Terminal clock and external clock difference synchronization method
An external clock and terminal technology, applied in the direction of synchronization devices, electrical components, wireless communication, etc., can solve the problems of less collection, poor versatility, and low degree of automation, and achieve the effect of ensuring complete reception
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
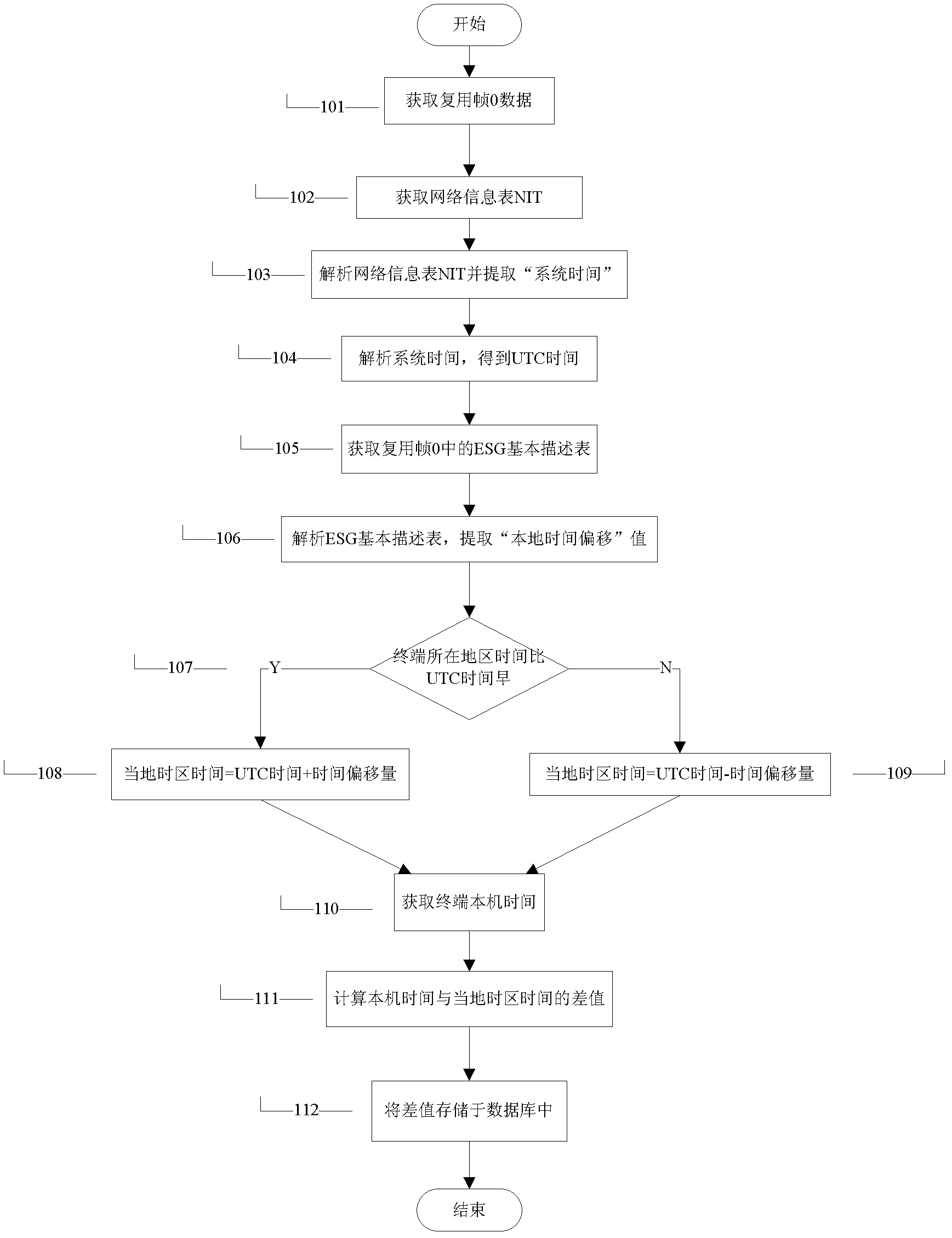
[0025] Embodiment 1. A clock synchronization method using ESG to obtain local time offset, such as figure 1 shown. The specific clock synchronization steps are as follows:
[0026] In step 101, the terminal starts up and acquires data of multiplexed frame O at the same time.
[0027] Step 102, obtain the network information table NIT of the control information table from the multiplexing frame O.
[0028] Step 103, analyze the network information table NIT and extract the "system time" field.
[0029] Step 104, analyze and format the system time to obtain UTC time, including MJD date conversion and BCD coded time extraction. MJD date conversion calculates the MJD date code defined by the first 16 bits of the system time to obtain the year, month, and day of UTC time; BCD code time extraction extracts the hour, minute, and second through the BCD code defined by the last 24 bits of the system time.
