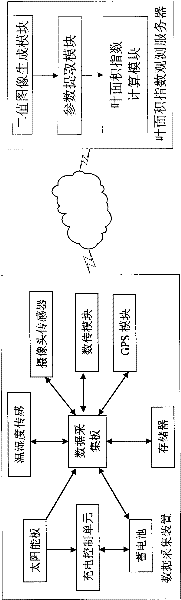
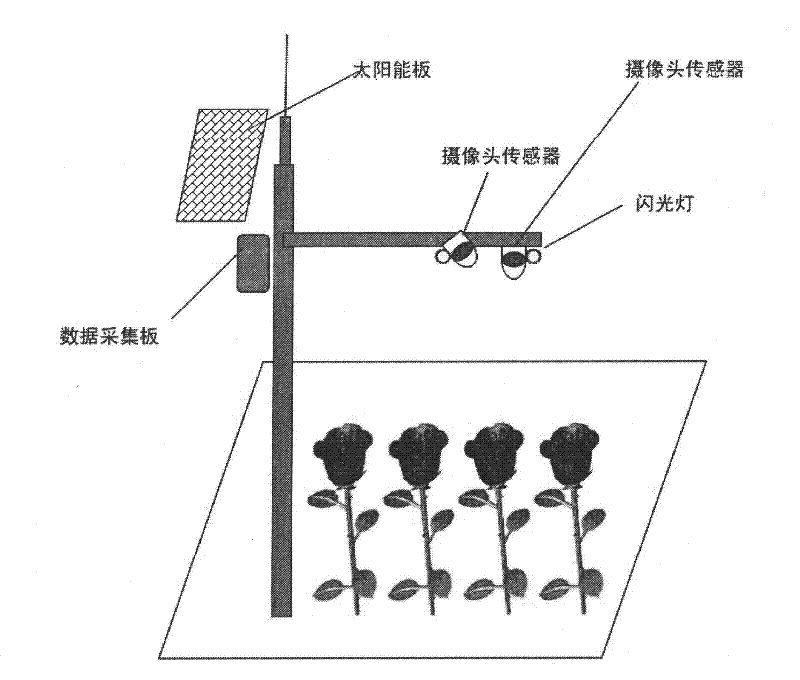
Automatic leaf area index observation system and method
A technology of leaf area index and automatic observation, applied in the field of agricultural observation, can solve the problems of no leaf area index, manual operation, and inability to achieve complete automation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0041] first embodiment : Improved K-means classification method
[0042] This method is implemented by the improved K-means classification module in the binary image generation module.
[0043] The improved K-means classification method uses the cluster analysis method, which needs to select the required number of classifications in the data, randomly find the cluster centers, and then reconfigure them iteratively until the optimal classification is achieved. The improved K-means classification method is first automatically divided into multiple categories according to the selected number of categories, and then thresholded according to the mean values of various bands, and merged into two categories: green vegetation, soil and background. The processing flow of the improved method is:
[0044] 1) Calculating K initial category mean values uniformly distributed on the image data space;
[0045] 2) Calculate the distance from the pixel to each initial category, and use...
no. 2 example
[0049] second embodiment : Automatic Threshold Classification Method
[0050] The method is implemented by the automatic threshold classification module in the binary image generation module.
[0051] For images with small winter wheat and corn leaves, four band threshold classification methods are provided. R, G, and B respectively represent the red, green, and blue bands of the RGB color space, and their value ranges are 0-255. H represents the chromaticity in the HSL color space, and its value range is 0°- 360°, the principle of classification is to distinguish between green leaves and soil background by setting the range of four variables R, G, B and H, so define four thresholds t1, t2, t3, t4 for setting R, G, B The scope of the four variables H and H, the variables limited by the four thresholds in each method are not fixed, and are only used for assigning values to the four variables. The following four methods provide recommended thresholds. In the application, a...
no. 3 example
[0060] third embodiment : block threshold classification method
[0061] The method is implemented by the block threshold classification module in the binary image generation module.
[0062] Preferably, block processing is performed on the image of larger corn leaves or the original image of other crops with larger leaves, and the original image becomes a uniform patch classification result, which is more accurate, and then binarized by band thresholding. The block diameter determines the size of the block image, and the user needs to set it according to the image.
[0063] The processing flow of this method is:
[0064] 1) Image segmentation. Image segmentation requires the user to input the diameter of the segmentation block and the number of iterations. After the segmentation is completed, the image generates a uniform patch, and there are often unassigned pixels at the boundary of the patch. After segmentation, the image is more uniform and the classification is more ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com