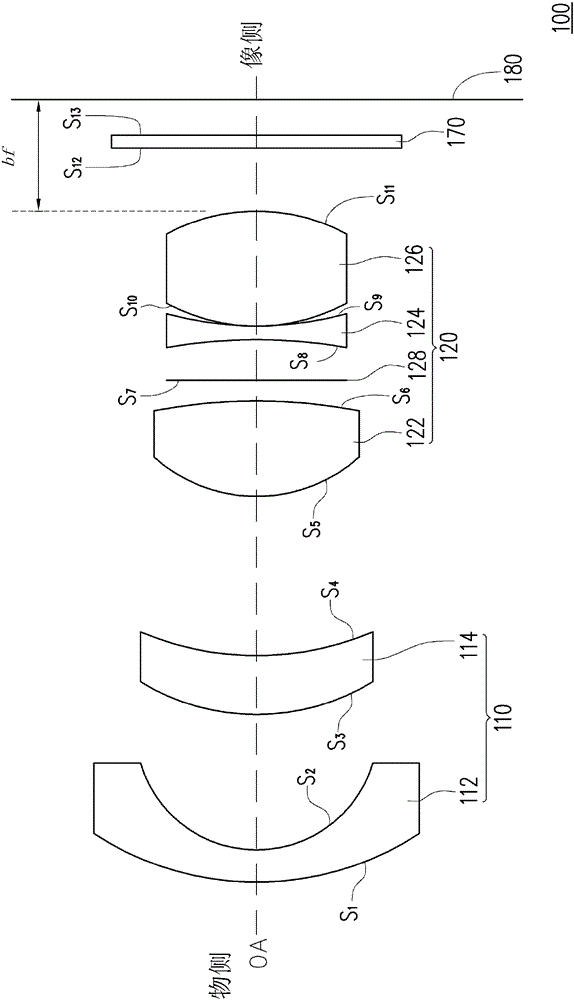
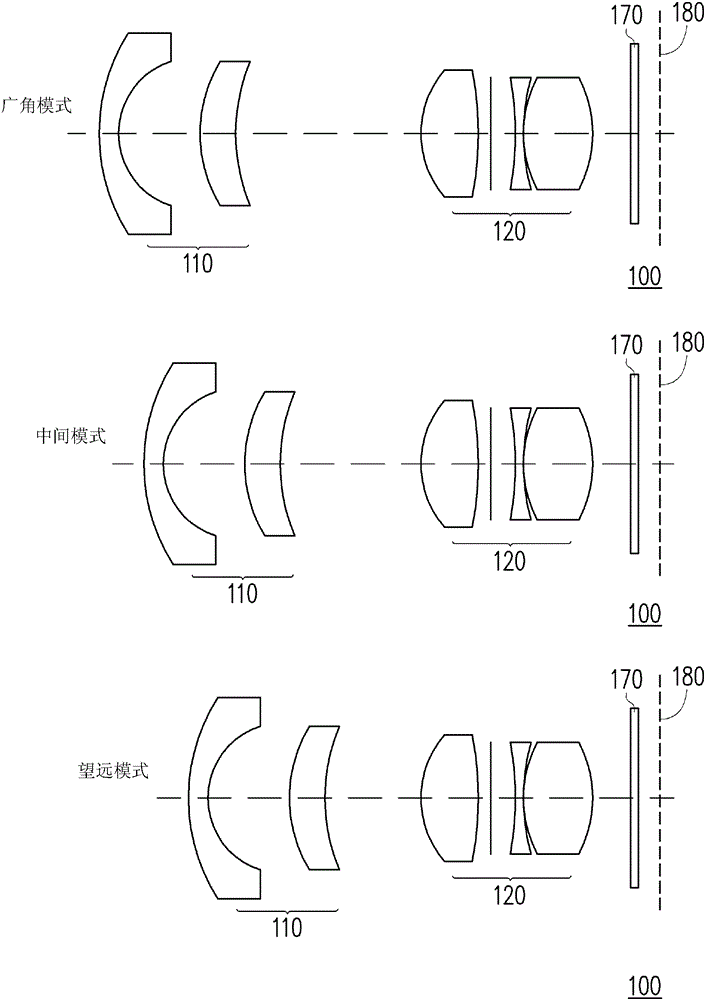
[0020] Figure 1A It is a schematic diagram of the zoom lens according to the first embodiment of the present invention. Please refer to Figure 1A , all optical components of the zoom lens 100 are arranged between the object side and the image side along the optical axis OA. The zoom lens 100 includes in sequence from the object side to the image side: a first lens group 110 and a second lens group 120 . The first lens group 110 has negative optical power (i.e. negative refractive power). The first lens group 110 includes in sequence from the object side to the image side: a negative meniscus lens 112 and a positive meniscus lens 114. The convex surface of the negative meniscus lens 112 faces the object side. The convex surface of the positive meniscus lens 114 faces the object side. The second lens group 120 has positive optical power (ie, positive refractive power). The second lens group 120 includes in sequence from the object side to the image side: a positive convex len...
no. 2 example
[0077] image 3 It is a schematic diagram of the zoom lens according to the second embodiment of the present invention. Please refer to image 3 , zoom lens 300 with Figure 1A The zoom lens 100 in has a similar structure.
[0078] Similarly, image 3 The zoom lens 300 includes in sequence from the object side to the image side: a first lens group 310 and a second lens group 320 . The first lens group 310 has negative optical power (i.e. negative refractive power). The first lens group 310 includes in sequence from the object side to the image side: a negative meniscus lens 312 and a positive meniscus lens 314. The convex surface of the negative meniscus lens 312 faces the object side. The convex surface of the positive meniscus lens 314 faces the object side. The second lens group 320 has positive optical power (ie, positive refractive power). The second lens group 320 includes in sequence from the object side to the image side: a positive convex lens 322 , a negative bicon...
no. 3 example
[0100] Figure 5 It is a schematic diagram of the zoom lens according to the third embodiment of the present invention. Please refer to Figure 5 , zoom lens 500 with Figure 1A The zoom lens 100 in has a similar structure.
[0101] Similarly, Figure 5 The zoom lens 500 includes in sequence from the object side to the image side: a first lens group 510 and a second lens group 520 . The first lens group 510 has negative optical power (i.e. negative refractive power). The first lens group 510 includes in sequence from the object side to the image side: a negative meniscus lens 512 and a positive meniscus lens 514. The convex surface of the negative meniscus lens 512 faces the object side. The convex surface of the positive meniscus lens 514 faces the object side. The second lens group 520 has positive optical power (ie, positive refractive power). The second lens group 520 includes in sequence from the object side to the image side: a positive convex lens 522 , a negative b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com