Optimal configuration method of distributed generations (DG) based on power moment algorithm
A technology of distributed power supply and optimized configuration, which is applied in circuit devices, reactive power adjustment/elimination/compensation, electrical components, etc. It can solve complex methods, the configuration results are easily affected by initial parameters, and the random load distribution is not considered. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0013] Specific implementation mode one: this implementation mode comprises the following steps:
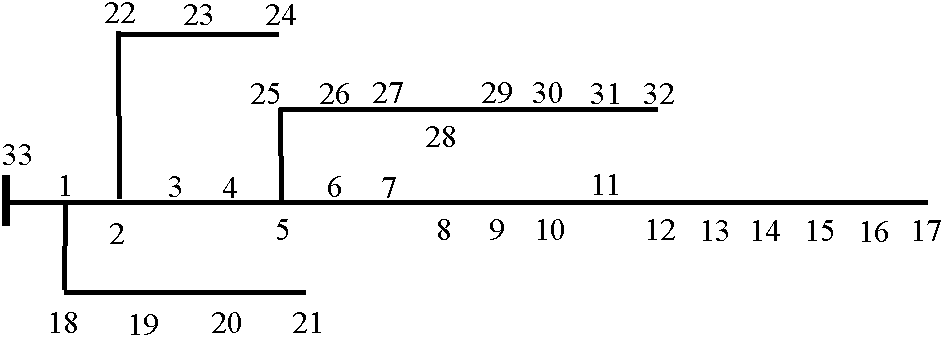
[0014] Step 1: Perform initial power flow calculation for the given distribution network connection structure, parameters of each branch, load power of each node and node voltage of the substation, and obtain the sum of the voltage of each node and the system active network loss before the distributed power supply is connected. Branch power, given the number m of distributed power access;
[0015] Step 2: Calculate the second moment of active power of each node, and arrange the values of the second moment of active power from large to small, and select the nodes whose values are in the first m as the position for configuring the power supply;
[0016] Step 3: Calculate the active primary moment of the m nodes according to the known number m of distributed power supply connections and the first m node positions determined by the active second moment, and solve m equations to o...
specific Embodiment approach 2
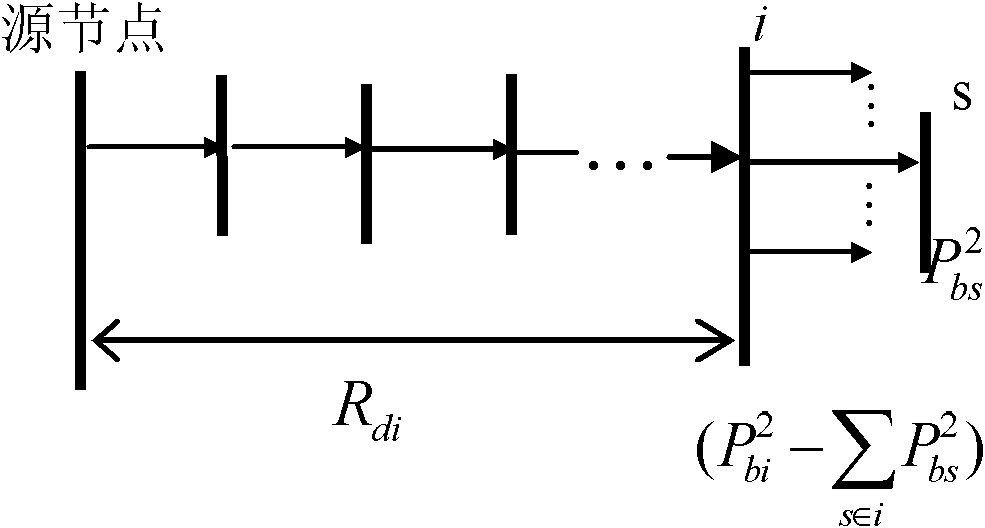
[0094] Specific embodiment two: the feature of this embodiment is that in step two, the active second moment is obtained by the following formula:
[0095] T P 2 ( i ) = R di × ( P bi 2 - Σ s ∈ i P bs 2 )
[0096] Among them, R di It is the sum of all branch resistances encountered upstream from the i-node to the source node.
[0097] P bi is the branch active power flowing into node i, obtained according to the power flow calculation result in step 1;
[0098] P bs is the branch active power flowing into node s,...
specific Embodiment approach 3
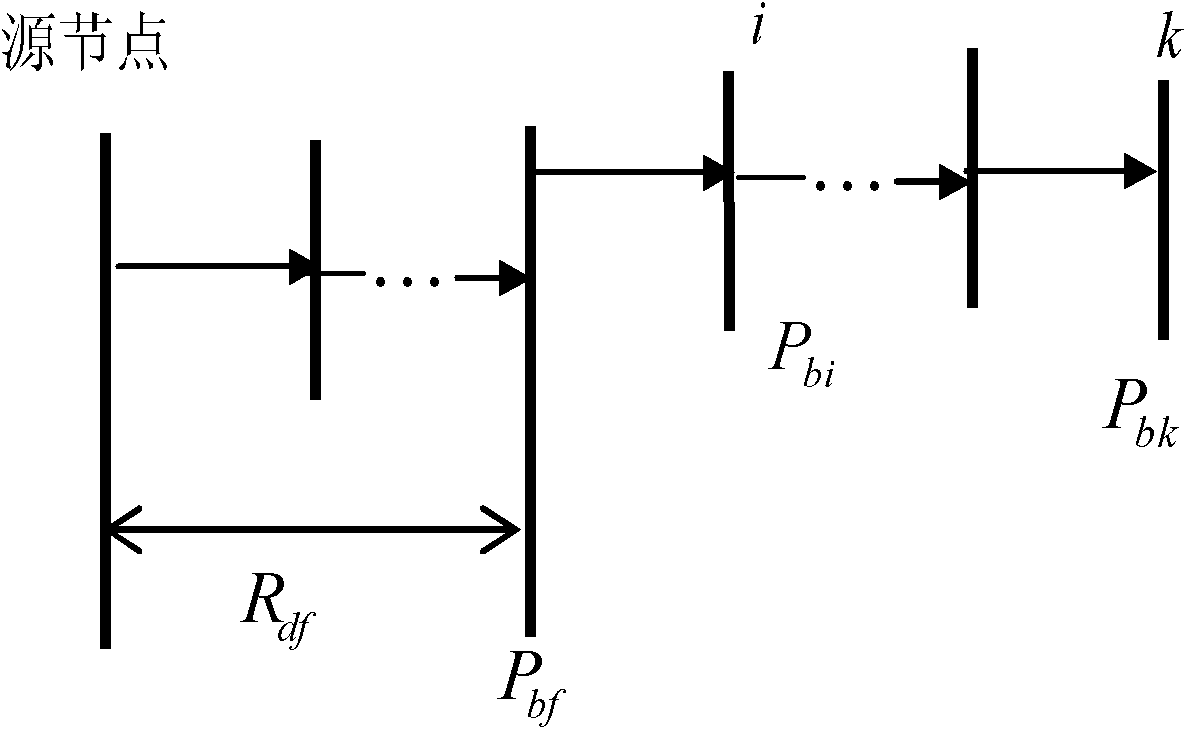
[0102] Specific embodiment three: the characteristic of this embodiment is that the active primary moment in step three can be calculated as follows:
[0103] T P 1 ( k ) = Σ i ⊇ k R df ( P bf - P bi ) + R dk P bk
[0104] where R df Indicates the electrical distance expressed in resistance from the parent node f of the i node to the source node, which can be calculated as follows:
[0105] R df = Σ j ⊇ f r ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com