[0030] Step 105, after reading and parsing the network information table, f...
Embodiment 2
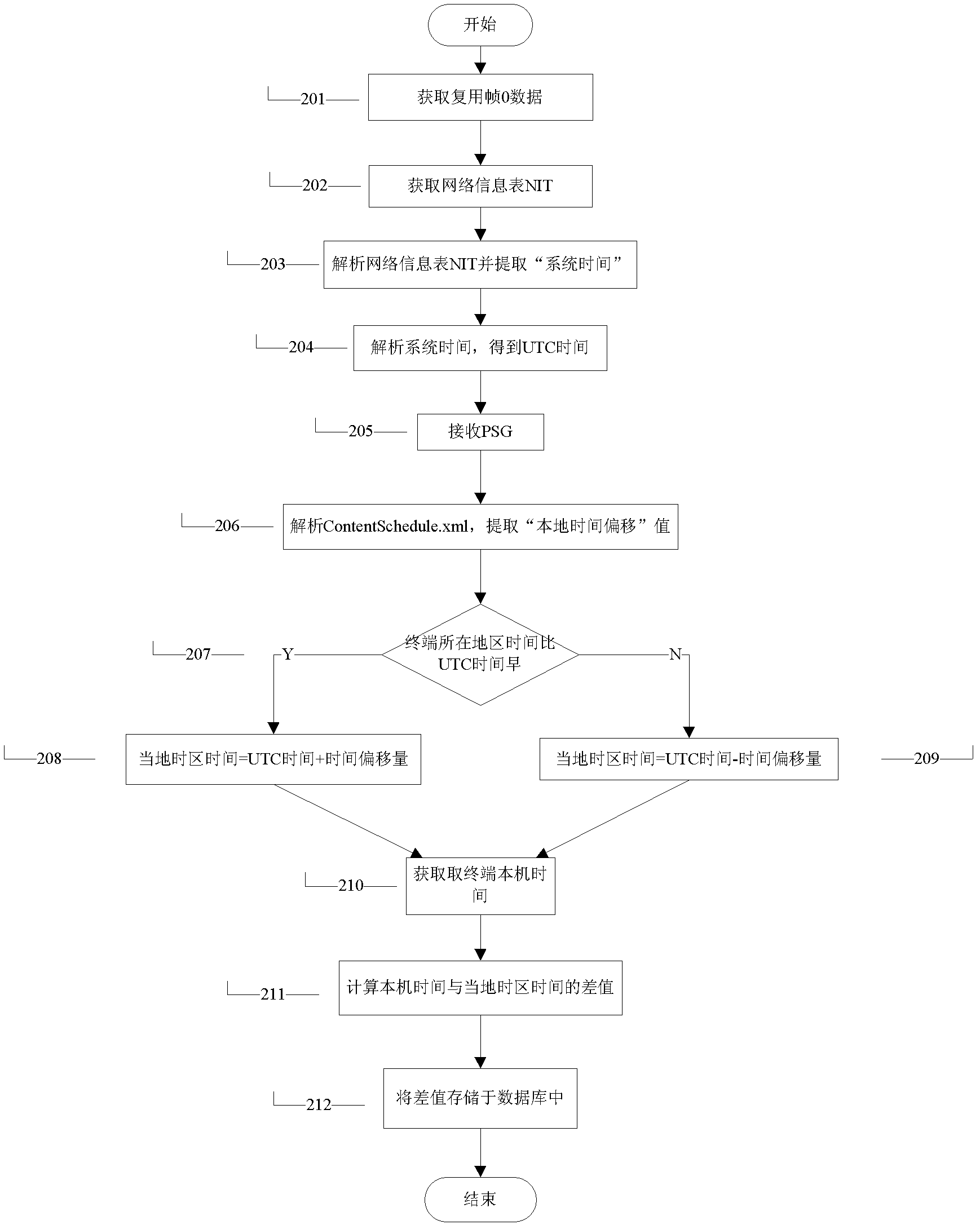
[0038] Embodiment 2. A method of clock synchronization using PS6 to obtain local time offset, such as figure 2 shown. The specific clock synchronization steps are as follows:
[0039] In step 201, the terminal starts up and obtains the data of the multiplexed frame O at the same time.
[0040] Step 202, obtain the network information table NIT of the control information table from the multiplexing frame O.
[0041] Step 203, analyze the network information table NIT and extract the "system time" field.
[0042] Step 204, analyze and format the system time to obtain UTC time, including MJD date conversion and BCD coded time extraction. MJD date conversion calculates the MJD date code defined by the first 16 bits of the system time to obtain the year, month, and day of UTC time; BCD code time extraction extracts the hour, minute, and second through the BCD code defined by the last 24 bits of the system time.
