Method, equipment and system for data switching based on tunnel
A tunnel and data technology, which is applied in network data management, electrical components, wireless communication, etc., can solve the problems of low resource utilization, high reuse operation cost, and low user security, so as to increase difficulty and save EID identification resources, reducing the effect of OpenX
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
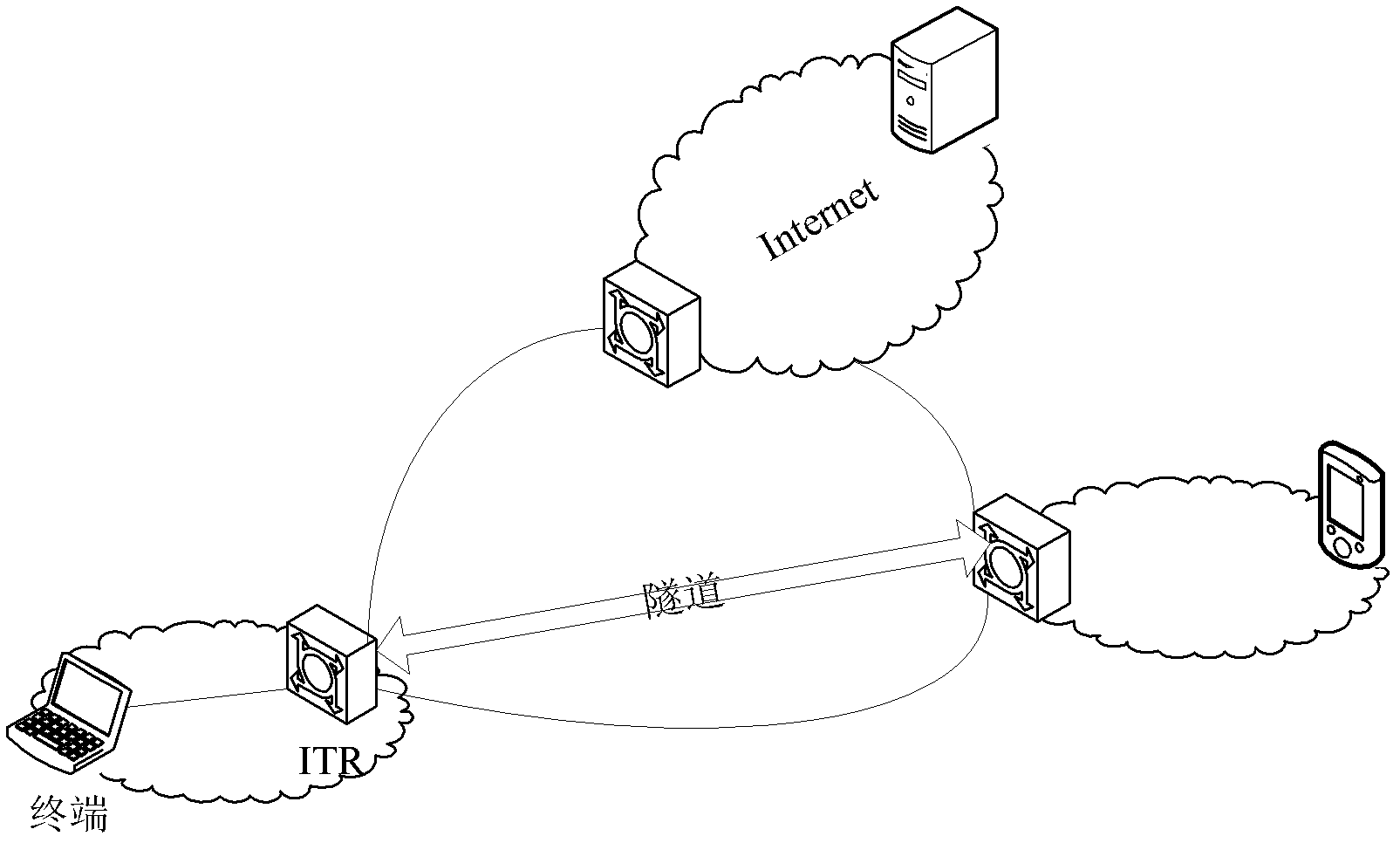
[0079] Such as Figure 4 In the network architecture shown, two terminals X and Y communicate. Both use a network with a private address (pEID1). The location identifier of X is RLOC1, and the location identifier of Y is RLOC2. When X and