Wheel state detecting method of sintering machines
A state detection, sintering machine technology, applied in the direction of wheel testing, etc., can solve problems such as large manpower consumption, achieve the effect of reducing production stop losses and improving operating efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
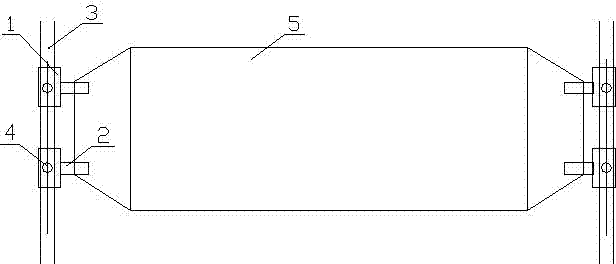
[0026] like figure 1 As shown, the principle of the method for detecting the wheel state of the sintering machine of the present invention is as follows: the failure of the wheel 1 on the sintering machine trolley 5 starts from the damage of the wheel bearing of the sintering machine. The wheel 1 on the outer ring of the bearing shakes, and the wheel 1 after shaking will accelerate the further damage of the damaged wheel bearing of the wheel during the high load of the trolley, the vibration and impact of tipping, and finally the outer ring of the bearing together with the The wheels fell together. The self-weight of each sintering machine trolley is about X tons, and the material on the trolley during production and operation is also about Y tons. At this time, the total weight of each trolley = X+Y tons, and the total weight of each trolley depends on X+Y The support of the four wheels 1 of the trolley runs on the circulating track 3 of the sintering machine.
[0027] The ...
Embodiment 2
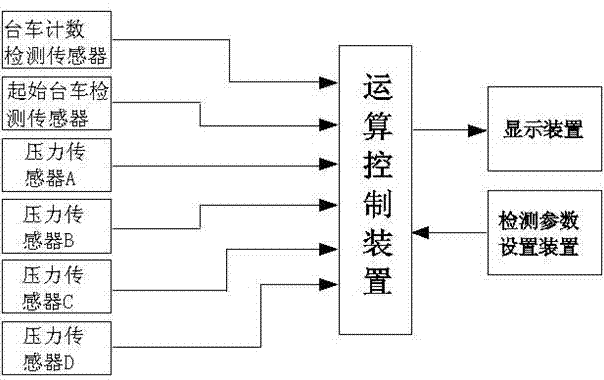
[0039] A method for detecting the wheel state of a sintering machine. The difference between Embodiment 2 and Embodiment 1 is that the out-of-tolerance method for judging in step 4 is as follows: first, the wheel fault judgment range reference value P1 is set by the detection parameter setting device. Usually, The value range of P1 is 0.1~0.9; then the pressure value H received by the four pressure sensors will be obtained by the calculation control device A 、H B 、H C 、H D Take the average value H; divide the pressure values received by the four pressure sensors by H to obtain I A , I B , I C , I D , when (I A , I B , I C , I D )∈(1±P1) is normal, when I A , I B , I C , I D When any one of them does not belong to (1±P1), it is an out-of-tolerance fault.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com