Course angle rotation-based multi-beam side-scan sonar image real-time splicing method
A side-scan sonar and heading angle technology, applied in image enhancement, image data processing, sound wave re-radiation, etc., can solve the problems that the analysis technology cannot be disclosed as a commercial secret, accurate real-time splicing cannot be performed, and the accumulation of errors is large. , to achieve the effect of improving the display effect, reducing the accumulated error, and improving the calculation speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] The present invention is described in more detail below in conjunction with accompanying drawing example:
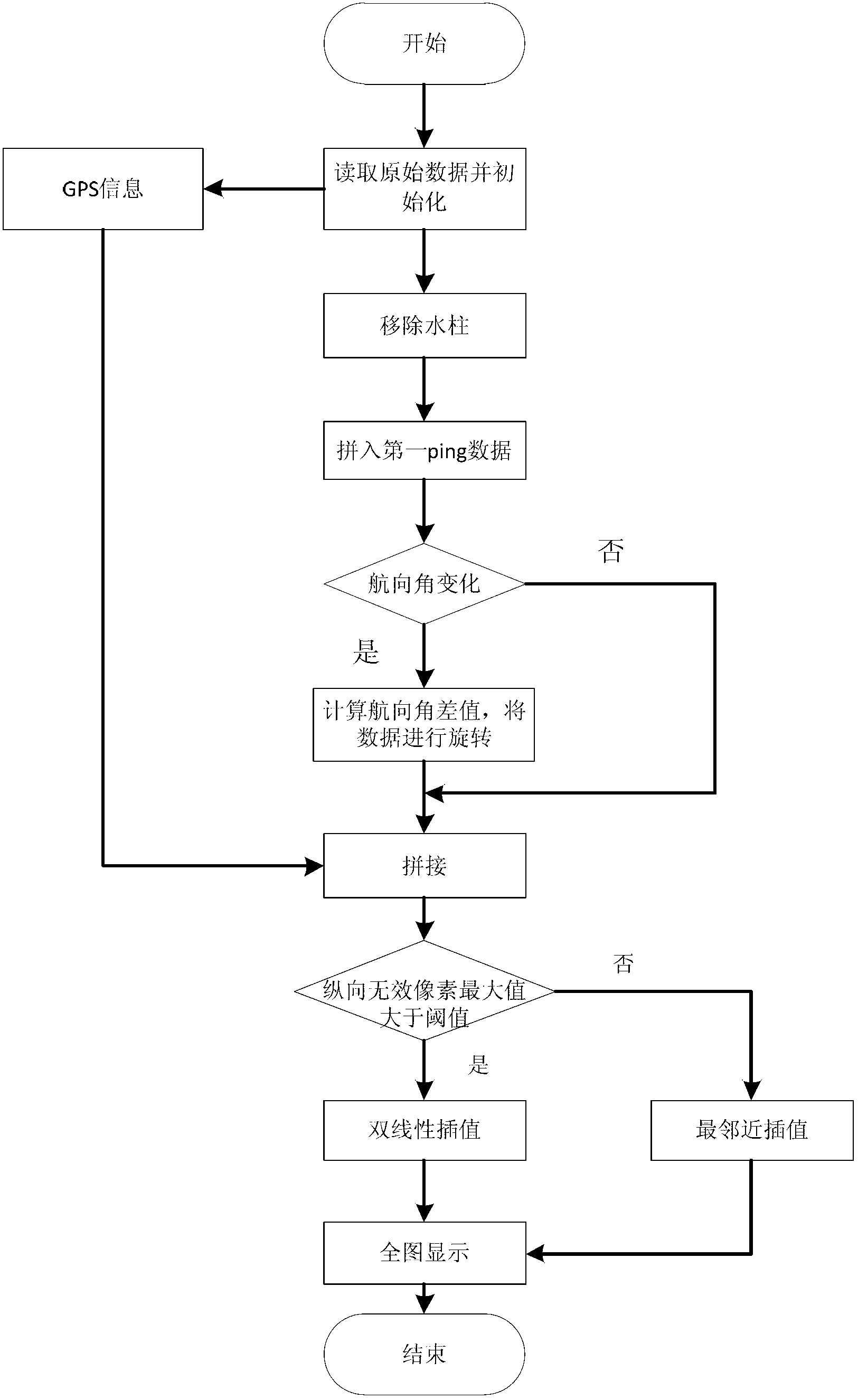
[0024] combine figure 1 , the concrete steps of the real-time splicing method of multi-beam side-scan sonar images based on heading angle rotation in the present invention are as follows:
[0025] The first step is to read the original information of the N channels on the left and right sides of the sonar file, and set the initial position of the stitched image;
[0026] The second step is to remove the water column area in the raw data because the transducer receives underwater noise before the first echo point returns;
[0027] The third step takes the GPS coordinates received by the towfish as the center, and writes the N channel data of the first ping in the original sonar file after removing the water column area as a whole to the canvas, avoiding the burden of calculating the echo points one by one. from the accumulated error, and record the current ping n...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com