Method and system for monitoring position shifting of low-mobility terminal
A technology of low mobility and terminal location, applied in the field of machines and machines, can solve problems such as illegal movement, load, and inability to solve well, and achieve the effect of reducing signaling load
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
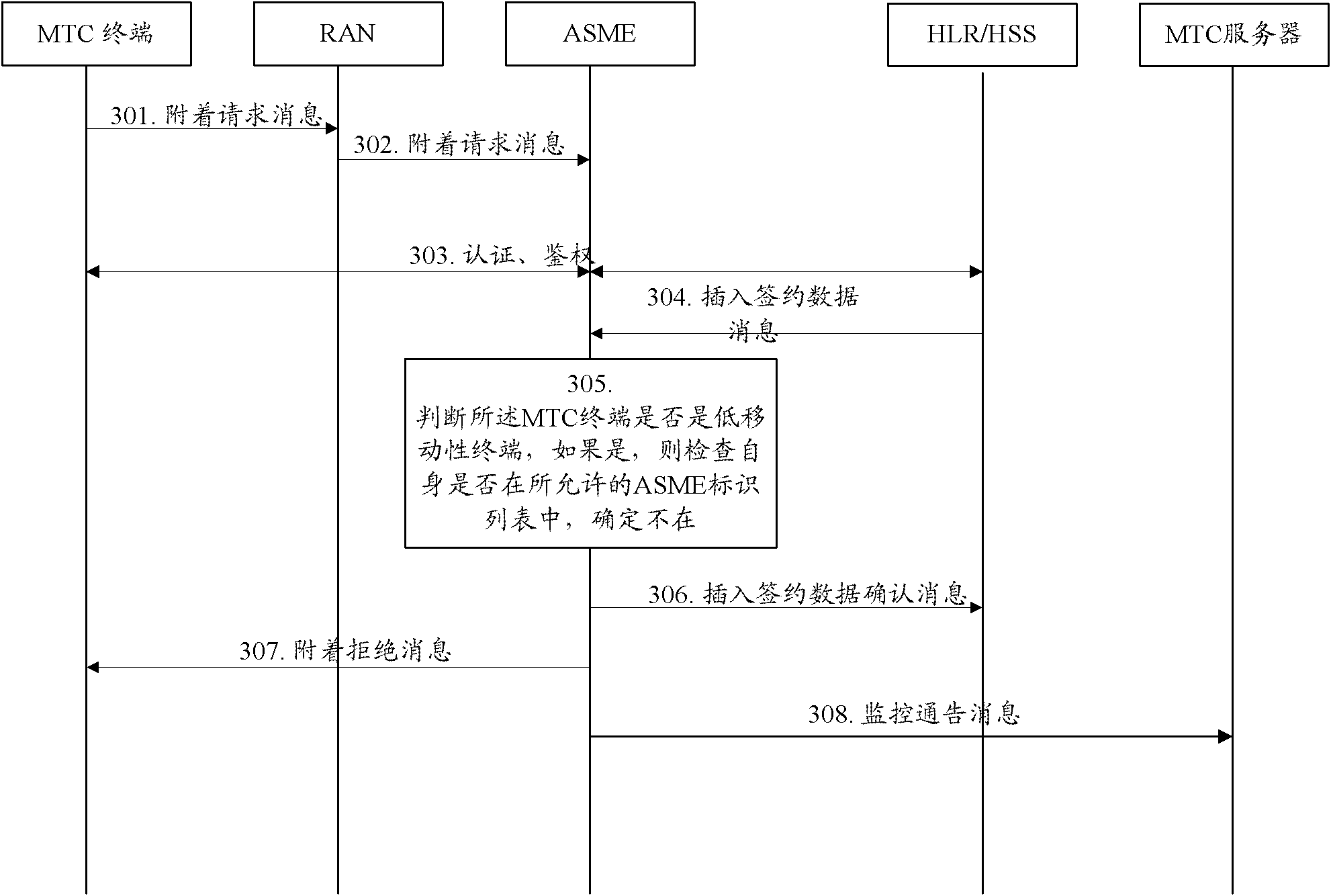
[0106] The application scenario of this embodiment is: when the MTC terminal initially attaches, the ASME that the MTC terminal currently requests to access checks whether the MTC terminal is a low-mobility MTC terminal, and if so, further determines whether it is in the allowed ASME identification list , if not, the MTC terminal is not allowed to access the network. In this embodiment, the method for monitoring the location movement of a low-mobility terminal, such as image 3 shown, including the following steps:
[0107] Step 301: when initially attaching, the MTC terminal sends an initial attach request message to the RAN.