Y are connected to the network, they both register their private EID-RLOC and domain name binding information with the mapping server. X wants to initiate a communication domain name request to Y, the specific data communication process is as follows Figure 5 :
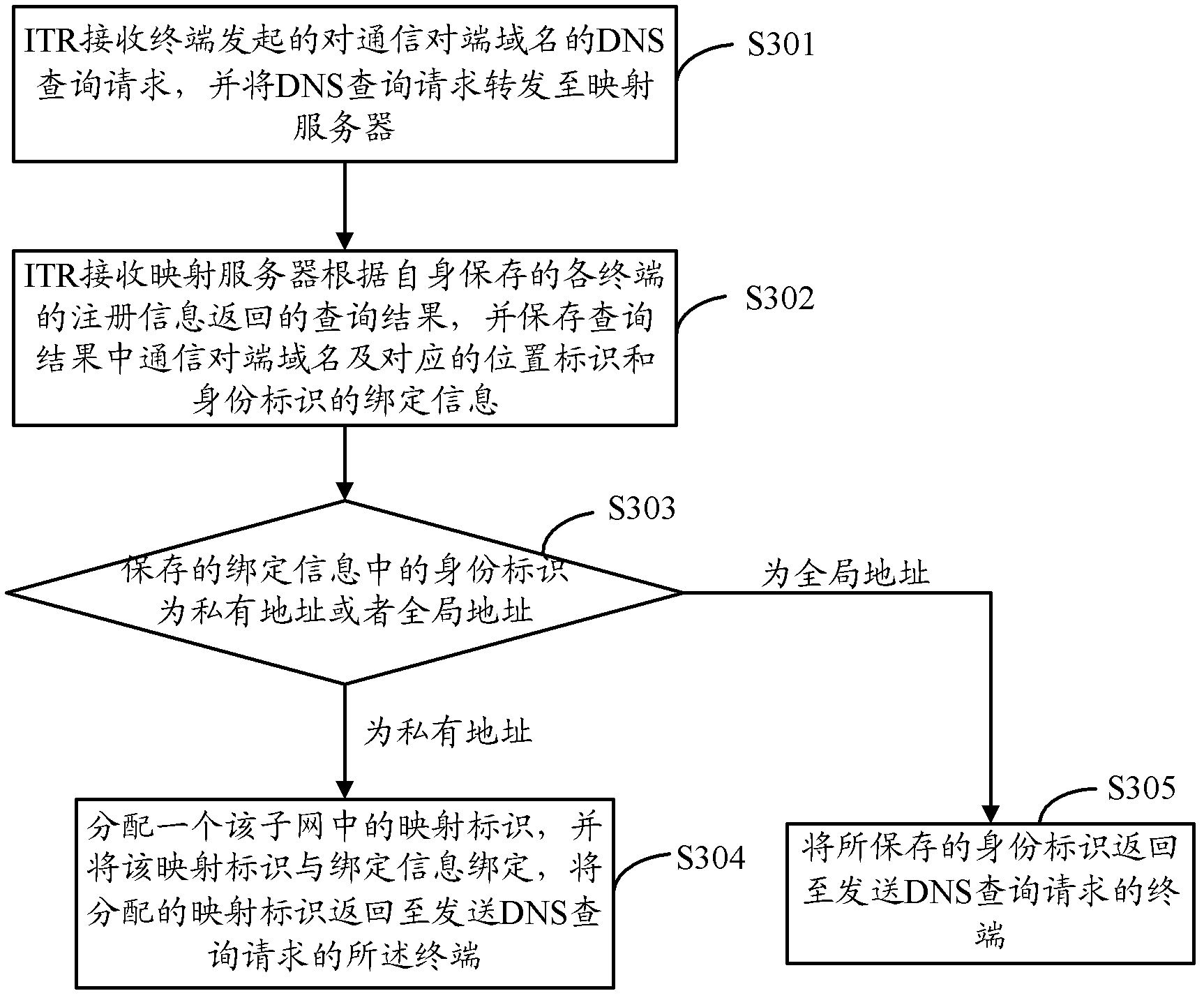
[0080] Step A: Terminal X queries the mapping server for the EID of destination node Y according to the domain name of destination node Y. The mapping server returns the registered binding information: Y-RLOC2-pEID1. ITR finds that this EID is a private identity after receiving it, then allocates and caches a mapped EID2 corresponding to Y's information RLOC2-pEID1, and replies to node X's DNS information as EID2.
