Devices and methods for controlling actin filaments growth and organization using micropatterned nucleation sites
A technology of actin filaments and actin, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, measuring devices, screening of compounds, etc., and can solve problems such as lack of orientation of actin filaments
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
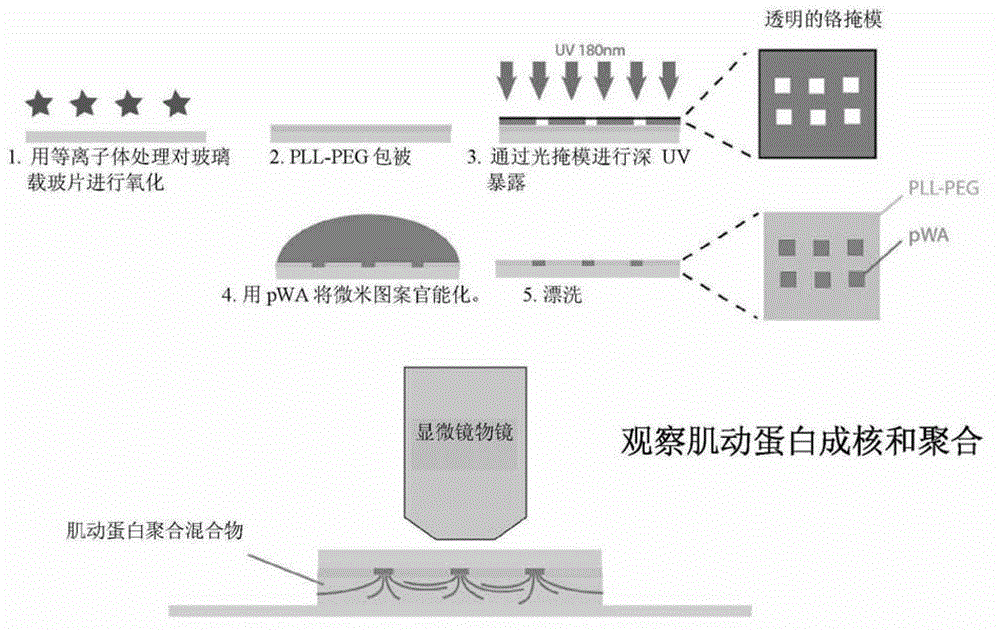
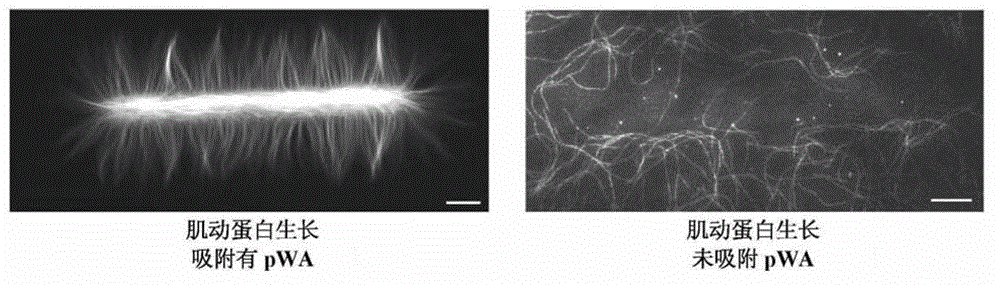
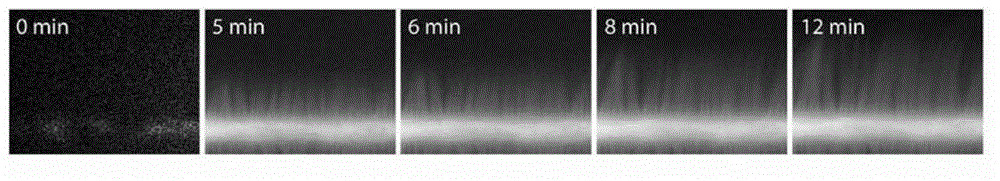
[0122]Actin filaments constitute one of the main components of the cytoskeleton. Specific actin cytoskeletal structures, such as branched networks or parallel actin filament bundles, drive well-defined cellular functions. Biochemical reconstruction of actin network assemblies in bulk solution or from purified proteins using biomimetic devices has emerged as a powerful tool to circumvent cellular complexity and decipher the molecular mechanisms governing actin assembly. These methods highlight how actin-binding proteins affect the growth and interaction of actin filaments in dynamic networks. However, how geometric boundaries such as those encountered in cells affect the dynamic formation of highly ordered actin structures remains largely unexplored.
[0123] Here, the inventors demonstrate that nucleation geometry itself may be the primary determinant of actin network architecture. They developed a micropatterning method that allows spatial control of actin nucleation sites ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com