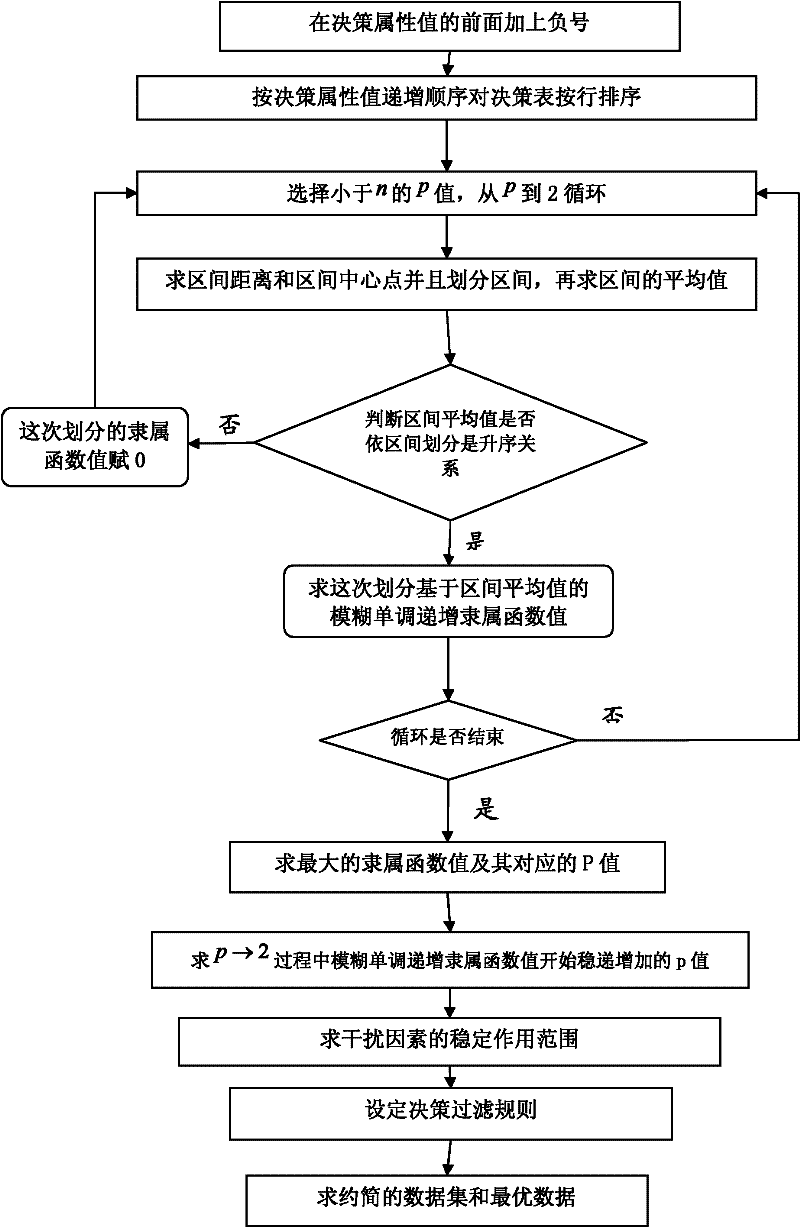
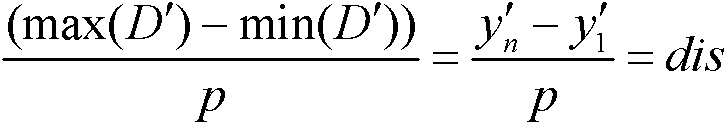Mining method for fuzzy rough monotonic data based on interval average
A data mining, fuzzy and rough technology, applied in electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of difficult expansion of attribute data, monotony, incomplete data, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing input attributes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment
[0061] First, let’s explain UCI’s sewage treatment data. This data set is the result of daily sensor tests from urban sewage plants. There are a total of 527 sets of sample data, and each set of data contains 38 attributes. Some data are missing and incomplete. . The information of the 29 main attributes is as follows:
[0062] (1) Q-E (input flow to plant): input flow to the plant;
[0063] (2) ZN-E (input Zinc to plant): Zinc input to the plant;
[0064] (3) PH-E (input pH to plant): pH input to the plant;
[0065] (4) DBO-E (input Biological demand of oxygen to plant): biological oxygen demand input to the plant;
[0066] (5) DQO-E (input chemical demand of oxygen to plant): chemical oxygen demand input to the plant;
[0067] (6) SS-E (input suspended solids to plant): suspended solids input to the plant;
[0068] (7) SSV-E (input volatile supended solids to plant): volatile solids input to the plant;
[0069] (8) SED-E (input sediments to plant): input sediments to the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com