S-MAC (Sensor-Media Access Control)-based defense method for sleep attack rejection in wireless sensor network
A wireless sensor and network technology, applied in network topology, wireless communication, transmission system, etc., can solve problems such as low-cost defense methods, and achieve the effect of resisting attacks, simple identification rules, and energy saving
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0036] The specific implementation examples of the S-MAC-based defense method against dormancy attacks in the wireless sensor network will be described below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
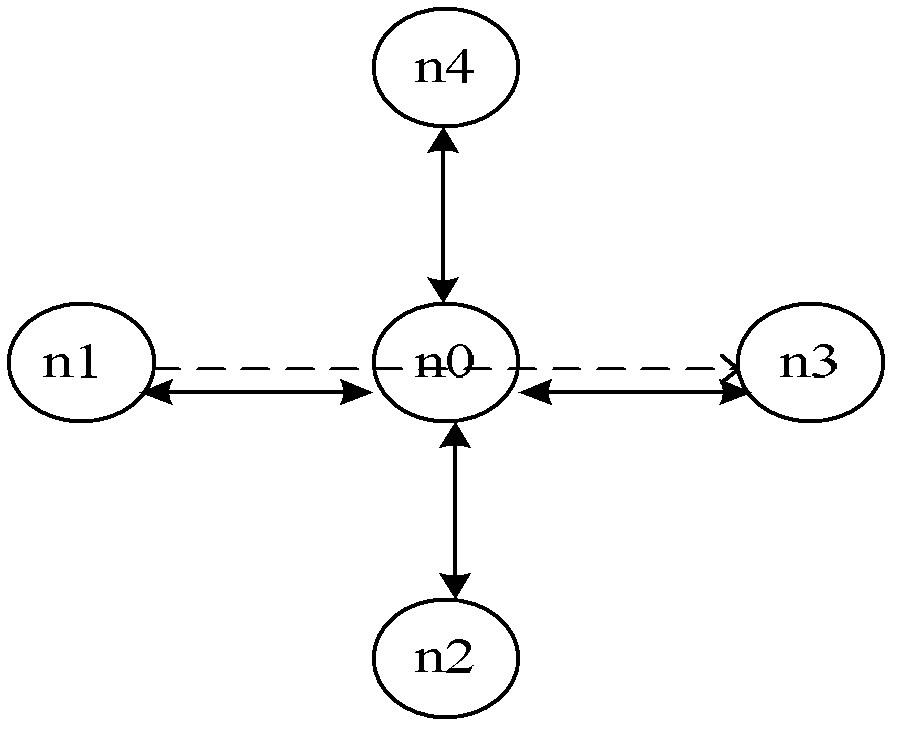
[0037] figure 1 is an experimental topology for simulating defensive attack methods. Use the ns2 simulation software to simulate the denial of dormancy attack in this example. Among them, n4 is the attack node, and n1 is the attacked node. The data flow is from n1 to n3, the simulation time is 100s, and the data packets are sent from 40s. The routing protocol adopts AODV. When attacking, n4 uses a protocol modified based on S-MAC, named A-MAC, and other nodes use standard S-MAC modules. The initial energy of the nodes is 1000 joules.
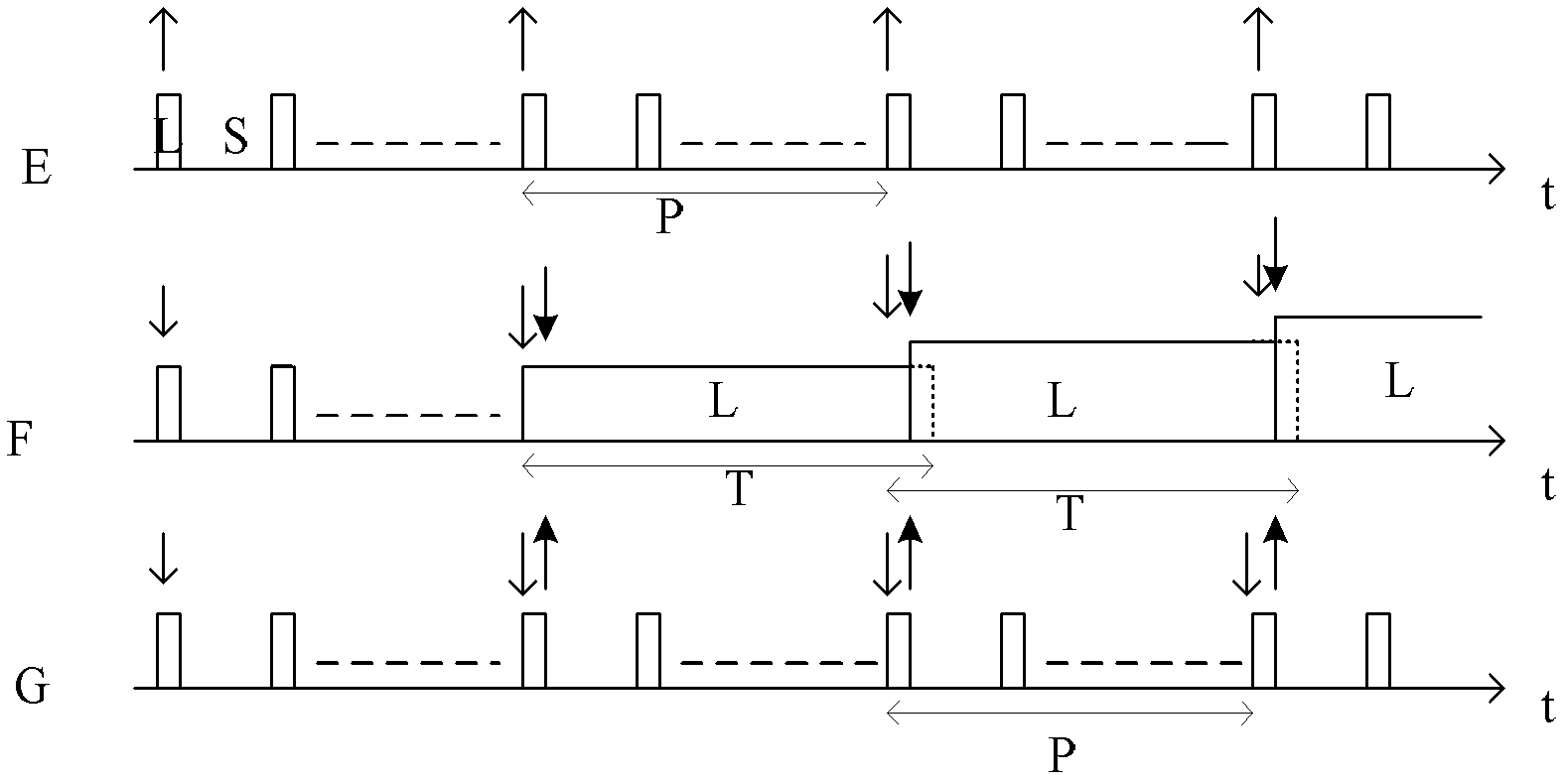
[0038] Utilizing the loopholes of the S-MAC protocol, n4 can continuously postpone the moment when the target node enters the dormant state by periodically sending forged synchronization packets until its energy is exhausted. The principl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com