Method for reusing saline-alkali waste cultivated land to grow plants
A technology of reuse and crops, applied in the field of soil agrochemicals, can solve problems such as inappropriate improvement measures, inability to discharge saline-alkali soil, and abandonment of saline-alkali land, so as to improve the production and living environment, buffer alkalinity, and reduce alkalinity soil fertility. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Embodiment 1 uses vermiculite + perlite + fine sand + shed film to cover and isolate
[0036] Matrix material: vermiculite, perlite, fine sand
[0037] Matrix ratio: perlite: vermiculite: fine sand = 1:1:1; 1:1.5:1; 1.5:1:1
[0038] Crop varieties: eggplant, pepper, tomato, melon, radish
[0039] Applying fertilizer: before planting, apply 35g / m of diamine and compound fertilizer in the groove 2 ; After planting, topdress two times of diamine and compound fertilizer each 15g / m 2
Embodiment approach
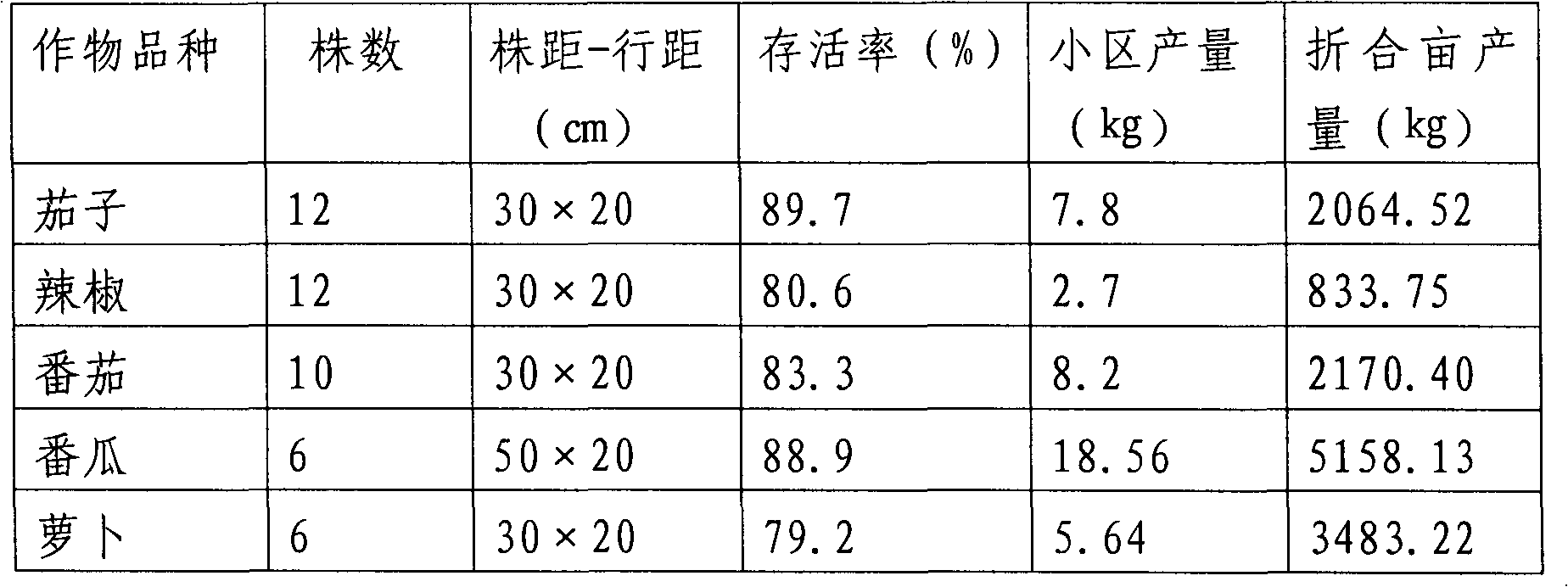
[0040] Implementation method: The size of the plot is 900cm×50cm, repeated three times, drip irrigation. Each replicate has 12 eggplants, 30cm×20cm; 12 peppers, 30cm×20cm; 10 tomatoes, 30cm×20cm; 6 pumpkins, 50cm (spacing)×20cm (row spacing); 6 radishes, 30cm×20cm. Routine management after crop planting, a small amount of drip irrigation for multiple times. The biological characteristics of the crops were investigated every week, and the yields were counted after the crops were harvested. During planting, the height of eggplant and tomato plants is moderate, and the growth of melon plants is relatively good. The leaves are yellow-green in the early stage of growth, and the color changes after topdressing. The fruiting ability is good.