[0108] Step 302: After receiving the initial attach request, the RAN sends an initial attach request message to ASME.
[0109] Step 303: The network and the UE perform AKA authentication and Security mode command processes.
[0110] Step 304: After the Security mode command process is completed, the HSS / HLR sends an insert subscription data message ...
Embodiment 2
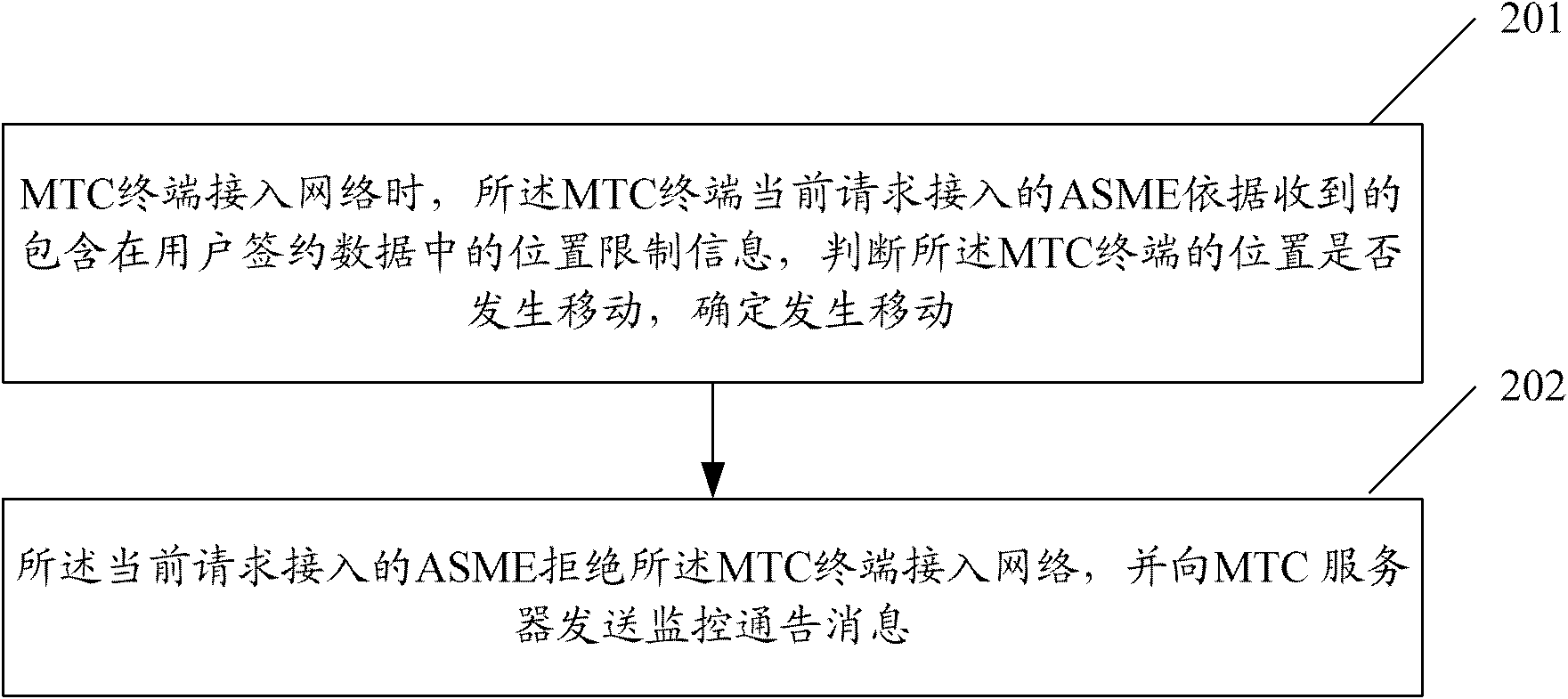
[0121] The application scenario of this embodiment is: the MTC terminal moves, the ASME that provides services for the MTC terminal before the move can identify the identity of the MTC terminal, and has obtained the user subscription data of the MTC terminal from the HSS / HLR, and the MTC terminal currently requests access ASME checks whether the MTC terminal is a low-mobility MTC terminal, and if so, further determines whether it is in the allowed ASME identification list, and if not, does not allow the MTC terminal to access the network. In the following description, the ASME that provided services for the MTC terminal before moving is called Old ASME, and the ASME that the MTC terminal currently requests to access is called New ASME. In this embodiment, the method for monitoring the location movement of a low-mobility terminal, such as Figure 4 shown, including the following steps:
[0122] Step 401: After the MTC terminal moves, send a Connection Request (Connection Reque...
