Vegetable soybean hull silage and preparation method thereof
A technology of bean pod shell green and vegetable soybeans, which is applied in the field of silage, can solve the problems of huge space for drying, limited application of fresh pod shells, easy deterioration and rot, etc., and achieves good palatability, improved feeding value, and soft texture Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] A kind of vegetable soybean pod shell silage (hereinafter referred to as pod shell silage), which is composed of the following raw materials:
[0019] 20% of dry corncobs with a crushed particle size of 5-10mm, 5% of potato skins, 0.2% of lactic acid bacteria, 0.3% of urea, 1.5% of dry corncobs with a crushed particle size of 3-5mm, and the balance is processed fresh edamame pod shell.
[0020] The preparation method of above-mentioned pod shell silage is as follows:
[0021] (1) The lactic acid bacteria, urea and dry corn cobs with a crushed particle size of 3-5 mm are evenly mixed in proportion to prepare a pod shell silage additive.
[0022] (2) Mix dry corncobs with a crushed particle size of 5-10 mm, potato skins, and processed fresh edamame pod shells with the above-mentioned pod shell silage additives in proportion, and place the mixed raw materials in the silage cellar for compaction layer by layer , the density reaches 550g~600g / L; silage fermentation at 20℃~...
Embodiment 2
[0031] A pod shell silage consisting of raw materials of the following components:
[0032] 10% of dry corncobs with a crushed particle size of 5-10mm, 5% of potato skins, 0.05% of lactic acid bacteria, 0.1% of urea, 0.55% of dry corncobs with a crushed particle size of 3-5mm, and the balance is processed fresh edamame pod shell.
[0033] The preparation method of above-mentioned pod silage is identical with embodiment 1.
[0034] Table 2 shows the comparison of nutritional components between the pod shell silage and the processed fresh bean pod shell in this embodiment.
[0035] Table 2: Comparison table of nutrients (dry matter basis %)
[0036] project Processed fresh pod shells pod shell silage dry matter 35.90 50.60 crude protein 12.40 12.25 crude ash 3.20 8.12 crude fat 1.70 — neutral detergent fiber 51.10 49.20 acid detergent fiber 37.30 33.91
[0037] How to use and instructions: replace alfalfa ha...
Embodiment 3
[0040] A pod shell silage consisting of raw materials of the following components:
[0041] 30% of dry corncobs with a crushed particle size of 5-10mm, 5% of potato skins, 0.75% of lactic acid bacteria, 1.5% of urea, 4.25% of dry corncobs with a crushed particle size of 3-5mm, and the balance is processed fresh edamame pod shell.
[0042] The preparation method of above-mentioned pod silage is identical with embodiment 1.
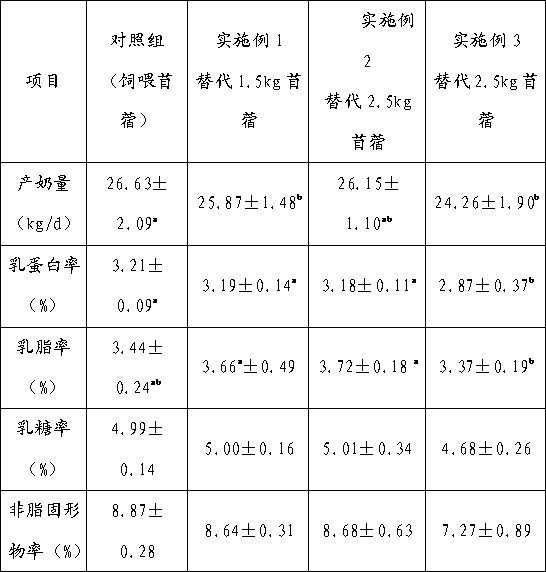
[0043] How to use and instructions: replace alfalfa hay with pod shell silage, the replacement amount is 9kg of pod shell silage instead of 2.5kg of alfalfa hay. In order to ensure that the milk production and milk quality of dairy cows are not affected, the roughage feed intake in dairy cows’ diets should not be too large. Therefore, when vegetable soybean pod shells that have been ensiled are used as roughage for dairy cows, when the diet is used instead of alfalfa The usage amount should not exceed 9kg at most.
[0044] Table 3 shows the comparison of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com