[0041] The implementation results are shown in the table below:
[0042]
Embodiment 2
[0044] Use slag + weathered coal + fly ash + shed film to cover and isolate
[0045] Matrix material: slag, weathered coal, fly ash
[0046] Matrix ratio: slag: weathered coal: fly ash = 1:1:1; 1:1.5:1; 1.5:1:1
[0047] Crop varieties: eggplant, pepper, tomato, melon, radish
[0048] Applying fertilizer: before planting, apply 32.5g / m of diamine and compound fertilizer in the groove 2 ; After planting, topdressing twice diamine and urea each 17g / m 2
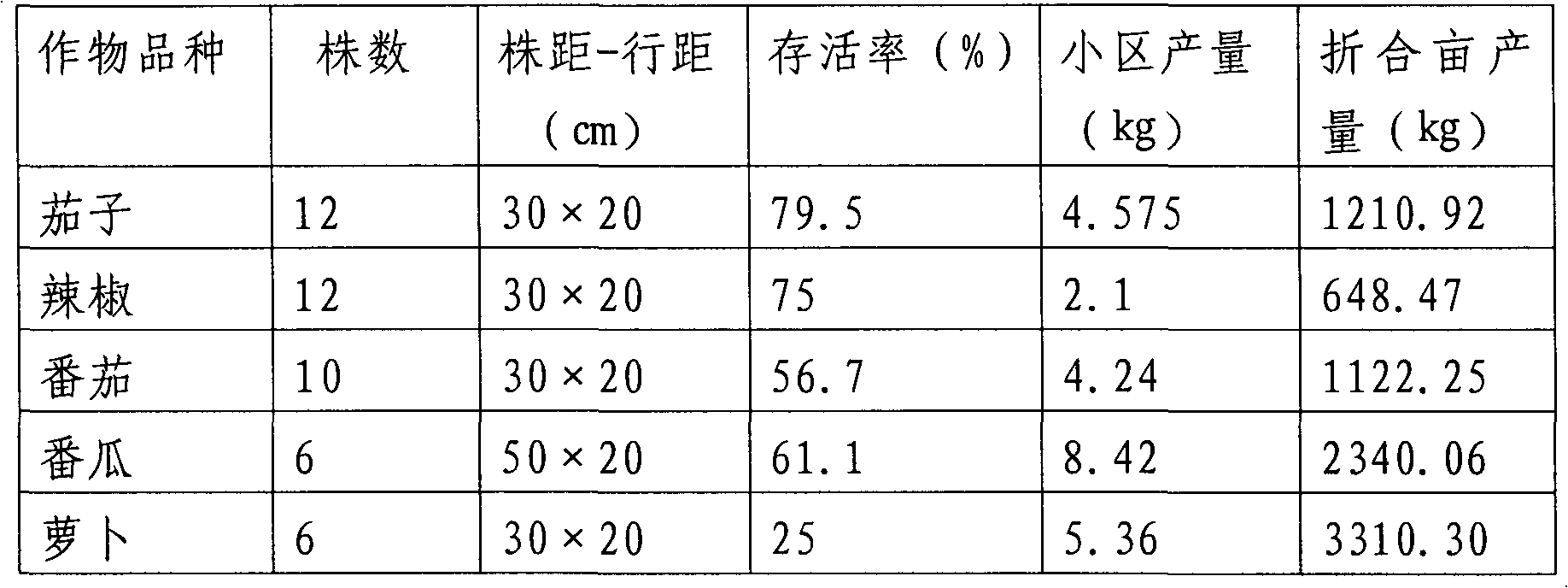
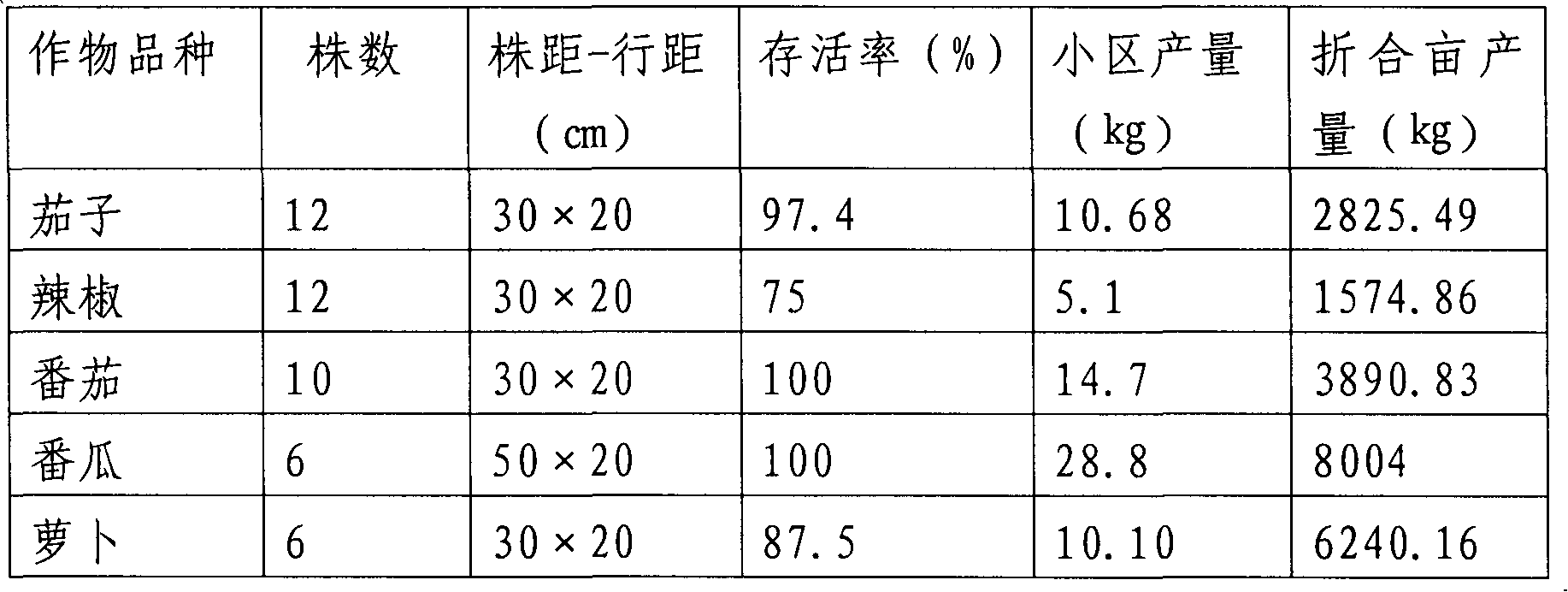
[0049] Implementation method: The size of the plot is 900cm×50cm, repeated three times, drip irrigation. Each replicate has 12 eggplants, 30cm×20cm; 12 peppers, 30cm×20cm; 10 tomatoes, 30cm×20cm; 6 pumpkins, 50cm (spacing)×20cm (row spacing); 6 radishes, 30cm×20cm. Routine management after crop planting, a small amount of drip irrigation for multiple times. The biological characteristics of the crops were investigated every week, and the yields were counted after the crops were harvested. During planting, the height of eggpl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com