[0081] Step B: The terminal X constructs a normal data packet ...
example 2
[0085] Such as Image 6 In the network architecture shown, a node X with a global address wants to communicate with a node Y with a private EID. Node X is identified as EID1 and its location is identified as RLOC1, and it knows the domain name Y of node Y. Node Y's identity is pEID2, and its location is RLOC2, both of which have registered the domain name, EID information and RLOC binding information on the mapping server. The communication process initiated by node X to node Y is as follows:
[0086] Step A: Terminal X queries the mapping server for the EID of destination node Y according to the domain name of destination node Y. It uses the global EID itself, so ITR does not perform NAT conversion binding. The mapping server returns the information binding RLOC2-pEID2 of the destination node Y. ITR finds that the EID of the peer node is a private identifier, then assigns a mapped EID2 to bind Y's information RLOC2-pEID2, and replies with the DNS information of node X as Y...
example 3
[0091] Such as Figure 7In the network architecture shown, node X in the identity and location separation network using private addresses wants to access node Y in the non-identity and location separation network, X’s identity is pEID1, the location is RLOC1, and Y uses the legal IP address IP1 . Node X knows Y's IP address. In this example, since the communication peer adopts the IP address, the terminal does not need to perform DNS query before sending the packet. The communication process is as follows:
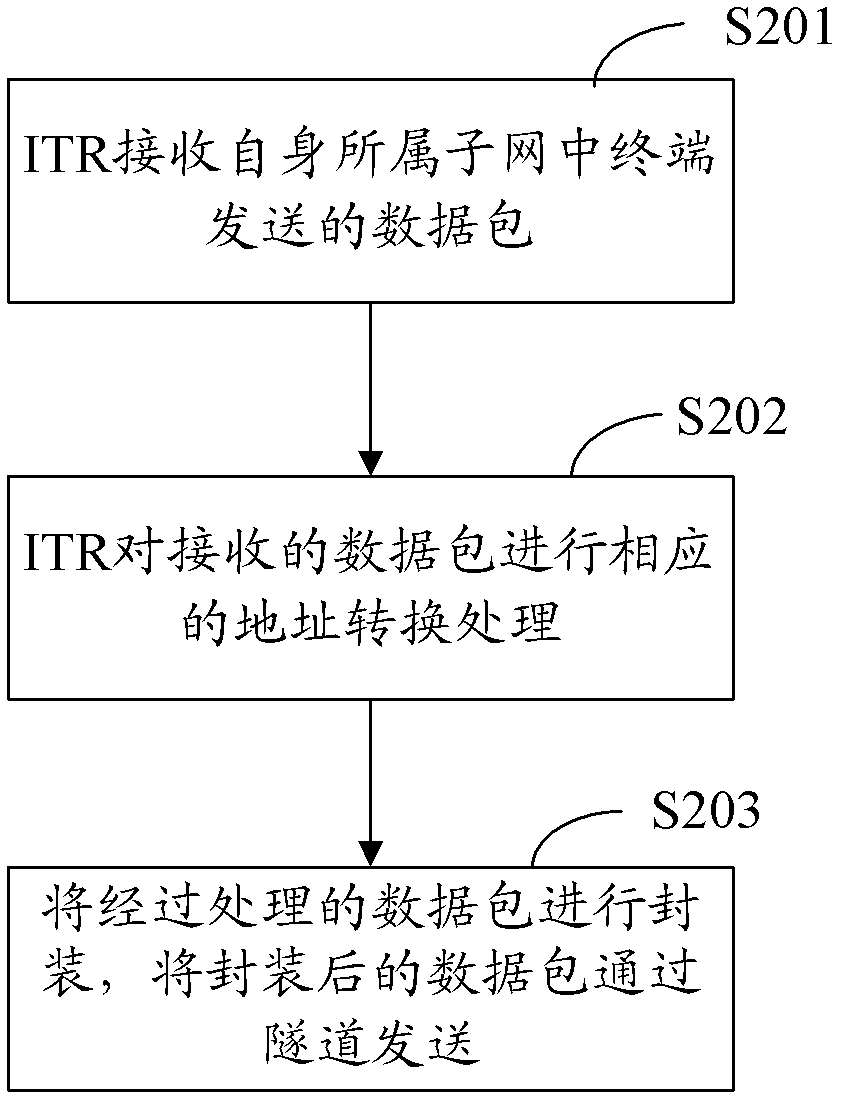
[0092] Step A: Node X constructs a normal identity- and location-separated network message, sends Y's IP address as the destination EID, and sends it to the ITR.
[0093] Step B: ITR finds that the source address of the data packet is a private EID, performs NAT mapping to EID1, and uses the IP address of the destination node as EID to query its corresponding RLOC address, and finds that there is no corresponding information in its own cache list, then sends EID to the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com