Implant for influencing the blood flow in arteriovenous defects
A technology for arteriovenous malformation and blood flow, applied in the direction of blood vessels, braids, devices of human tubular structures, etc., can solve the problems of weakening the characteristics and hazards of implants to prevent trauma, and achieve the effect of small overall implant diameter
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
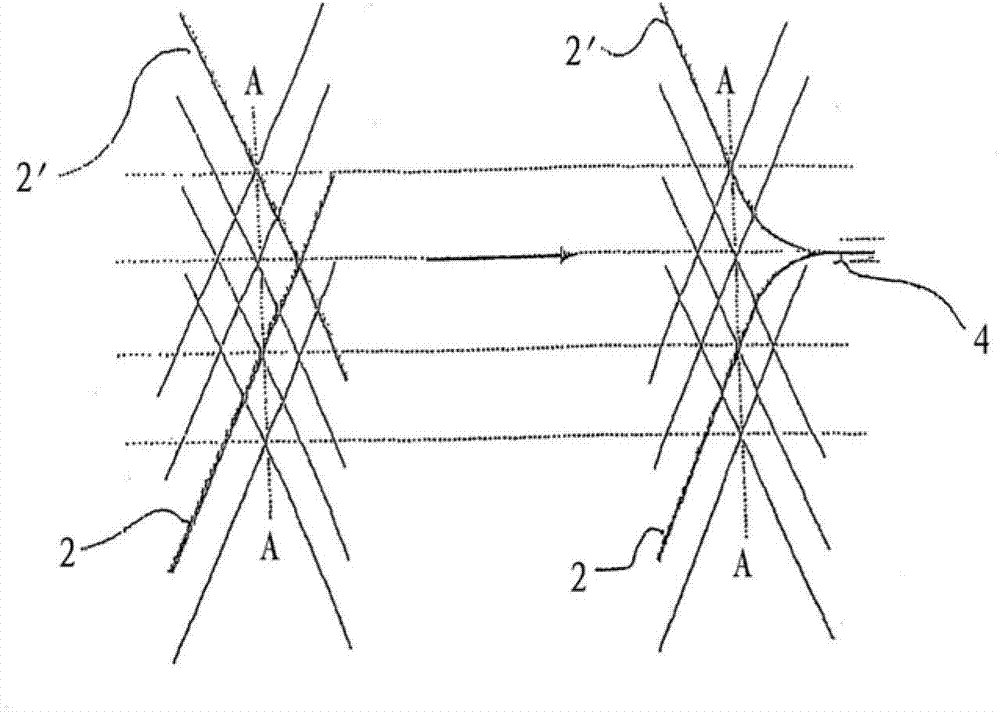
[0084] figure 1 The braided structure of the implant 1 according to the invention is shown, which consists of filaments 2 entangled with each other. In the illustrated embodiment, the individual filaments intersect at an angle of approximately 120°, with the open side of the angle pointing towards the open end of the braid. The illustration shows the braid adopting a slightly stretched / elongated state, ie a reduced diameter.
[0085] The angle Θ represents the braid angle relative to the longitudinal axis, which can reach 80° in the untensioned condition and at nominal diameter. When the braid is in an elongated position inside the catheter, the angle Θ can be reduced to about 7°.
[0086] It will be appreciated that the nominal diameter of the braid will match the lumen of the target vessel at the site being treated.
[0087] Braids are produced in endless braided structures by conventional braiding machines. Braiding takes place on mandrels whose outer dimensions correspon...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com