[0043] Step 205, after reading and parsing the network informati...
Embodiment 3
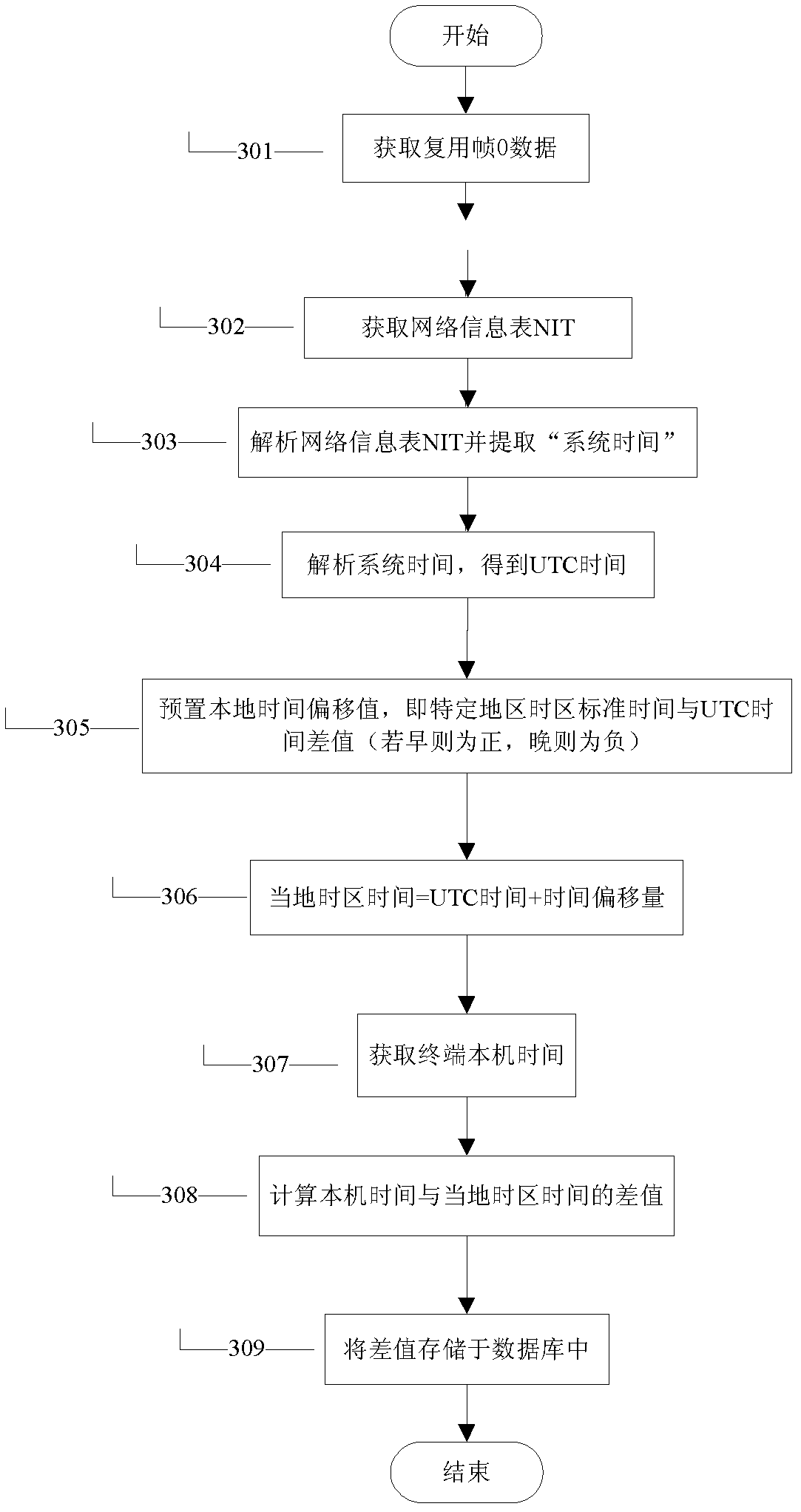
[0051] Embodiment 3, a clock synchronization method in a preset mode, such as image 3 shown. The specific clock synchronization steps are as follows:
[0052] In step 301, the terminal starts up and obtains the data of the multiplexed frame O at the same time.
[0053] Step 302, obtain the network information table NIT of the control information table from the multiplexing frame O.
[0054] Step 303, analyze the network information table NIT and extract the "system time" field.
[0055] Step 304, analyze and format the system time to obtain UTC time, including MJD date conversion and BCD coded time extraction. MJD date conversion calculates the MJD date code defined by the first 16 bits of the system time to obtain the year, month, and day of UTC time; BCD code time extraction extracts the hour, minute, and second through the BCD code defined by the last 24 bits of the system time.
[0056] Step 305, preset the local time offset value, that is, the time difference between...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com