Embodiment 3
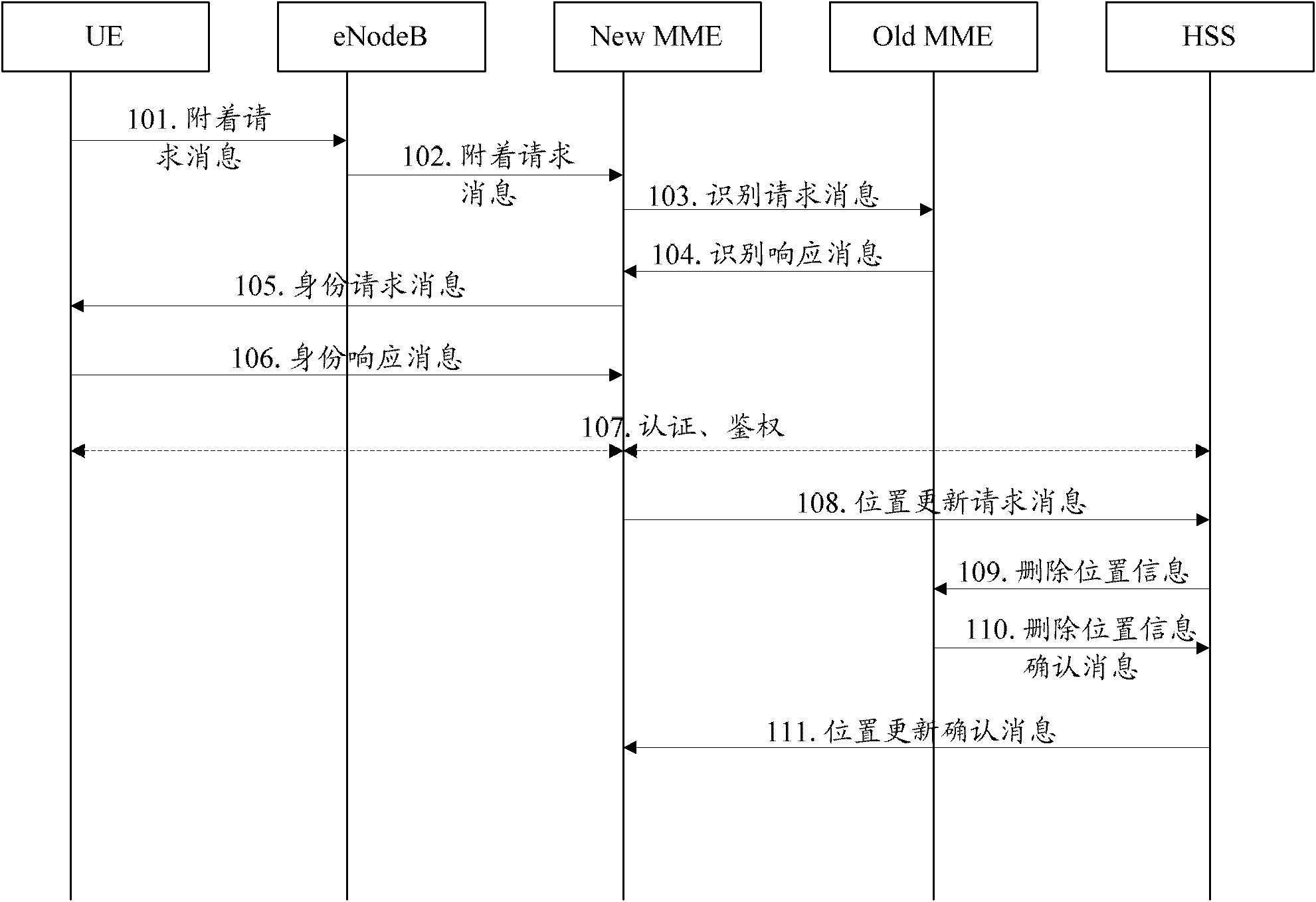
[0139] The application scenario of this embodiment is: the MTC terminal moves, and the ASME that provides services for the MTC terminal before the move cannot identify the identity of the MTC terminal, or thinks that the identification message is not credible, or the unique identifier reported by the MTC terminal is a permanent identity, such as IMSI , the ASME that the MTC terminal currently requests to access checks whether the MTC terminal is a low-mobility MTC terminal, and if so, further determines whether it is in the allowed ASME identification list, and if not, does not allow the MTC terminal to access the network. In the following description, the ASME that provided services for the MTC terminal before moving is called Old ASME, and the ASME that the MTC terminal currently requests to access is called New ASME. In this embodiment, the method for monitoring the location movement of a low-mobility terminal, such as Figure 5 shown, including the following steps:
[014...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com