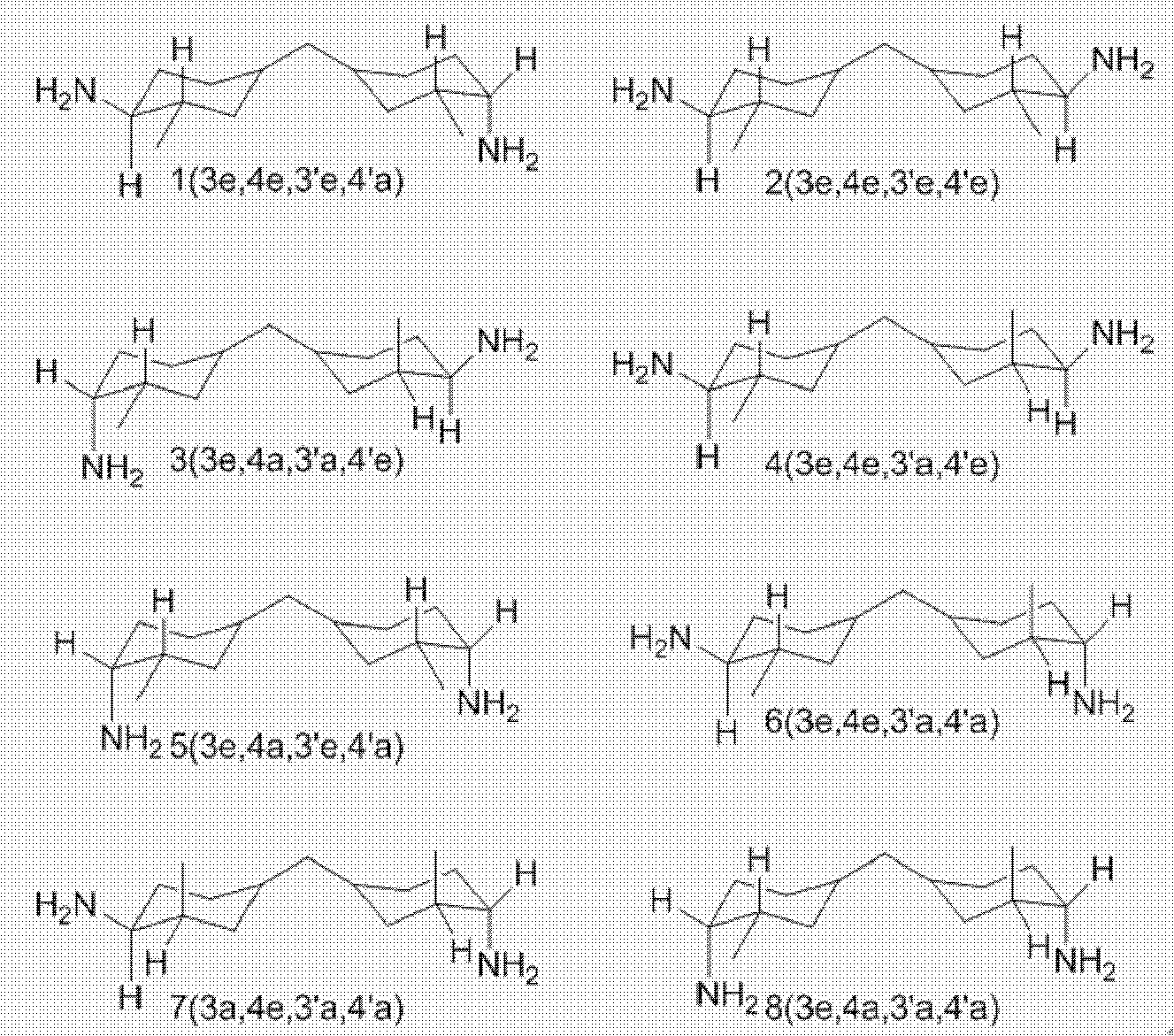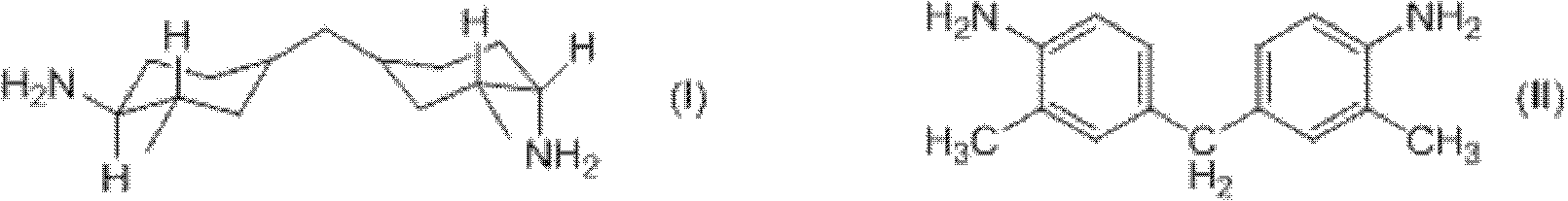Method for synthesizing 3,3'-dimethyl-4,4'-diamino dicyclohexyl methane
A technology of diaminodicyclohexylmethane and diaminodiphenylmethane, which is applied in the fields of MACM products and synthesis, can solve problems such as turbidity or even crystallization, inconvenient production, storage, transportation and use, and affect the quality of downstream products, and achieve Low freezing point, quality improvement effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1、3、5 and comparative example 1~2
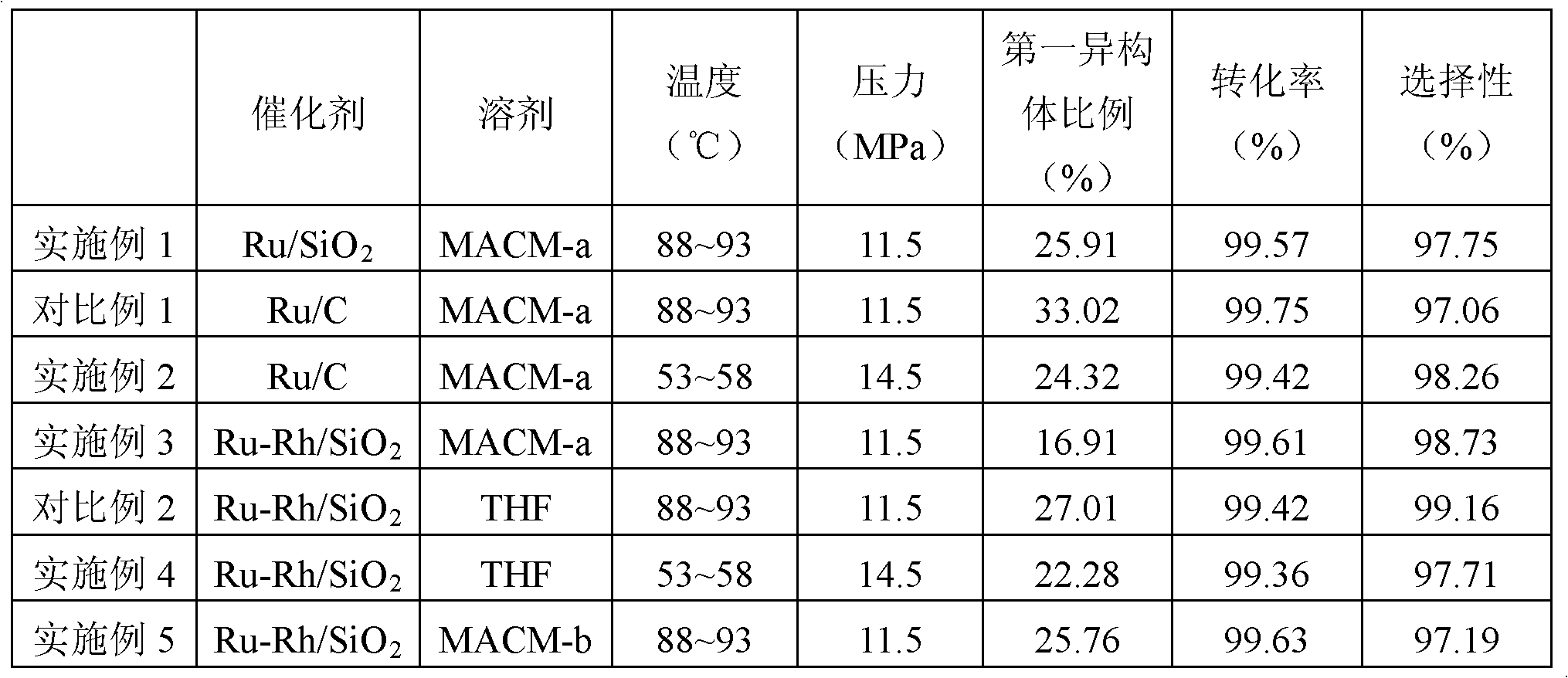
[0028] 200 grams of MDT, 280 grams of solvent as described in Table 2, 10 grams of catalyst were put into a 1L hydrogenation kettle, and 1.60 grams of BaO was added. Start stirring, raise the temperature to 90°C after the leak test, and control the temperature at 88-93°C and the pressure at 11.5MPa. The reaction is stirred for 10 hours to complete the hydrogen absorption, and the temperature is continued for 1.5 hours to obtain the MACM product. Wherein MACM-a refers to MACM with a first isomer ratio of 20.1%; MACM-b refers to MACM with a first isomer ratio of 32.6%.
Embodiment 2 and 4
[0030] 200 grams of MDT, 280 grams of solvent as described in Table 2, 10 grams of catalyst were put into a 1L hydrogenation kettle, and 1.60 grams of BaO was added. Start stirring, raise the temperature to 55°C after leak testing, and control the temperature at 53-58°C and the pressure at 14.5MPa. The reaction is stirred for 10 hours to complete the hydrogen absorption, and the temperature is continued for 1.5 hours to obtain the MACM product. Wherein MACM-a refers to MACM with a first isomer ratio of 20.1%.
[0031] Table 2
[0032]
[0033] It can be seen from the data of the corresponding Examples 1 to 5 and Comparative Examples 1 to 2 in Table 2 that the first isomer ratios of the products obtained by catalyzing MDT hydrogenation by different catalysts are different, and the ruthenium-rhodium bimetallic catalyst Ru-Rh / SiO is used. 2 The resulting product has a low ratio of the first isomer. Different solvents are used in the catalytic MDT hydrogenation process so tha...
Embodiment 6~8 and comparative example 3
[0035] Put 200 grams of MDT, 160 grams of MACM with a peak of 20.1% as solvent, and 2.4 grams of Ru-Rh / SiO into a 1L hydrogenation kettle. 2 The catalyst was added with 1.0 g of alkali metal auxiliary as shown in Table 3 or no auxiliary was added, and after the feeding was completed, it was replaced with nitrogen three times, and then replaced with hydrogen three times. Start stirring, raise the temperature to 85°C after leak testing, and control the temperature to be between 83-88°C and the pressure of 11.5MPa. The reaction is stirred for 10 hours to complete the hydrogen absorption, and the temperature is continued for 1.5 hours to obtain the MACM product.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| freezing point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| freezing point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com